Android高级进阶——自定义View实践篇(一)自定义标签流布局
开篇
前面已经介绍了一系列的 View 的自定义,后面的几篇会找几个实际的例子来动手练一下,今天就先瞅瞅 标签流容器
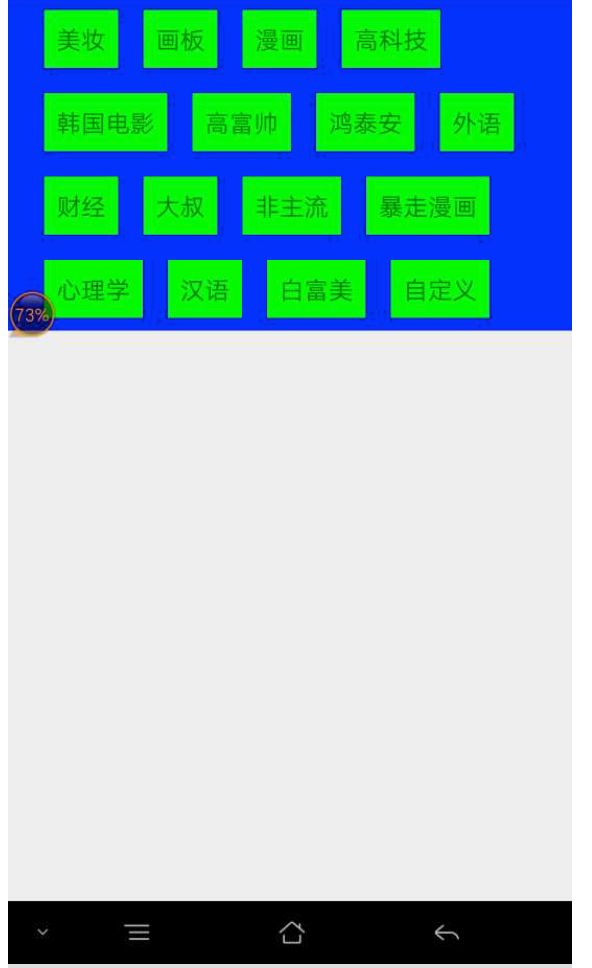
先给出效果图:
这个自定义 View 是非常简单的,只要你把前面的 view 的工作原理一、二、三 大致看一遍就可以很轻松的撸出来
自定义 View 的种类
自定义 View 的分类标准不唯一,大致可以分为 4 类
- 1、继承 View 重写 onDraw 方法
这种方法主要用于实现一些不规则的效果,即这种效果不方便通过布局的组合方式来达到,往往需要静态或者动态地显示一些不规则的图形。很显然这需要通过绘制的方式来实现,即重写 onDraw 方法。采用这种方式需要自己支持 wrap_content,并且 padding 也需要自己处理。
- 2、继承 ViewGroup 派生特殊的 Layout
这种方法主要用于实现自定义的布局,即除了 LinearLayout、RelativeLayout、FrameLayout 这几种系统的布局之外,我们重新定义一种新布局,当某种效果看起来很像几种 View 组合在一起的时候,可以采用这种方法来实现。采用这种方式稍微复杂一些,需要合适地处理 ViewGroup 的测量、布局这两个过程,并同时处理子元素的测量和布局过程。
3、继承特定的 View (比如 TextView)
这种方法比较常见,一般是用于扩展某种已有的 View 的功能,比如 TextView,这种方法比较容易实现。这种方法不需要自己支持 wrap_content 和 padding 等。
4、继承特定的 ViewGroup (比如 LinearLayout)
这种方法也比较常见,当某种效果看起来很像几种 View 组合在一起的时候,可以采用这种方法来实现。采用这种方法不需要自己处理 ViewGroup 的测量和布局这两个过程。需要注意这种方法和方法 2 的区别,一般来说 方法 2 能实现的效果方法 4 也都能实现,两者的主要差别在于 方法 2 更接近 View 的底层。
自定义 View 常见注意事项
这里我们会列举一些自定义 View 过程中的一些注意事项,这些问题如果处理不好,有些会影响 View 的正常使用,而有些会导致内存泄漏等。
- 1、让 View 支持 wrap_content
这是因为直接继承 View 或者 ViewGroup 的控件,如果不在 onMeasure 中对 wrap_content 做特殊处理,那么外界在布局中使用 wrap_content 时就无法达到预期的效果,这个就不在这里细说了,有兴趣的可以去看一下我 CSDN 上的简单介绍 Android——View的工作原理(一)
- 2、如果有必要,让你的 View 支持 padding
这是因为直接继承 View 的控件,如果不在 draw 方法中处理 padding,那么 padding 属性是无法起作用的。另外,直接继承自 ViewGroup 的控件需要在 onMeasure 和 onLayout 中考虑 padding 和 子元素的 margin 对其造成的影响,不然将导致 padding 和 子元素的 margin 失效。
- 3、尽量不要在 View 中使用 Handler,没必要
这是因为 View 内部本身就提供了 post 系列方法,完全可以替代 Handler 的作用,当然除非你很明确地要使用 Handler 来发送消息。
- 4、View 中如果有线程或动画,需要及时停止,参考 View#onDetachedFromWindow
这一条也很好理解,如果有线程或者动画需要停止时,那么 onDetachedFromWindow 方法是一个很好的时机。当包含此 View 的 Activity 退出或者当前 View 被 remove 时,View 的 onDetachedFromWindow 方法会被调用,和此方法对应的是 onAttachedToWindow 方法,当包含此 View 的 Activity 启动时,View 的 onAttachedToWindow 方法会被调用。同时,当 View 变得不可见时我们也需要停止线程和动画,如果不及时处理这种问题,有可能会造成内存泄漏。
- 5、View 带有滑动嵌套情形时,需要处理号滑动冲突
如果有滑动冲突的话,那么要合适地处理滑动冲突,否则将会严重影响 View 的效果
自定义 标签流容器
onMeasure 方法:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int usedWidth = 0; //已使用的宽度
int remaining = 0; //剩余可用宽度
int totalHeight = 0; //总高度
int lineHeight = 0; //当前行高
int maxLineHeight = 0; //最大行高
//for 循环遍历 子 view
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
