图论算法之最短路径(Dijkstra算法)
1 算法介绍
如果图是有向赋权图,那么问题将比无权图困难。
Dijkstra算法向无权图最短路径算法一样。按阶段进行。在每一个阶段,Dijkstra算法选择一个顶点v。它在所有未知顶点中具有最小距离的dist,同时算法声明从s到v的最短路径是已知的。阶段的其余更新邻接点的信息。
表1表示初始配置。假设开始s是v0。第一个选择的顶点是v0.路径长0.该顶点标记为已知。既然v0已知,那么某些表项就需要调整。邻接到v0的顶点是v1到v3.这两个顶点的项得到调整。如表2。
下一步,选取v4并标记为已知。顶点v2,v4,v5,v6是邻接的顶点,而实际上都需要调整。如表3。
接着选择v1。v3是邻接的点,但已经是已知的,因此对它没有工作要做。v4是邻接点但不做调整,因为经过v1的值为2 + 10 = 12,而长为3的路径已经是已知的。如表4。
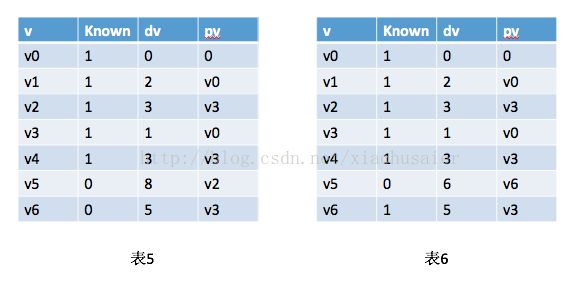
下一个被选取的顶点是v4,其值为3。v6是唯一的邻接顶点。但是它不用调整。因为 3 + 6 > 5。然后选取v2,对v5的距离下调到3 + 5 = 8。如表5。
再下一个选取的顶点是v6。v5下调到5 + 1 = 6。如表6。
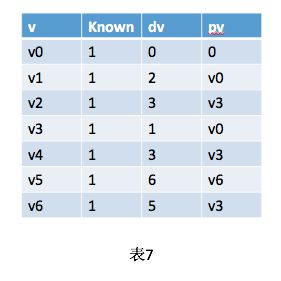
最后,我们选择v5。如表7。
下图是最后的结果。
2 算法实现
dijkstra函数是核心算法,initGraph和initArr负责初始化图G。算法用到二叉堆以及链表,我把它们放在下面附录中。
//
// LinkList.c
// Unweighted
//
// Created by Wuyixin on 2017/6/6.
// Copyright © 2017年 Coding365. All rights reserved.
//
#include "LinkList.h"
int UNAVAILABLE = INT_MIN;
/* 链表初始化 */
LinkedList initList(){
LinkedList h = malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if (h == NULL)
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
h->next = NULL;
h->data = UNAVAILABLE;
return h;
}
/* 插入元素 */
ElemType insert_l(ElemType x,LinkedList list){
PtoNode current;
current = list;
while (current->next != NULL)
current = current->next;
/* 生成新节点 */
PtoNode n = (PtoNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if (n == NULL)
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
n->data = x;
n->next = NULL;
current->next = n;
return x;
}
/* 删除链表 */
void deleteList(LinkedList list){
if (list == NULL)
return;
PtoNode node,old;
node = list;
while (node->next != NULL){
old = node;
node = node->next;
free(old);
}
}
/* 打印链表 */
void printList(LinkedList list){
PtoNode node;
node = list->next;
while (node!= NULL ) {
printf("%d ",node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
3 附录:二叉堆与链表
3.1 Node结构
//
// Node.h
// Dijkstra2
//
// Created by Wuyixin on 2017/6/11.
// Copyright © 2017年 Coding365. All rights reserved.
//
#ifndef Node_h
#define Node_h
#include
typedef int ElemType;
struct Node{
ElemType data;
struct Node* next;
int dist;
int known;
int path;
int cost;
};
#endif /* Node_h */
3.2 二叉堆
(1)头文件
//
// BinHeap.h
// PriorityQueue
//
// Created by Wuyixin on 2017/5/29.
// Copyright © 2017年 Coding365. All rights reserved.
