DnCNN代码学习—data_generator.py
DnCNN代码学习—data_generator.py
一、源代码+注释
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# =============================================================================
# @article{zhang2017beyond,
# title={Beyond a {Gaussian} denoiser: Residual learning of deep {CNN} for image denoising},
# author={Zhang, Kai and Zuo, Wangmeng and Chen, Yunjin and Meng, Deyu and Zhang, Lei},
# journal={IEEE Transactions on Image Processing},
# year={2017},
# volume={26},
# number={7},
# pages={3142-3155},
# }
# by Kai Zhang (08/2018)
# [email protected]
# https://github.com/cszn
# modified on the code from https://github.com/SaoYan/DnCNN-PyTorch
# =============================================================================
# no need to run this code separately
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import operator
import glob ##文件名操作模块glob
import cv2 #读取图像首先要导入OpenCV包
import numpy as np #
# from multiprocessing import Pool
from torch.utils.data import Dataset #torch.utils.data.Dataset 是一个表示数据集的抽象类
import torch ##包 torch 包含了多维张量的数据结构以及基于其上的多种数学操作。
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
patch_size, stride = 4, 1 #补丁大小 40 步长10
aug_times = 1
scales = [1, 0.9, 0.8, 0.7]
batch_size = 128 #批量大小
#加噪声类
class DenoisingDataset(Dataset):
"""Dataset wrapping tensors.
Arguments:
xs (Tensor): clean image patches
sigma: noise level, e.g., 25
"""
def __init__(self, xs):
super(DenoisingDataset, self).__init__()
self.xs = xs #清洁图像
def __getitem__(self, index):
batch_x = self.xs[index]
#torch.randn:返回一个张量,包含了从区间[0,1)的均匀分布中抽取的一组随机数,形状由可变参数sizes 定义
#在PyTorch中,数学运算有in-place和none-in-place两种形式。 #in-place,就是计算结果替换原始内存中的值 相乘:mul_
#noise = torch.randn(batch_x.size()).mul_(self.sigma/255.0)
noise = torch.randn(batch_x.size()).mul_( np.random.randint(55)/255.0)
print('noise.shape',noise.shape)
batch_y = batch_x + noise #加噪声
return batch_y, batch_x #返回批量batch_y, batch_x
def __len__(self):
print(self.xs. size(0))
return self.xs. size(0) #xs.size(0)指batchsize的值
#展示图片
def show(x, title=None, cbar=False, figsize=None):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# # 图像的长和宽(英寸) #Figure返回的实例也将传递给后端的new_figure_manage
plt.figure(figsize=figsize)
# #interpolation 插值方法 #cmap: 颜色图谱(colormap), 默认绘制为RGB(A)颜色空间
plt.imshow(x, interpolation='nearest', cmap='gray')
if title:
plt.title(title)
if cbar:
plt.colorbar() ##将颜色条添加到绘图中。
plt.show() #输出图片
def data_aug(img, mode=0):
# data augmentation #数据增强
if mode == 0: #返回原图
return img
elif mode == 1: #翻转变换(flip): 沿着水平或者垂直方向翻转图像 #flipud(a) 上下翻转
return np.flipud(img)
elif mode == 2: #将矩阵A逆时针旋转90°以后返回
return np.rot90(img)
elif mode == 3: #先反转再旋转
return np.flipud(np.rot90(img))