//获取 layoutParams
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
throw new RuntimeException("FlowLayout 的 \"layout_width\" 必须为 \"match_parent\" 或者 精确数值");
} else {
//测量 子 view
measureChild(childView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 剩余可用 width
remaining = widthSize - usedWidth - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight();
//当剩余空间不足以放下一个新 view 时,换行
if (childView.getMeasuredWidth() > remaining) {
//累加高度,用于作为当前 FlowLayout 的最终高度
totalHeight += maxLineHeight;
//重置
maxLineHeight = 0;
usedWidth = 0;
}
//已使用 width 进行 累加
usedWidth += lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin + childView.getMeasuredWidth();
//当前 view 的高度
lineHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
//取出每行 view 的最大高度
maxLineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, maxLineHeight);
}
}
//最终高度,记得加上最后一行的view 的高度
totalHeight += maxLineHeight + getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
heightSize = totalHeight;
}
//去较大的一个作为 FlowLayout 的最终高度
heightSize = Math.max(totalHeight, heightSize);
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, heightSize);
}其实就是一个遍历的过程,通过遍历获取子 view 的 layoutParams,然后进行一个模拟排版过程,最终拿到 FlowLayout 的最终高度,并设置
需要注意的地方:
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams(); 这是一个强制转换过程,因为我们在 addView 时,addView 内部会去获取并创建一个 LayoutParams,而这个 LayoutParams 是需要我们自己自定的
addView 内部实现代码:
...
public void addView(View child) {
addView(child, -1);
}
public void addView(View child, int index) {
LayoutParams params = child.getLayoutParams();
if (params == null) {
params = generateDefaultLayoutParams(); //返回默认地LayoutParams类,作为该View的属性值
if (params == null) {//如果不能获取到LayoutParams对象,则抛出异常。
throw new IllegalArgumentException("generateDefaultLayoutParams() cannot return null");
}
}
addView(child, index, params);
}
public void addView(View child, int width, int height) {
//返回默认地LayoutParams类,作为该View的属性值
final LayoutParams params = generateDefaultLayoutParams();
params.width = width; //重新设置width值
params.height = height; //重新设置height值
addView(child, -1, params); //这儿,我们有指定width、height的大小了。
}
public void addView(View child, LayoutParams params) {
addView(child, -1, params);
}
public void addView(View child, int index, LayoutParams params) {
...