//
#ifndef BinHeap_h
#define BinHeap_h
#include
#include
#include
#include "Node.h"
#define PRIORITY_QUEUE_SIZE_MIN 50
struct HeapStruct;
typedef struct HeapStruct *PriorityQueue;
/* 元素类型 */
typedef struct Node * ElementType;
/* 差值 */
typedef int DIFFERENCE;
extern const int DATA_MIN;//最小值,用来标记空节点
/* 自定义非法值 */
void defineInvalidValue(ElementType invalid);
/* 初始化 */
PriorityQueue init_queue(int max_elements);
/* 构建堆操作,把n个关键字(任意顺序)作为输入并把它们放入到空堆中*/
PriorityQueue build_heap(PriorityQueue h ,ElementType arr,unsigned int n,int (*compare)(void*,void*));
/* 销毁堆 */
void destroy(PriorityQueue h);
/* 置空堆 */
void make_empty(PriorityQueue h);
/* 插入 */
void insert_h(ElementType x,PriorityQueue h,int (*compare)(void*,void*));
/* 删除最小 */
ElementType delete_min(PriorityQueue h,int (*compare)(void*,void*));
/* 删除元素 */
ElementType delete_element(int p ,PriorityQueue h,DIFFERENCE infinity,ElementType (*change)(ElementType,DIFFERENCE),int (*compare)(void*,void*));
/* 查找最小 */
ElementType find_min(PriorityQueue h);
/* 降低关键字的值 */
ElementType decrease_key(int p,DIFFERENCE d,ElementType (*change)(ElementType,DIFFERENCE),PriorityQueue h,int (*compare)(void*,void*));
/* 增加关键字的值 */
ElementType increase_key(int p,DIFFERENCE d,ElementType (*change)(ElementType,DIFFERENCE),PriorityQueue h,int (*compare)(void*,void*));
/* 是否空 */
int is_empty(PriorityQueue h);
/* 是否满 */
int is_full(PriorityQueue h);
/* 遍历堆 */
void travel_queue(PriorityQueue h,void handle(ElementType));
struct HeapStruct
{
int capacity;
int size;
ElementType *elements;
};
#endif /* BinHeap_h */
(2)实现文件
//
// BinHeap.c
// PriorityQueue
//
// Created by Wuyixin on 2017/5/29.
// Copyright © 2017年 Coding365. All rights reserved.
//
#include "BinHeap.h"
const int DATA_MIN = INT_MIN;
static ElementType binHeapInvalidValue;
static int percolate_up(int p,ElementType value,PriorityQueue h,int (*compare)(void*,void*));
static int percolate_down(int p,ElementType value,PriorityQueue h,int (*compare)(void*,void*));
static void error(char* message){
printf("%s\n",message);
}
static void fatal_error(char* message){
error(message);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
/* 上滤 */
/* 一个元素的值降低,或者在堆的末尾增加新值,都会用到此操作。此操作的特点是让节点“往上升” */
/* return 返回上滤后的新位置*/
static int percolate_up(int p,ElementType value,PriorityQueue h,int (*compare)(void*,void*)){
if (is_empty(h)) return DATA_MIN;
if (p < 1 || p > h->size) return DATA_MIN;
/* 由于h->elements[0]的值是DATA_MIN,所以可以作为循环终止的条件 */
int i;
for (i = p; h->elements[i/2] != NULL && compare(value,h->elements[i/2]) < 0; i /= 2) {
h->elements[i] = h->elements[i/2];
}
return i;
}
/* 下滤 */
/* 一个元素的值增加,或者删除堆的最小元(根),都会用到此操作。此操作的特点是让节点“往下降” */
static int percolate_down(int p,ElementType value,PriorityQueue h,int (*compare)(void*,void*)){
if (is_empty(h)) return DATA_MIN;
if (p < 1 || p > h->size) return DATA_MIN;
int i;
int child;
for (i = p; 2 * i <= h->size; i = child) {
child = 2 * i;
/* 比较左右孩子,取出小的元素上滤*/
/* 直到"空穴"来到最后一层(树叶)或者 “空穴”的两个孩子都比last_elem的值要大,找到这个位置*/
if (child != h->size && compare( h->elements[child + 1],h->elements[child]) < 0)
child++;
if (compare(value,h->elements[child]) > 0){
h->elements[i] = h->elements[child];
}
else
break;
}
return i;
}
void defineInvalidValue(ElementType invalid){
binHeapInvalidValue = invalid;
}
PriorityQueue init_queue(int max_elements){
/* 给堆分配的长度太小 */
if (max_elements < PRIORITY_QUEUE_SIZE_MIN)
error("Priority queue size is too small");
PriorityQueue h = malloc(sizeof(struct HeapStruct));
if (h == NULL) fatal_error("Out of space!!!");
/* 数组第一个元素不存储节点,根从第二个元素开始,因为这样节点的父亲、左孩子、右孩子的表达式比较清楚。因此实际分配的大小要比max_elements大1 */
h->elements = malloc((max_elements + 1) * sizeof(ElementType));
if (h->elements == NULL) fatal_error("Out of space!!!");
h->size = 0;
h->capacity = max_elements;
h->elements[0] = binHeapInvalidValue;/* 做标记用 */
return h;
}
PriorityQueue build_heap(PriorityQueue h ,ElementType arr,unsigned int n,int (*compare)(void*,void*)){
if (h == NULL) return h;
if (n == 0) return h;
int i = 0;
/* 将数组中的元素的值复制到堆中(无序) */
ElementType* p = h->elements + 1;
while (i < n){
*p++ = (arr + i++),h->size++;
}
i = n / 2;
while(i > 0)
percolate_down(i, h->elements[i], h,compare),i--;