elif mode == 4: #将矩阵逆时针旋转(90×k)°以后返回,k取负数时表示顺时针旋转,再翻转
return np.rot90(img, k=2)
elif mode == 5: #先旋转再翻转
return np.flipud(np.rot90(img, k=2))
elif mode == 6: #将矩阵逆时针旋转(90×k)°以后返回,k取负数时表示顺时针旋转
return np.rot90(img, k=3)
elif mode == 7: #先旋转再翻转
return np.flipud(np.rot90(img, k=3))
#从一张图像中获取多尺度的补丁
def gen_patches(file_name):
# get multiscale patches from a single image
#使用opencv读取图像,直接返回numpy.ndarray 对象,通道顺序为BGR ,注意是BGR,通道值默认范围0-255
# flag = 0 八位深度 1通道 位深度指的是存储每个像素所用的位数,主要用于存储
img = cv2.imread(file_name, 0) # gray scale
plt.show()
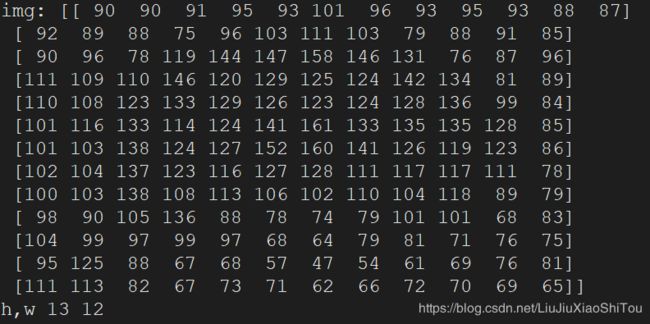
print('img:',img)
h, w = img.shape
print('h,w',h,w,)
patches = []
for s in scales:
h_scaled, w_scaled = int(h*s), int(w*s)
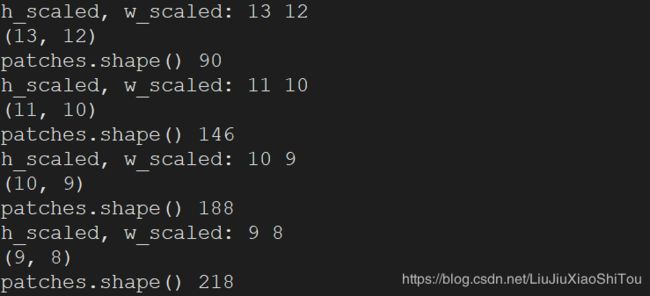
print('h_scaled, w_scaled:',h_scaled, w_scaled)
# 图像缩放使用cv2.resize时,参数输入是 宽×高×通道 INTER_CUBIC:4x4像素邻域的双三次插值 缩小图像
img_scaled = cv2.resize(img, (w_scaled,h_scaled ), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
print(img_scaled.shape)
# extract patches
for i in range(0, h_scaled-patch_size+1, stride):
for j in range(0, w_scaled-patch_size+1, stride):
x = img_scaled[i:i+patch_size, j:j+patch_size]
for k in range(0, aug_times):
#调用数据增强 自定义函数 random.randint产生 0 到 8 的一个整数型随机数
x_aug = data_aug(x, mode=np.random.randint(0, 8))
#print('x_aug',x_aug)
# #print(i,j)
patches.append(x_aug)
print('patches.shape()',len(patches))
#返回补丁值
print('patches:',patches)
print('patches.shape()',len(patches))
return patches #patches 是列表类型的
#从数据集中生成干净的补丁
def datagenerator(data_dir='testdata', verbose=True):
# generate clean patches from a dataset
file_list = glob.glob(data_dir+'/*.png') # 得到文件列表get name list of all .png files
# initrialize
data = []
# generate patches
for i in range(len(file_list)):
#调用自定义函数gen_patches
patches = gen_patches(file_list[i])
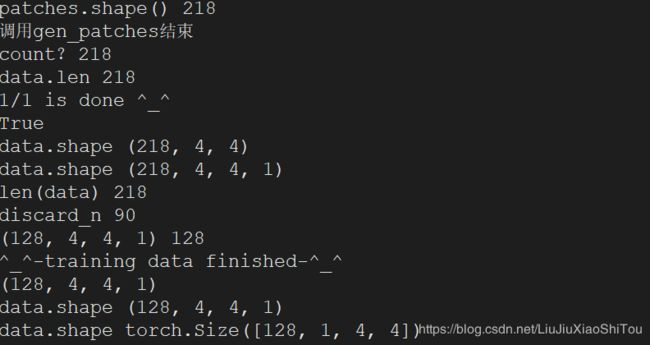
print('调用gen_patches结束')
count= 0
for patch in patches:
#print(patch)
count = count+1
data.append(patch)
print('count?',count)
print('data.len',len(data))
if verbose:
print(str(i+1) + '/' + str(len(file_list)) + ' is done ^_^')
#转换数据类型无符号整数(0到255)
print(operator.eq(patches,data))
#print('data:',data)
data = np.array(data, dtype='uint8')
#print(data)
print('data.shape',data.shape)
#np.expand_dims 扩展维度
data = np.expand_dims(data, axis=3)
print('data.shape',data.shape)
print('len(data)',len(data))
discard_n = len(data)-len(data)//batch_size*batch_size # because of batch namalization
print('discard_n',discard_n)
#delete是可以删除数组的整行和整列的
data = np.delete(data, range(discard_n), axis=0)
print(data.shape,len(data))
print('^_^-training data finished-^_^')
return data
if __name__ == '__main__':
data = datagenerator(data_dir='testdata')
print(data.shape)
#print(data)
