基于QT的上位机多线程设计模型
前言:
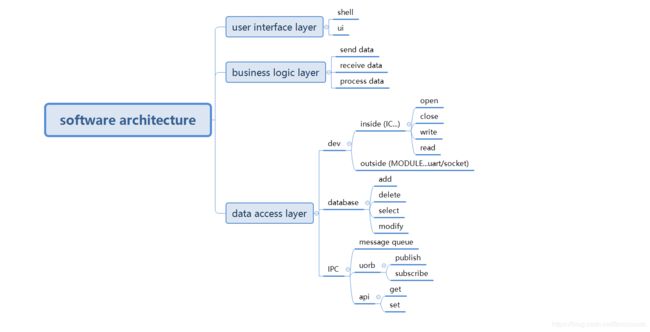
对于一般的上位机开发,无论是使用QT还是C#,主要功能包含:1.接收并解析下位机上传的数据、2.打包并发送数据到下位机、3.业务逻辑,对数据实时显示到界面或者存储到数据库。从软件分层的角度来看,底层是数据层、中间是业务逻辑处理、上层是UI。
在处理大数据量时,为了不让界面假死或者卡顿,需要采用多线程的方式来实现。
1.抽象实现,建立模型
无论是QT/C#上位机,还是基于linux/nuttx…的APP,只要有需求,那就一定有实现需求的框架,这个框架就是对需求的抽象,建立需求的模型。
1.1 数据的来源:可以来自底层的设备、远程的下位机;本地的数据库;本地的进程。
1.2 数据的逻辑:收数据、解析数据;打包数据、发送数据;按照具体的业务处理数据。
1.3 数据的显示:基于linux/nuttx…shell终端;基于QT的ui(可以是曲线、数值等)。
QT的多线程实现有两种方式:
1.继承QThread,重载run函数;
2.继承QObject,moveToThread(QThread *)。
两种方式都可以,但需要注意的是:重载run函数,只有run函数中的代码属于该线程;moveToThread(QThread *)时,整个继承QObject的对象都属于该线程。特别是使用signal/slot时尤其注意slot函数到底在那个线程执行?
建议采用方式2,使用更加灵活:这里实现了数据接收者类(硬件接口serial/udpSocket)。
在mainwindow.cpp中实例化数据接收者,再调用moveToThread(Thread ),实现了多线程。
1.dataRecieve.h
#ifndef DATARECIEVE_H
#define DATARECIEVE_H
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/* params struct */
struct params_t{
int a;
float b;
uint8_t c;
short d;
};
union payload_u{
uint8_t data[64];
struct params_t params;
};
/* message struct */
struct data_msg_t{
uint8_t head;
uint8_t addr;
uint8_t cmd;
uint8_t length;
union payload_u payload;
uint8_t checksum;
};
class dataRecieve : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
/* constructor function */
dataRecieve(int type);
/* set socket ip address and port */
bool setIp();
bool setPort(int port);
bool setSerialName(QString name);
signals:
/* when get completly a message, emit the signal*/
void dataPush(struct data_msg_t *data_msg);
private slots:
/* 1.read raw data form socket or serial
* 2.decode raw data to data_msg_t
* 3.emit the signal:dataPush()
*/
void dataRecieveSlots();
void dataReadAll();
private:
/* network */
QUdpSocket *UdpSocket;
QTcpSocket *TcpSocket;
int udpListenPort;
public:
/* serial */
QSerialPort *serial;
QString serialName;
/* configure the serial params */
bool configSerial();
};
#endif // DATARECIEVE_H
2…dataRecieve.cpp
#include "datarecieve.h"
#include "qdebug.h"
#include
/*
* constructor function
* 1.select the interface type
* 2.new the object
*/
dataRecieve::dataRecieve(int type)
{
if(type == 0){
/* connect */
//serial = new QSerialPort();
//QObject::connect(serial,&QSerialPort::readyRead,this,&dataRecieve::dataReadAll);
qDebug() << QString("dataRecieve constructor id:") << QThread::currentThreadId();
}else {
UdpSocket = new QUdpSocket();
}
}
/*
* configure the serial params
*/
bool dataRecieve::configSerial()
{
qDebug() << QString("configSerial id:") << QThread::currentThreadId();
serial = new QSerialPort();
serial->setPortName(serialName);
if(serial->open(QIODevice::ReadWrite) == true) {
//set baudRate
serial->setBaudRate(QSerialPort::Baud115200);
//set dataBits
serial->setDataBits(QSerialPort::Data8);
//set parity
serial->setParity(QSerialPort::NoParity);
//set stopBits
serial->setStopBits(QSerialPort::OneStop);
//set flowcontrol
serial->setFlowControl(QSerialPort::NoFlowControl);
QObject::connect(serial,&QSerialPort::readyRead,this,&dataRecieve::dataReadAll);
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
bool dataRecieve::setSerialName(QString name)
{
serialName = name;
return true;
}
/*
* decode raw data
*/
void dataRecieve::dataRecieveSlots()
{
char buffer[1024];
data_msg_t data_msg;
configSerial();