return h;
}
void destroy(PriorityQueue h){
free(h->elements);
free(h);
}
void make_empty(PriorityQueue h){
/* 其实就是把size变成零,虽然堆里的每个节点的值还在,但都是无效的。 */
h->size = 0;
}
void insert_h(ElementType x,PriorityQueue h,int (*compare)(void*,void*)){
int i;
if (is_full(h)) error("Priority queue is full");
/* 插入元素先放在堆的末尾,然后经过上滤的过程找到合适的位置并插入 */
/* 注意++h->size已经把size加1 */
i = percolate_up(++h->size, x, h,compare);
h->elements[i] = x;
}
ElementType delete_min(PriorityQueue h,int (*compare)(void*,void*)){
if (is_empty(h)) return binHeapInvalidValue;
/* 注意h->size--已经把size减1 */
ElementType last_elem = h->elements[h->size--];
ElementType min_elem = h->elements[1];
/* 把最小元删除,经过下滤过程,把堆序重新调整*/
int i = percolate_down(1, last_elem, h,compare);
if (i != DATA_MIN)
h->elements[i] = last_elem;
return min_elem;
}
/* 删除位置p的节点。这通过首先执行decrease_key(p,∞,h),然后在执行delete_min(h)来完成*/
ElementType delete_element(int p ,PriorityQueue h,DIFFERENCE infinity,ElementType (*change)(ElementType,DIFFERENCE),int (*compare)(void*,void*)){
if (is_empty(h)) return binHeapInvalidValue;
if (p < 1 || p > h->size) return h->elements[0];
ElementType elem = h->elements[p];
decrease_key(p, infinity,change, h,compare);
delete_min(h,compare);
return elem;
}
ElementType find_min(PriorityQueue h){
if (is_empty(h)) return h->elements[0];
return h->elements[1];
}
/* 该操作降低位置p处的关键值,降值的幅度为正的量d。由于这可能破坏堆的序,因此必须通过上滤对堆进行调整 */
ElementType decrease_key(int p,DIFFERENCE d,ElementType (*change)(ElementType,DIFFERENCE),PriorityQueue h,int (*compare)(void*,void*)){
if (is_empty(h)) return binHeapInvalidValue;
if (p < 1 || p > h->size) return h->elements[0];
if (d <= 0) return h->elements[0];
ElementType value = change(h->elements[p],-d);
int i = percolate_up(p, value, h,compare);
h->elements[i] = value;
return value;
}
/* 该操作增加位置p处的关键值,增值的幅度为正的量d。由于这可能破坏堆的序,因此必须通过下滤对堆进行调整 */
ElementType increase_key(int p,DIFFERENCE d,ElementType (*change)(ElementType,DIFFERENCE),PriorityQueue h,int (*compare)(void*,void*)){
if (is_empty(h)) return binHeapInvalidValue;
if (p < 1 || p > h->size) return h->elements[0];
if (d <= 0) return h->elements[0];
ElementType value = change(h->elements[p] , d) ;
int i = percolate_down(p, value, h,compare);
h->elements[i] = value;
return value;
}
int is_empty(PriorityQueue h){
return h->size == 0;
}
int is_full(PriorityQueue h){
return h->size >= h->capacity;
}
void travel_queue(PriorityQueue h,void handle(ElementType)){
if (!is_empty(h)){
int i = 0;
while (i++ < h->size)
handle(h->elements[i]);
}
}
3.3 链表
(1)头文件
//
// LinkList.h
// Unweighted
//
// Created by Wuyixin on 2017/6/6.
// Copyright © 2017年 Coding365. All rights reserved.
//
#ifndef LinkList_h
#define LinkList_h
#include
#include
#include
#include "Node.h"
typedef struct Node *LinkedList,*PtoNode;
extern int UNAVAILABLE;
/* 链表初始化 */
LinkedList initList();
/* 插入元素 */
ElemType insert_l(ElemType x,LinkedList list);
/* 删除链表 */
void deleteList(LinkedList list);
/* 打印链表 */
void printList(LinkedList list);
#endif /* LinkList_h */
(2)实现文件
//
// LinkList.c
// Unweighted
//
// Created by Wuyixin on 2017/6/6.
// Copyright © 2017年 Coding365. All rights reserved.
//
#include "LinkList.h"
int UNAVAILABLE = INT_MIN;
/* 链表初始化 */
LinkedList initList(){
LinkedList h = malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if (h == NULL)
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
h->next = NULL;
h->data = UNAVAILABLE;
return h;
}
/* 插入元素 */
ElemType insert_l(ElemType x,LinkedList list){
PtoNode current;
current = list;
while (current->next != NULL)
current = current->next;
/* 生成新节点 */
PtoNode n = (PtoNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if (n == NULL)
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
n->data = x;
n->next = NULL;
current->next = n;
return x;
}
/* 删除链表 */
void deleteList(LinkedList list){
if (list == NULL)
return;
PtoNode node,old;
node = list;
while (node->next != NULL){
old = node;
node = node->next;
free(old);
}
}
/* 打印链表 */
void printList(LinkedList list){
PtoNode node;
node = list->next;
while (node!= NULL ) {
printf("%d ",node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("\n");
}