Spring Boot框架搭建实例
目录
1 项目结构
2 pom.xml
3 配置文件
3.1 application.properties
3.2 application-dev.properties
4 Java代码
4.1 启动类
4.2 配置类
4.2.1 Redis配置类
4.2.2 RabbitMQ配置类
4.3 Controller
4.3.1 HelloWorldController
4.3.2 PersonController
4.3.3 UserReditRestController
4.4 Service
4.4.1 MyBatis
4.4.2 Redis
4.4.3 RabbitMQ
4.5 Model
4.5.1 Person
4.5.2 Order
4.6 DAO
4.7 Mapper
5 JSP页面
6 运行结果
6.1 页面结果
6.2 Redis结果
6.3 RabbitMQ结果
笔者使用的Java版本是jdk-8u201,IDE使用的是Eclipse Jee 2019-03。
1 项目结构
2 pom.xml
笔者使用的Spring Boot版本为2.1.5.RELEASE,mybatis-spring-boot-starter的版本为2.0.1。
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.1.5.RELEASE
com.hys
spring-boot
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
war
SpringBoot
Demo project for Spring Boot
1.8
2.0.1
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
runtime
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-tomcat
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-undertow
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-jdbc
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-aop
mysql
mysql-connector-java
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
${mybatis-spring-boot-starter.version}
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
org.apache.commons
commons-pool2
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-cache
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-security
org.springframework.session
spring-session-data-redis
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-amqp
org.apache.tomcat.embed
tomcat-embed-jasper
javax.servlet
jstl
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
3 配置文件
Spring Boot的配置文件可以配置多个,比如开发环境需要的配置文件、准上线环境需要的配置文件、上线环境需要的配置文件,等等...只需要在主配置文件application.properties中配置spring.profiles.active这个配置项即可动态加载需要的配置文件。以下演示了一个加载开发环境的配置文件application-dev.properties的代码。
3.1 application.properties
spring.profiles.active=dev3.2 application-dev.properties
#服务器配置
server.port=8080
server.servlet.context-path=/springboot
#日志配置
logging.level.root=info
logging.level.org=warn
logging.level.com.hys.springboot=debug
logging.path=E:/logs
#视图配置
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/WEB-INF/jsp/
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
#MySQL数据源配置
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/person?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
#MyBatis配置
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.hys.springboot.entity
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
#Redis配置
spring.redis.host=192.168.253.129
spring.redis.port=6379
spring.redis.password=
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=50
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle=50
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-wait=1000
#Spring Cache配置
spring.cache.type=none
spring.cache.redis.time-to-live=${random.int[300000,600000]}
spring.cache.redis.key-prefix=com.hys.cache.
#Spring Session配置
spring.session.store-type=redis
#RabbitMQ配置
spring.rabbitmq.addresses=127.0.0.1
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=root
spring.rabbitmq.password=root
spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host=/
spring.rabbitmq.connection-timeout=15000
spring.rabbitmq.publisher-confirms=true
spring.rabbitmq.publisher-returns=true
spring.rabbitmq.template.mandatory=true
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.acknowledge-mode=manual
4 Java代码
4.1 启动类
package com.hys.springboot;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.hys.springboot.dao")
@EnableCaching
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude = {SecurityAutoConfiguration.class})
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
上面的自动配置中去掉了SecurityAutoConfiguration类,如果不去掉,则会有一个默认的Spring Security登录页面。
4.2 配置类
4.2.1 Redis配置类
package com.hys.springboot.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
/**
* Redis配置类
* @author Robert Hou
* @date 2019年6月25日
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
/**
* JSON序列化方式
* @param redisConnectionFactory RedisConnectionFactory
* @return RedisTemplate
*/
@Bean
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
return template;
}
}
默认的RedisTemplate的序列化方式会在Redis中生成的key和value前加上一段元数据的信息,然后拼接上相应的key和value值,对使用者来说并不友好。所以这里使用自定义的序列化方式:将RedisTemplate中的key改用了String的序列化方式,而值则采用了json的序列化方式。
4.2.2 RabbitMQ配置类
package com.hys.springboot.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CachingConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.ConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
/**
* RabbitMQ配置类
* @author Robert Hou
* @date 2019年7月1日
*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig {
/**
* EXCHANGE名称
*/
public static final String FANOUT_EXCHANGE = "test.fanout";
public static final String DIRECT_EXCHANGE = "test.direct";
public static final String TOPIC_EXCHANGE = "test.topic";
/**
* QUEUE名称
*/
public static final String FANOUT_QUEUE = "test.fanout.queue";
public static final String DIRECT_QUEUE = "test.direct.queue";
public static final String TOPIC_QUEUE = "test.topic.queue";
/**
* ROUTINGKEY名称
*/
public static final String DIRECT_ROUTINGKEY = "direct";
public static final String TOPIC_ROUTINGKEY = "topic.#";
@Bean
public ConnectionFactory connectionFactory(Environment environment) {
String addresses = environment.getProperty("spring.rabbitmq.addresses");
int port = environment.getProperty("spring.rabbitmq.port", Integer.class);
String username = environment.getProperty("spring.rabbitmq.username");
String password = environment.getProperty("spring.rabbitmq.password");