# print('Shape of result = ' + str(res.shape))
# print('Saving data...')
# if not os.path.exists(save_dir):
# os.mkdir(save_dir)
# np.save(save_dir+'clean_patches.npy', res)
# print('Done.')
data = data.astype('float32')/255.0 #对数据进行处理,位于【0 1】
print('data.shape',data.shape)
#torch.from_numpy将numpy.ndarray 转换为pytorch的 Tensor。 transpose多维数组转置
data = torch.from_numpy(data.transpose((0, 3, 1, 2))) # tensor of the clean patches, N X C X H X W
print('data.shape',data.shape)
print(data)
#加噪声函数
DDataset=DenoisingDataset(data)
#DLoader = DataLoader(dataset=DDataset, num_workers=4, drop_last=True, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)二、为了更好理解数据生成的过程
1、将patch_size大小更改为4*4,步长stride修改为1。图片大小利用画图工具将图片大小修改为h*w=13*12,只选区一张图片存放在文件夹testdata里面。主要为测试class DenoisingDataset(Dataset)和datagenerator函数。为了更好理解过程,增加了许多print()语句。
2、修改下面一处代码,cv2.resize时,参数输入是 宽×高×通道,若输入(h_scaled ,w_scaled ),则会出现错误提示:ValueError: setting an array element with a sequence。错误原因是高宽不等时,不正确的参数顺序会导致生成的patch_size小于4*4,所以不可以转换为数组。这种错误再高宽相同的情况下不会发生。
# 图像缩放使用cv2.resize时,参数输入是 宽×高×通道 INTER_CUBIC:4x4像素邻域的双三次插值 缩小图像
img_scaled = cv2.resize(img, (w_scaled,h_scaled ), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)3、测试数据:数据原始大小为h*w=500*500,选择图像文件打开方式为画图工具,点击重新调整大小—>像素点—>取消‘保持纵横比’—>修改大小,保存。
三、模块运行过程(部分)
在模块if_name_=='__main__'先调用datagenerator()函数,对testdata文件夹里面的每一张图片,都调用gen_patches()函数。我们文件夹只有一张图片,现在进入gen_patches()函数。执行如下代码。
def gen_patches(file_name):
# get multiscale patches from a single image
#使用opencv读取图像,直接返回numpy.ndarray 对象,通道顺序为BGR ,注意是BGR,通道值默认范围0-255
# flag = 0 八位深度 1通道 位深度指的是存储每个像素所用的位数,主要用于存储
img = cv2.imread(file_name, 0) # gray scale
plt.show()
print('img:',img)
h, w = img.shape
print('h,w',h,w,)patches=[ ]用于存储生成的patch,patches是列表类型。patch大小4*4,stride步长为1,并且对图像进行处理,获得不同尺度的图像,对获得的图像矩阵进行遍历,每获得一个patch对其进行数据增强处理,调用data_aug()函数,旋转和翻转操作。将生成的patch存放在patches[]。
patches = []
for s in scales:
h_scaled, w_scaled = int(h*s), int(w*s)
print('h_scaled, w_scaled:',h_scaled, w_scaled)
# 图像缩放使用cv2.resize时,参数输入是 宽×高×通道 INTER_CUBIC:4x4像素邻域的双三次插值 缩小图像
img_scaled = cv2.resize(img, (w_scaled,h_scaled ), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
print(img_scaled.shape)
# extract patches
for i in range(0, h_scaled-patch_size+1, stride):
for j in range(0, w_scaled-patch_size+1, stride):
x = img_scaled[i:i+patch_size, j:j+patch_size]
for k in range(0, aug_times):
#调用数据增强 自定义函数 random.randint产生 0 到 8 的一个整数型随机数
x_aug = data_aug(x, mode=np.random.randint(0, 8))
#print('x_aug',x_aug)
# #print(i,j)
patches.append(x_aug)
print('patches.shape()',len(patches))
#返回补丁值
print('patches:',patches)
print('patches.shape()',len(patches))
return patches #patches 是列表类型的每一个图像文件都会调用一次gen_patches(file_name)函数,将所有的paches[]都存放在data[]并转换为数组类型,扩展维度,因为分为batch_size=128,所以执行discard_n = len(data)-len(data)//batch_size*batch_size,并删除多余的。返回data。datagenerator()执行完毕。返回if __name__ == '__main__',对数据进行处理,位于【0 1】,转换为pytorch的 Tensor,data目前为Tensor类型,再调用DenoisingDataset(Dataset),对data进行加噪处理。
四、如何计算patches大小
以测试数据图像为例,图像大小为h*w=13*12 ,patch_size,= 4,stride = 1 scales = [1, 0.9, 0.8, 0.7],batch_size = 128 。
当scales=1时,图像大小为13*12,pacthes=(13-4+1)(12-4+1) = 90
当scales=0.9时,图像大小为11*10,pacthes=(11-4+1)(10-4+1) = 56
当scales=0.8时,图像大小为10*9,pacthes=(10-4+1)(9-4+1) = 42
当scales=0.7时,图像大小为9*8,pacthes=(9-4+1)(8-4+1) = 30
所以patches[] = 218。因为batch_size = 128 ,要整除,所以要删除余数,最后为大小128。