// addViewInner() will call child.requestLayout() when setting the new LayoutParams
// therefore, we call requestLayout() on ourselves before, so that the child's request
// will be blocked at our level
requestLayout();
invalidate();
addViewInner(child, index, params, false);
}
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
//width 为 WRAP_CONTENT大小 , height 为WRAP_CONTENT
//ViewGroup的子类可以重写该方法,达到其特定要求。
return new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
private void addViewInner(View child, int index, LayoutParams params,
boolean preventRequestLayout) {
if (!checkLayoutParams(params)) { //params对象是否为null
params = generateLayoutParams(params); //如果params对象是为null,重新构造个LayoutParams对象
}
//preventRequestLayout值为false
if (preventRequestLayout) {
child.mLayoutParams = params; //为View的mLayoutParams属性赋值
} else {
child.setLayoutParams(params);//为View的mLayoutParams属性赋值,但会调用requestLayout()请求重新布局
}
//if else 语句会设置View为mLayoutParams属性赋值
...
}
...
} onLayout 方法
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
final int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft();
final int paddingRight = getPaddingRight();
final int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();
int childTop = paddingTop;
int childLeft = paddingLeft;
int childRight = 0;
int childBottom = 0;
// FlowLayout 的 width
final int width = right - left;
//当前 FlowLayout 中 子 View 可使用的最大宽度
int childWidthSpace = width - paddingLeft - paddingRight;
//行高
int lineHeight = 0;
//最大行高
int maxLineHeight = 0;
//已使用 width
int usedWidth = 0;
//总高度
int totalHeight = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
int childWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();
//已使用的 width 计算
usedWidth += lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin + childWidth;
//当前 view 的高度
lineHeight = childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
//当剩余空间不足时,换行
if (usedWidth > childWidthSpace) {
totalHeight += maxLineHeight;
//重置 left
childLeft = paddingLeft;
//增加 top 值
childTop = paddingTop + totalHeight;
maxLineHeight = 0;
usedWidth = lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin + childWidth;
}
maxLineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, maxLineHeight);
childLeft += lp.leftMargin;
childTop += lp.topMargin;
childRight = childLeft + childWidth;
childBottom = childTop + childHeight;
childView.layout(childLeft, childTop, childRight, childBottom);
childLeft = childRight + lp.rightMargin;
}
}代码都非常简单,而且注释也挺全,就不在一步一步详细说了
添加子 View
//添加 子 view
public void setAdapter(BaseAdapter mAdapter) {
this.mAdapter = mAdapter;
if (mAdapter == null || mAdapter.getCount() == 0) {
return;
}
removeAllViews();
for (int i = 0; i < mAdapter.getCount(); i++) {
View view = mAdapter.getView(i, null, null);
;
; Log.e("=========",view.getLayoutParams()+"");
final int position = i;
view.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (mListener != null) {
mListener.itemClick(position);
}
}
});
addView(view);
}
//这个 requestLayout 其实没必要现式调用,addView 方法内部其实已经调用了 requestLayout 方法
//requestLayout();
}其他重写方法 LayoutParams 的创建
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new MarginLayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(LayoutParams p){
return new MarginLayoutParams(p);
}具体使用
final List list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("美妆");
list.add("画板");
list.add("漫画");
list.add("高科技");
list.add("韩国电影");
list.add("高富帅");
list.add("鸿泰安");
list.add("外语");
list.add("财经");
list.add("大叔");
list.add("非主流");
list.add("暴走漫画");
list.add("心理学");
list.add("汉语");
list.add("白富美");
list.add("自定义");
flowLayout.setAdapter(new BaseAdapter() {
@Override
public int getCount() {
return list.size();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return null;
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
View view = LayoutInflater.from(FlowLayoutActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.item_tag, parent, false);
TextView textView = view.findViewById(R.id.tv_text);
textView.setText(list.get(position));
return view;
}
});
flowLayout.setItemClickListener(new FlowLayout.TagItemClickListener() {
@Override
public void itemClick(int position) {
Toast.makeText(FlowLayoutActivity.this, list.get(position), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}); 给出完整代码:
package com.summary.hecom.custom.view;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
/** * Created by hecom on 2018/4/28. */
public class FlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
private Context mContext;
private BaseAdapter mAdapter;
private TagItemClickListener mListener;
public FlowLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
this.mContext = context;
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int usedWidth = 0; //已使用的宽度
int remaining = 0; //剩余可用宽度
int totalHeight = 0; //总高度
int lineHeight = 0; //当前行高
int maxLineHeight = 0; //最大行高
//for 循环遍历 子 view
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
//获取 layoutParams
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
throw new RuntimeException("FlowLayout 的 \"layout_width\" 必须为 \"match_parent\" 或者 精确数值");
} else {
//测量 子 view
measureChild(childView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 剩余可用 width
remaining = widthSize - usedWidth - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight();
//当剩余空间不足以放下一个新 view 时,换行
if (childView.getMeasuredWidth() > remaining) {
//累加高度,用于作为当前 FlowLayout 的最终高度
totalHeight += maxLineHeight;
//重置
maxLineHeight = 0;
usedWidth = 0;
}
//已使用 width 进行 累加
usedWidth += lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin + childView.getMeasuredWidth();
//当前 view 的高度
lineHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
//取出每行 view 的最大高度
maxLineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, maxLineHeight);
}
}
//最终高度,记得加上最后一行的view 的高度
totalHeight += maxLineHeight + getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
heightSize = totalHeight;
}
//去较大的一个作为 FlowLayout 的最终高度
heightSize = Math.max(totalHeight, heightSize);
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, heightSize);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
final int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft();
final int paddingRight = getPaddingRight();
final int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();
int childTop = paddingTop;
int childLeft = paddingLeft;
int childRight = 0;
int childBottom = 0;
// FlowLayout 的 width
final int width = right - left;
//当前 FlowLayout 中 子 View 可使用的最大宽度
int childWidthSpace = width - paddingLeft - paddingRight;
//行高
int lineHeight = 0;
//最大行高
int maxLineHeight = 0;
//已使用 width
int usedWidth = 0;
//总高度
int totalHeight = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
int childWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();
//已使用的 width 计算
usedWidth += lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin + childWidth;
//当前 view 的高度
lineHeight = childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
//当剩余空间不足时,换行
if (usedWidth > childWidthSpace) {
totalHeight += maxLineHeight;
//重置 left
childLeft = paddingLeft;
//增加 top 值
childTop = paddingTop + totalHeight;
maxLineHeight = 0;
usedWidth = lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin + childWidth;
}
maxLineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, maxLineHeight);
childLeft += lp.leftMargin;
childTop += lp.topMargin;
childRight = childLeft + childWidth;
childBottom = childTop + childHeight;
childView.layout(childLeft, childTop, childRight, childBottom);
childLeft = childRight + lp.rightMargin;
}
}
//添加 子 view
public void setAdapter(BaseAdapter mAdapter) {
this.mAdapter = mAdapter;
if (mAdapter == null || mAdapter.getCount() == 0) {
return;
}
removeAllViews();
for (int i = 0; i < mAdapter.getCount(); i++) {
View view = mAdapter.getView(i, null, null);
;
; Log.e("=========",view.getLayoutParams()+"");
final int position = i;
view.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (mListener != null) {
mListener.itemClick(position);
}
}
});
addView(view);
}
requestLayout();
}
public void setItemClickListener(TagItemClickListener mListener) {
this.mListener = mListener;
}
public interface TagItemClickListener {
void itemClick(int position);
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new MarginLayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(LayoutParams p) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(p);
}
}
现在的 FlowLayout 就已经支持了 padding 以及 margin ,代码非常简单,因为只是一个练手项目,也没对外提供其他功能,下篇可能会实现 点击拖拽排序 功能。