String virtualHost = environment.getProperty("spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host");
CachingConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new CachingConnectionFactory(addresses, port);
connectionFactory.setUsername(username);
connectionFactory.setPassword(password);
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(virtualHost);
connectionFactory.setPublisherConfirms(true);
return connectionFactory;
}
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() {
return new FanoutExchange(FANOUT_EXCHANGE, true, false);
}
@Bean
public DirectExchange directExchange() {
return new DirectExchange(DIRECT_EXCHANGE, true, false);
}
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicExchange() {
return new TopicExchange(TOPIC_EXCHANGE, true, false);
}
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue() {
return new Queue(FANOUT_QUEUE, true);
}
@Bean
public Queue directQueue() {
return new Queue(DIRECT_QUEUE, true);
}
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue() {
return new Queue(TOPIC_QUEUE, true);
}
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBinding() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
@Bean
public Binding directBinding() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue()).to(directExchange()).with(DIRECT_ROUTINGKEY);
}
@Bean
public Binding topicBinding() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue()).to(topicExchange()).with(TOPIC_ROUTINGKEY);
}
}
4.3 Controller
4.3.1 HelloWorldController
package com.hys.springboot.controller;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import com.hys.springboot.service.IRedisService;
@Controller
public class HelloWorldController {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(HelloWorldController.class);
@Autowired
private IRedisService redisService;
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String say() {
redisService.test();
return "test/index";
}
@RequestMapping("/putsession.html")
@ResponseBody
public String putSession(HttpServletRequest request) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
logger.info(session.getClass());
logger.info(session.getId());
String name = "Robert Hou";
session.setAttribute("user", name);
return name;
}
}
4.3.2 PersonController
package com.hys.springboot.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import com.hys.springboot.entity.Person;
import com.hys.springboot.service.IPersonService;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/person")
public class PersonController {
@Autowired
private IPersonService personService;
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index(Model model) {
List allPerson = personService.getAllPerson();
model.addAttribute("allPerson", allPerson);
return "test/index";
}
}
4.3.3 UserReditRestController
package com.hys.springboot.controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class UserReditRestController {
@RequestMapping("/usercredit/{id}")
public Integer getCreditLevel(@PathVariable String id, Model model) {
return Integer.valueOf(id);
}
}
4.4 Service
4.4.1 MyBatis
和MyBatis相关联的接口层和实现层的代码如下所示:
package com.hys.springboot.service;
import java.util.List;
import com.hys.springboot.entity.Person;
public interface IPersonService {
List getAllPerson();
}
package com.hys.springboot.service.impl;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.hys.springboot.dao.IPersonDao;
import com.hys.springboot.entity.Person;
import com.hys.springboot.service.IPersonService;
@Service
public class PersonServiceImpl implements IPersonService {
@Autowired
private IPersonDao personDao;
@Override
@Cacheable("allPerson")
public List getAllPerson() {
return personDao.getAllPerson();
}
}
4.4.2 Redis
Redis的接口层和实现层的代码如下所示:
package com.hys.springboot.service;
public interface IRedisService {
void test();
}
package com.hys.springboot.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.hys.springboot.entity.Person;
import com.hys.springboot.service.IRedisService;
@Service
public class RedisServiceImpl implements IRedisService {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Override
public void test() {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("key", "value");
String string = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("key");
Person person = new Person();
person.setId("123");
person.setName("test");
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("key-0", person);
Person person1 = (Person) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("key-0");
}
}
4.4.3 RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ生产者的接口层和实现层代码如下所示:
package com.hys.springboot.service;
import java.util.Map;
import com.hys.springboot.entity.Order;
public interface IRabbitSenderService {
void send(String exchange, String routingKey, Object message, Map properties);
void sendOrder(String exchange, String routingKey, Order order);
}
package com.hys.springboot.service.impl;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.UUID;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate.ReturnCallback;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.messaging.Message;
import org.springframework.messaging.MessageHeaders;
import org.springframework.messaging.support.MessageBuilder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.hys.springboot.entity.Order;
import com.hys.springboot.service.IRabbitSenderService;
@Service
