基于Android的计步器(Pedometer)的讲解(四)——后台记步
今天先不说Pedometer(计步器)项目UI方面的了,今天讲一个基于重力加速度的记步功能传感器(Sensor),然后
在后台开启记步。
计步器(Pedometer)整个项目的源代码,感兴趣的朋友可以下载来看看(记得帮小弟在github打个星~)
github下载
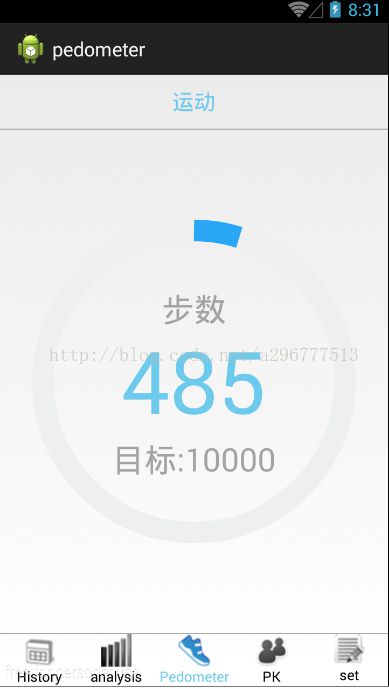
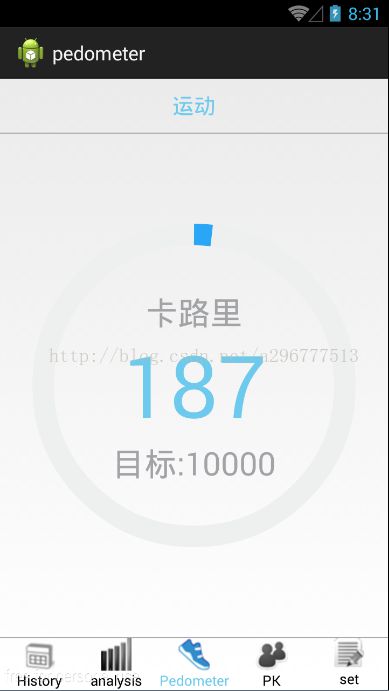
先上几张效果图:(效果和上一篇讲到的CircleBar非常的相似,因为记步功能在后台)
如图所示,能根据你的一些基本参数,来记步。有一个缺点,因为这个是根据感应加速度来计算是否走一步,所以你在原地晃手机,也会记步,不过正常的走路还是挺准确的。
首先给出StepDetector类的代码:
package com.example.histogram.widet;
import android.content.Context;
import android.hardware.Sensor;
import android.hardware.SensorEvent;
import android.hardware.SensorEventListener;
import android.hardware.SensorManager;
/**
* 这是一个实现了信号监听的记步的类
* 这是从谷歌找来的一个记步的算法,看不太懂
* @author Liyachao Date:2015-1-6
*
*/
public class StepDetector implements SensorEventListener {
public static int CURRENT_SETP = 0;
public static float SENSITIVITY = 10; // SENSITIVITY灵敏度
private float mLastValues[] = new float[3 * 2];
private float mScale[] = new float[2];
private float mYOffset;
private static long end = 0;
private static long start = 0;
/**
* 最后加速度方向
*/
private float mLastDirections[] = new float[3 * 2];
private float mLastExtremes[][] = { new float[3 * 2], new float[3 * 2] };
private float mLastDiff[] = new float[3 * 2];
private int mLastMatch = -1;
/**
* 传入上下文的构造函数
*
* @param context
*/
public StepDetector(Context context) {
super();
int h = 480;
mYOffset = h * 0.5f;
mScale[0] = -(h * 0.5f * (1.0f / (SensorManager.STANDARD_GRAVITY * 2)));
mScale[1] = -(h * 0.5f * (1.0f / (SensorManager.MAGNETIC_FIELD_EARTH_MAX)));
}
//当传感器检测到的数值发生变化时就会调用这个方法
public void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent event) {
Sensor sensor = event.sensor;
synchronized (this) {
if (sensor.getType() == Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER) {
float vSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
final float v = mYOffset + event.values[i] * mScale[1];
vSum += v;
}
int k = 0;
float v = vSum / 3;
float direction = (v > mLastValues[k] ? 1
: (v < mLastValues[k] ? -1 : 0));
if (direction == -mLastDirections[k]) {
// Direction changed
int extType = (direction > 0 ? 0 : 1); // minumum or
// maximum?
