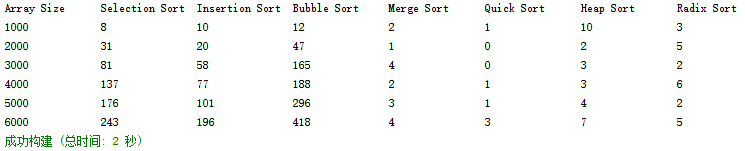
(8)七种排序算法的对比
下面我们写一个程序来比较选择排序、插入排序、冒泡排序、合并排序、快速排序、堆排序、基数排序这七种排序算法对同样的整型数组的排序所用的时间。
public class AllSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Array Size\tSelection Sort\tInsertion Sort"
+ "\tBubble Sort\tMerge Sort\tQuick Sort\tHeap Sort\tRadix Sort");
int[] list;
Integer[] list1;
Integer[] list2;
Integer[] list3;
Integer[] list4;
Integer[] list5;
Integer[] list6;
long startTime;
long endTime;
long[][] executionTime = new long[6][7];
final int BASE = 1000;
for (int k = 0; k < 6; k++) {
list=new int[k * BASE + BASE];
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
list[i] = (int)(Math.random() * 100000);
}
list1=initList(list);
list2=initList(list);
list3=initList(list);
list4=initList(list);
list5=initList(list);
list6=initList(list);
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
selectionSort(list1);
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
executionTime[k][0] = endTime - startTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
insertionSort(list2);
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
executionTime[k][1] = endTime - startTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
bubbleSort(list3);
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
executionTime[k][2] = endTime - startTime;
//print(list4);
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
mergeSort(list4);
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
executionTime[k][3] = endTime - startTime;
//print(list4);
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
quickSort(list5);
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
executionTime[k][4] = endTime - startTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
heapSort(list6);
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
executionTime[k][5] = endTime - startTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
radixSort(list, 5);
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
executionTime[k][6] = endTime - startTime;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
System.out.print(BASE + i * BASE + " ");
for (int j = 0; j < 7; j++)
System.out.print("\t\t" + executionTime[i][j]);
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void print(Integer[] list){
int len=list.length;
for(int i=0;i" ");
System.out.println();
}
public static Integer[] initList(int[] array){
int len=array.length;
Integer[] list=new Integer[len];
for(int i=0;ireturn list;
}
/** The method for sorting the numbers */
public static > void selectionSort(E[] list) {
for (int i = list.length - 1; i >= 1; i--) {
// Find the maximum in the list[0..i]
E currentMax = list[0];
int currentMaxIndex = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
if (currentMax.compareTo(list[j]) < 0) {
currentMax = list[j];
currentMaxIndex = j;
}
}
// Swap list[i] with list[currentMaxIndex] if necessary;
if (currentMaxIndex != i) {
list[currentMaxIndex] = list[i];
list[i] = currentMax;
}
}
}
/** The method for sorting the numbers */
public static > void insertionSort(E[] list) {
for (int i = 1; i < list.length; i++) {
/** insert list[i] into a sorted sublist list[0..i-1] so that list[0..i] is sorted. */
E currentElement = list[i];
int k;
for (k = i - 1; k >= 0 && list[k].compareTo(currentElement) > 0; k--) {
list[k + 1] = list[k];
}
// Insert the current element into list[k+1]
list[k + 1] = currentElement;
}
}
/** The method for sorting the numbers */
public static > void bubbleSort(E[] list) {
boolean needNextPass = true;
for (int k = 1; k < list.length && needNextPass; k++) {
// Array may be sorted and next pass not needed
needNextPass = false;
for (int i = 0; i < list.length - k; i++) {
if (list[i].compareTo(list[i + 1]) > 0) {
// Swap list[i] with list[i + 1]
E temp = list[i];
list[i] = list[i + 1];
list[i + 1] = temp;
needNextPass = true; // Next pass still needed
}
}
}
}
/** The method for sorting the numbers */
public static > void mergeSort(E[] list) {
if (list.length > 1) {
// Merge sort the first half
E[] firstHalf = (E[])new Comparable[list.length / 2];
System.arraycopy(list, 0, firstHalf, 0, list.length / 2);
mergeSort(firstHalf);
// Merge sort the second half
int secondHalfLength = list.length - list.length / 2;
E[] secondHalf = (E[])new Comparable[secondHalfLength];
System.arraycopy(list, list.length / 2,
secondHalf, 0, secondHalfLength);
mergeSort(secondHalf);
// Merge firstHalf with secondHalf
E[] temp = merge(firstHalf, secondHalf);
System.arraycopy(temp, 0, list, 0, temp.length);
}
}
private static> E[] merge(E[] list1, E[] list2) {
E[] temp = (E[])new Comparable[list1.length + list2.length];
int current1 = 0; // Index in list1
int current2 = 0; // Index in list2
int current3 = 0; // Index in temp
while (current1 < list1.length && current2 < list2.length) {
if (list1[current1].compareTo(list2[current2]) < 0) {
temp[current3++] = list1[current1++];
}
else {