public class RabbitSenderServiceImpl implements IRabbitSenderService {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(RabbitSenderServiceImpl.class);
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
private final ConfirmCallback CONFIRM_CALLBACK = (correlationData, ack, cause) -> {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("correlationData:" + correlationData + " ack:" + ack);
}
if (!ack) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("需要异常处理");
}
}
};
private final ReturnCallback RETURN_CALLBACK = (message, replyCode, replyText, exchange, routingKey) -> {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("replyCode:" + replyCode + " replyText:" + replyText + " exchange:" + exchange + " routingKey:" + routingKey);
}
};
@Override
public void send(String exchange, String routingKey, Object message, Map properties) {
MessageHeaders messageHeaders = new MessageHeaders(properties);
Message send方法使用的是默认的Message来发送信息,而sendOrder方法则使用的是Java Bean的方式来发送信息。而相关的生产者测试代码如下所示:
package com.hys.springboot;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import com.hys.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.hys.springboot.entity.Order;
import com.hys.springboot.service.IRabbitSenderService;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private IRabbitSenderService rabbitSenderService;
@Test
public void testSender1() {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS");
Map properties = new HashMap<>();
properties.put("number", "12345");
properties.put("send_time", sdf.format(new Date()));
rabbitSenderService.send(RabbitMQConfig.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, "topic.user", "Hello World", properties);
}
@Test
public void testSender2() {
Order order = new Order();
order.setId("001");
order.setName("订单一");
rabbitSenderService.sendOrder(RabbitMQConfig.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, RabbitMQConfig.DIRECT_ROUTINGKEY, order);
}
}
RabbitMQ消费者的接口层和实现层代码如下所示:
package com.hys.springboot.service;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.messaging.Message;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Headers;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Payload;
import com.hys.springboot.entity.Order;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
public interface IRabbitReceiverService {
void receiveTopicMessage(Messagepackage com.hys.springboot.service.impl;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.ExchangeTypes;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.AmqpHeaders;
import org.springframework.messaging.Message;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Headers;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Payload;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.hys.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.hys.springboot.entity.Order;
import com.hys.springboot.service.IRabbitReceiverService;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
@Service
public class RabbitReceiverServiceImpl implements IRabbitReceiverService {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(RabbitReceiverServiceImpl.class);
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue(value = RabbitMQConfig.TOPIC_QUEUE, durable = "true"), exchange = @Exchange(value = RabbitMQConfig.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, durable = "true", type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC), key = RabbitMQConfig.TOPIC_ROUTINGKEY))
@RabbitHandler
@Override
public void receiveTopicMessage(Message4.5 Model
4.5.1 Person
package com.hys.springboot.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Person implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String id;
private String name;
private String sex;
private String address;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", sex=" + sex + ", address=" + address + "]";
}
}
4.5.2 Order
package com.hys.springboot.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Order implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String id;
private String name;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Order [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
4.6 DAO
package com.hys.springboot.dao;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import com.hys.springboot.entity.Person;
public interface IPersonDao {
List getAllPerson();
void insertPerson(@Param("person") Person person);
}
4.7 Mapper
id,
name,
sex,
address
INSERT INTO person (
5 JSP页面
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
test
${item.id}
${item.name}
${item.sex}
${item.address}
6 运行结果
6.1 页面结果
6.2 Redis结果
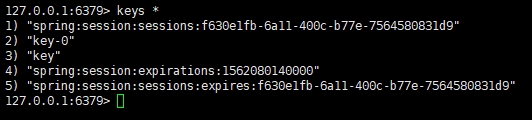
打开Redis的redis-cli客户端,查看所有的key,结果如下:
由上可以看到,不仅存在“key”和“key-0”这样的在service层插入Redis的数据,session数据也一并存入到Redis中。如果在配置文件中将缓存打开并使用Redis的缓存,那么Redis中也会保存相关的缓存数据:
spring.cache.type=redis6.3 RabbitMQ结果
运行之前的JUnit测试代码,同时保证之前启动的Spring Boot程序没有关闭,在控制台中便可以看到结果:
2019-07-02 22:45:06.194 DEBUG 17304 --- [ 127.0.0.1:5672] c.h.s.s.impl.RabbitSenderServiceImpl : correlationData:CorrelationData [id=bb329cec-12df-42a9-ba93-d2506223c33c-1562078706182] ack:true
2019-07-02 22:45:06.199 DEBUG 17304 --- [ 127.0.0.1:5672] c.h.s.s.impl.RabbitSenderServiceImpl : correlationData:CorrelationData [id=5fa5793f-cb54-45e4-a8b3-d7eafa5aa575-1562078706196] ack:true2019-07-02 22:45:06.204 DEBUG 14944 --- [ntContainer#0-1] c.h.s.s.impl.RabbitReceiverServiceImpl : 消费端Payload:Hello World
2019-07-02 22:45:06.204 DEBUG 14944 --- [ntContainer#1-1] c.h.s.s.impl.RabbitReceiverServiceImpl : 消费端Payload:Order [id=001, name=订单一]