while(true)
{
memset(buffer,0,sizeof(buffer));
//1.block: read data form socket or serial
serial->waitForReadyRead(3000);
serial->read(buffer,1024);
//2.decode: raw data to data_msg_t
memcpy(&data_msg.payload.data[0],&buffer[0],64);
//3.emit the signal:dataPush
emit dataPush(&data_msg);
//4.debug
qDebug() << QString("dataRecieveSlots id:") << QThread::currentThreadId();
}
}
/*
* read all serial data to buffer,and decode
*/
void dataRecieve::dataReadAll()
{
//1.read data form serial
QByteArray buff;
buff = serial->readAll();
//2.decode: raw data to data_msg_t
data_msg_t data_msg;
if(buff.size() >= 4){
data_msg.payload.data[0] = buff.at(0);
data_msg.payload.data[1] = buff.at(1);
data_msg.payload.data[2] = buff.at(2);
data_msg.payload.data[3] = buff.at(3);
//3.emit the signal:dataPush
emit dataPush(&data_msg);
//4.debug
qDebug() << QString("dataRecieveSlots id:") << QThread::currentThreadId();
}
}
3.mainwindow.cpp
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include "ui_mainwindow.h"
#include
#include
#include "datasend.h"
#include "datarecieve.h"
#include
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) :
QMainWindow(parent),
ui(new Ui::MainWindow)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
datarecieve = new dataRecieve(0);
datasend = new dataSend(0);
QThread *sendThread = new QThread();
QThread *recieveThread = new QThread();
/* moveToThread function
* key point !!!
*/
datasend->moveToThread(sendThread);
datarecieve->moveToThread(recieveThread);
/*
* connect function
* inter-thread conmunication: signals/slots
*/
QObject::connect(this,SIGNAL(send_data(int)),datasend,SLOT(dataSendSlots(int)),Qt::QueuedConnection);
QObject::connect(this,SIGNAL(recieve_data()),datarecieve,SLOT(dataRecieveSlots()),Qt::QueuedConnection);
QObject::connect(datarecieve,SIGNAL(dataPush(struct data_msg_t *)),this,SLOT(recieve_msg_Data(struct data_msg_t *)),Qt::QueuedConnection);
sendThread->start();
recieveThread->start();
}
MainWindow::~MainWindow()
{
delete ui;
}
void MainWindow::on_pushButton_recieve_released()
{
if(datarecieve->setSerialName("/dev/ttyUSB0")){
emit recieve_data();
}
qDebug() << QString("mainwindow on_pushButton_recieve thread id:") << QThread::currentThreadId();
}
void MainWindow::on_pushButton_send_released()
{
int a = 3000;
emit send_data(a);
qDebug() << QString("mainwindow on_pushButton_send thread id:") << QThread::currentThreadId();
}
/*
* recieve the msg
*
*/
void MainWindow::recieve_msg_Data(struct data_msg_t *data_msg)
{
//1.show the data to textBrowser
//ui->textBrowser_recieve->insertPlainText(QString::number(data_msg->payload.params.a));
//ui->textBrowser_recieve->insertPlainText(" ");
//2.save the data to database
//3.show the data to curve
//4.debug
qDebug() << QString("mainwindow recieve_msg_Data thread id:") << QThread::currentThreadId();
}
3.线程间如何通信?
线程间采用signal/solt来进行通信,线程同步、并将数据通过函数参数的形式进行交互、通信。
这里需要注意connect时的第5 个参数:连接方式
enum ConnectionType {
AutoConnection,
DirectConnection,
QueuedConnection,
BlockingQueuedConnection,
UniqueConnection = 0x80
};
其中的DirectConnection,相当于直接调用slot函数,在哪线程发射信号,slot函数就在那线程运行;QueuedConnection,要看slot函数所在的对象依附于那个线程,slot就在被依附的线程中运行。
4.总结:
在面向对象编程中,实现需求分三步:
1.首先将问题进行抽象、分层。
2.再规划线程模型,规划类。
3.最后在类的方法中实现具体的流程。