temp[current3++] = list2[current2++];
}
}
while (current1 < list1.length) {
temp[current3++] = list1[current1++];
}
while (current2 < list2.length) {
temp[current3++] = list2[current2++];
}
return temp;
}
public static>void quickSort(E[] list) {
quickSort(list, 0, list.length - 1);
}
private static>void quickSort(E[] list, int first, int last) {
if (last > first) {
int pivotIndex = partition(list, first, last);
quickSort(list, first, pivotIndex - 1);
quickSort(list, pivotIndex + 1, last);
}
}
/** Partition the array list[first..last] */
private static>int partition(E[] list, int first, int last) {
E pivot = list[first]; // Choose the first element as the pivot
int low = first + 1; // Index for forward search
int high = last; // Index for backward search
while (high > low) {
// Search forward from left
while (low <= high && list[low].compareTo(pivot) <= 0) {
low++;
}
// Search backward from right
while (low <= high && list[high].compareTo(pivot) > 0) {
high--;
}
// Swap two elements in the list
if (high > low) {
E temp = list[high];
list[high] = list[low];
list[low] = temp;
}
}
while (high > first && list[high].compareTo(pivot) >= 0) {
high--;
}
// Swap pivot with list[high]
if (pivot.compareTo(list[high]) > 0) {
list[first] = list[high];
list[high] = pivot;
return high;
}
else {
return first;
}
}
public static>void heapSort(E[] list) {
Heap heap = new Heap(); // Create a Heap
// Add elements to the heap
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
heap.add(list[i]);
}
// Remove elements from the heap
for (int i = list.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
list[i] = heap.remove();
}
}
/** Sort the int array list. numberOfDigits is the number of digits * in the largest number in the array */
public static void radixSort(int[] list, int numberOfDigits) {
java.util.ArrayList[] buckets = new java.util.ArrayList[10];
for (int i = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
buckets[i] = new java.util.ArrayList();
}
for (int position = 0; position <= numberOfDigits; position++) {
// Clear buckets
for (int i = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
buckets[i].clear();
}
// Distribute the elements from list to buckets
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
int key = getKey(list[i], position);
buckets[key].add(list[i]);
}
// Now move the elements from the buckets back to list
int k = 0; // k is an index for list
for (int i = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
if (buckets[i] != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < buckets[i].size(); j++)
list[k++] = buckets[i].get(j);
}
}
}
}
/** Return the digit at the specified position. * The last digit's position is 0. */
public static int getKey(int number, int position) {
int result = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < position; i++)
result *= 10;
return (number / result) % 10;
}
static class Heap > {
java.util.ArrayList list = new java.util.ArrayList();
/** Create a default heap */
public Heap() {
}
/** Create a heap from an array of objects */
public Heap(E[] objects) {
for (int i = 0; i < objects.length; i++) {
add(objects[i]);
}
}
/** Add a new object into the heap */
public void add(E newObject) {
list.add(newObject); // Append to the heap
int currentIndex = list.size() - 1; // The index of the last node
while (currentIndex > 0) {
int parentIndex = (currentIndex - 1) / 2;
// Swap if the current object is greater than its parent
if (list.get(currentIndex).compareTo(list.get(parentIndex)) > 0) {
//最小堆
//if (list.get(currentIndex).compareTo(list.get(parentIndex)) < 0) {
E temp = list.get(currentIndex);
list.set(currentIndex, list.get(parentIndex));
list.set(parentIndex, temp);
}
else {
break; // the tree is a heap now
}
currentIndex = parentIndex;
}
}
/** Remove the root from the heap */
public E remove() {
if (list.size() == 0) {
return null;
}
E removedObject = list.get(0);
list.set(0, list.get(list.size() - 1));
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
int currentIndex = 0;
while (currentIndex < list.size()) {
int leftChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 1;
int rightChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 2;
// Find the maximum between two children
if (leftChildIndex >= list.size()) {
break; // The tree is a heap
}
int maxIndex = leftChildIndex;
if (rightChildIndex < list.size()) {
if (((Comparable)(list.get(maxIndex))).compareTo(
list.get(rightChildIndex)) < 0) {//>0
maxIndex = rightChildIndex;
}
}
// Swap if the current node is less than the maximum
if (((Comparable)(list.get(currentIndex))).compareTo(
list.get(maxIndex)) < 0) {//>0
E temp = list.get(maxIndex);
list.set(maxIndex, list.get(currentIndex));
list.set(currentIndex, temp);
currentIndex = maxIndex;
}
else {
break; // The tree is a heap
}
}
return removedObject;
}
/** Get the number of nodes in the tree */
public int getSize() {
return list.size();
}
}
}