mLastExtremes[extType][k] = mLastValues[k];
float diff = Math.abs(mLastExtremes[extType][k]
- mLastExtremes[1 - extType][k]);
if (diff > SENSITIVITY) {
boolean isAlmostAsLargeAsPrevious = diff > (mLastDiff[k] * 2 / 3);
boolean isPreviousLargeEnough = mLastDiff[k] > (diff / 3);
boolean isNotContra = (mLastMatch != 1 - extType);
if (isAlmostAsLargeAsPrevious && isPreviousLargeEnough
&& isNotContra) {
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (end - start > 500) {// 此时判断为走了一步
CURRENT_SETP++;
mLastMatch = extType;
start = end;
}
} else {
mLastMatch = -1;
}
}
mLastDiff[k] = diff;
}
mLastDirections[k] = direction;
mLastValues[k] = v;
}
}
}
//当传感器的经度发生变化时就会调用这个方法,在这里没有用
public void onAccuracyChanged(Sensor arg0, int arg1) {
}
}
下来是后台服务StepService的代码:
package com.example.histogram.widet;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.hardware.Sensor;
import android.hardware.SensorManager;
import android.os.IBinder;
public class StepService extends Service {
public static Boolean flag = false;
private SensorManager sensorManager;
private StepDetector stepDetector;
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
//这里开启了一个线程,因为后台服务也是在主线程中进行,这样可以安全点,防止主线程阻塞
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
startStepDetector();
}
}).start();
}
private void startStepDetector() {
flag = true;
stepDetector = new StepDetector(this);
sensorManager = (SensorManager) this.getSystemService(SENSOR_SERVICE);//获取传感器管理器的实例
Sensor sensor = sensorManager
.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER);//获得传感器的类型,这里获得的类型是加速度传感器
//此方法用来注册,只有注册过才会生效,参数:SensorEventListener的实例,Sensor的实例,更新速率
sensorManager.registerListener(stepDetector, sensor,
SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_FASTEST);
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
flag = false;
if (stepDetector != null) {
sensorManager.unregisterListener(stepDetector);
}
}
}
最后把FragmentPedometer测试页面的代码也给大家,如果大家看过之前的博客,应该知道这是一个碎片。如果没看过,看兴趣的朋友可以看看之前的博文:
package com.example.histogram;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import com.example.changepage1.R;
import com.example.histogram.widet.CircleBar;
import com.example.histogram.widet.StepDetector;
import com.example.histogram.widet.StepService;
import com.example.histogram.widet.Weather;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
/**
* 这是记步的碎片
* Author: 李垭超 email:[email protected]
* Date: 2015-1-6
* Time: 下午8:39
*/
public class FragmentPedometer extends Fragment implements OnClickListener{
private View view;
private CircleBar circleBar;
private int total_step = 0;
private Thread thread;
private int Type = 1;
private int calories = 0;
private int step_length = 50;
private int weight = 70;
private Weather weather;
private String test;
private boolean flag = true;// 来判断第三个页面是否开启动画
@SuppressLint("HandlerLeak")
Handler handler = new Handler() {
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
total_step = StepDetector.CURRENT_SETP;
if (Type == 1) {
circleBar.setProgress(total_step, Type);
} else if (Type == 2) {
calories = (int) (weight * total_step * step_length * 0.01 * 0.01);
circleBar.setProgress(calories, Type);
} else if (Type == 3) {
if (flag) {
circleBar.startCustomAnimation();
flag = false;
}
if (test != null || weather.getWeather() == null) {
weather.setWeather("正在更新中...");
weather.setPtime("");
weather.setTemp1("");
weather.setTemp2("");
circleBar.startCustomAnimation();
circleBar.setWeather(weather);
} else {
circleBar.setWeather(weather);
}
}
}
};
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.pedometer, container, false);
init();
mThread();
return view;
}
private void init() {
Intent intent = new Intent(getActivity(), StepService.class);
getActivity().startService(intent);
weather = new Weather();
circleBar = (CircleBar) view.findViewById(R.id.progress_pedometer);
circleBar.setMax(10000);
circleBar.setProgress(StepDetector.CURRENT_SETP, 1);
circleBar.startCustomAnimation();
circleBar.setOnClickListener(this);
}
private void mThread() {
if (thread == null) {
thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (StepService.flag) {
Message msg = new Message();
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
}
}
});
thread.start();
}
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.progress_pedometer:
if (Type == 1) {
Type = 2;
} else if (Type == 2) {
flag = true;
Type = 3;
} else if (Type == 3) {
Type = 1;
}
Message msg = new Message();
handler.sendMessage(msg);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
如果大家有什么建议,可以提出来哦。