高性能服务器编程--多进程和多线程
今天我们来看看高性能服务器编程--多进程和多线程。有的人就会想高性能服务器高性能在哪里了?
在之前的TCP和UDP编程中,链接的客户端如果没有断开链接,服务器则不能在连接别的客户端,导致服务器同时只能处理一个客户端,这样就大大降低了服务器的效率,所以为了解决这个问题,就提出了高性能服务器编程。下面我们就来看看具体是怎么实现的。
一、高性能服务器编程--多进程
思路: 父进程只负责accept--->fork,具体和客户端通讯由子进程来完成。
这里需要注意的是:
1、父子进程共享文件描述符,所以创建出子进程后,没必要单独传递文件描述符。
2、父进程创建出子进程后,关闭accept 返回的文件描述符。
这里就有一问题??父进程要关闭连接的文件描述符!为什么??
因为:1、父进程不关闭文件描述符,则后续的创建的子进程会将所有的文件描述符继承下来。
2、父进程不关闭文件描述符,则后续的链接的文件描述符不断增大,链接的客户端的数量就受一个进程最多打开的文件的限制。
ser.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
void fun(int sign)
{
wait(NULL);
}
void main()
{
signal(SIGCHLD, fun);
int sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
assert(sockfd != -1);
struct sockaddr_in ser, cli;
memset(&ser, 0, sizeof(ser));
ser.sin_family = AF_INET;
ser.sin_port = htons(6500);
ser.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("192.168.1.120");
int res = bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&ser, sizeof(ser));
assert(res != -1);
listen(sockfd, 5);
while(1)
{
int len = sizeof(cli);
int c = accept(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&cli, &len);
if(c < 0)
{
printf("error\n");
continue;
}
pid_t n = fork();
assert(n != -1);
if(n == 0)
{
while(1)
{
char buff[128] = {0};
int n = recv(c, buff, 127, 0);
if(n <= 0)
{
break;
}
printf("addr::%s port::%d\n",
inet_ntoa(cli.sin_addr), ntohs(cli.sin_port));
printf("%s\n", buff);
send(c, "OK", 2, 0);
}
printf("%d unlink\n", c);
close(c);
exit(0);
}
close(c);
}
}
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
void main()
{
int sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
assert(sockfd != -1);
struct sockaddr_in ser, cli;
memset(&ser, 0, sizeof(ser));
ser.sin_family = AF_INET;
ser.sin_port = htons(6500);
ser.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("192.168.1.120");
int res = connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&ser, sizeof(ser));
assert(res != -1);
while(1)
{
printf("please input: ");
fflush(stdout);
char buff[128] = {0};
fgets(buff, 128, stdin);
if(strncmp(buff, "end", 3) == 0)
{
close(sockfd);
break;
}
send(sockfd, buff, strlen(buff) - 1, 0);
memset(buff, 0, 128);
recv(sockfd, buff, 127, 0);
printf("%s\n", buff);
}
} 二、高性能服务器编程--多线程
与多进程编程对比:
1、创建多进程会消耗大量的系统资源
2、如果子进程在很短的时间内结束,系统负担会加重
多线程的优点:
1、创建线程资源消耗相对较小
2、线程之间数据共享更容易
3、线程结束释放资源比较少
思路:主线程负责接受客户端链接,函数线程负责和客户端通讯。
注意:
1、主线程接受链接,链接的文件描述符如何传递给函数线程?
文件描述符必须通过创建函数线程时值传递给函数线程。
2、主线程能不能关闭文件描述符??
不可以。线程共用一个PCB,即就是多线程用一个文件描述符,主线程关闭文件描述符,整个进程也就关闭了文件描述符,函数线程就没办法使用。
ser.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
void *pthread_fun(void *arg)
{
int c=(int)arg;
while(1)
{
char buff[128]={0};
int n=recv(c,buff,127,0);
if(n<=0)
{
close(c);
break;
}
printf("%s\n",buff);
send(c,"ok",2,0);
}
}
void main()
{
int sockfd=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
assert(sockfd!=-1);
struct sockaddr_in ser,cli;
memset(&ser,0,sizeof(ser));
ser.sin_family=AF_INET;
ser.sin_port=htons(6500);
ser.sin_addr.s_addr=inet_addr("127.0.0.1");
int re=bind(sockfd,(struct sockaddr*)&ser,sizeof(ser));
assert(re!=-1);
listen(sockfd,5);
while(1)
{
int len=sizeof(cli);
int c=accept(sockfd,(struct sockaddr*)&cli,&len);
if(c<0)
{
printf("error\n");
continue;
}
pthread_t id;
int res=pthread_create(&id,NULL,pthread_fun,(void*)c);
assert(res==0);
}
} #include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
void main()
{
int sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
assert(sockfd != -1);
struct sockaddr_in ser, cli;
memset(&ser, 0, sizeof(ser));
ser.sin_family = AF_INET;
ser.sin_port = htons(6500);
ser.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("192.168.1.120");
int res = connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&ser, sizeof(ser));
assert(res != -1);
while(1)
{
printf("please input: ");
fflush(stdout);
char buff[128] = {0};
fgets(buff, 128, stdin);
if(strncmp(buff, "end", 3) == 0)
{
close(sockfd);
break;
}
send(sockfd, buff, strlen(buff) - 1, 0);
memset(buff, 0, 128);
recv(sockfd, buff, 127, 0);
printf("%s\n", buff);
}
} 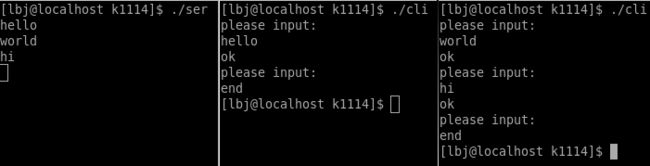
可以看到我们可以开启多个客户端进行数据发送,并且其中一个客户端关闭并不会影响到其他的客户端。