实验三 Huffman编解码算法实现与压缩效率分析
一、Huffman编解码原理
1. Huffman编码
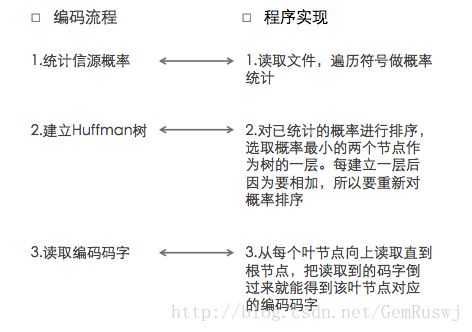
对原始文件进行Huffman编码,首先需要解决以下几点问题:
- 文件符号的概率分布情况是怎样的?
- Huffman树是如何建立的?
- 建立起Huffman树后,又是怎样读出符号对应码字的?
这三个问题在程序中的实现思路如下图:
将待编码文件里的数据参照已形成的Huffman码表一一进行转换,就可以得到编码后的文件了。
2. Huffman解码
Huffman解码是查表+翻译的过程。读取随接收文件传来的码表后,再逐位读取文件实际数据,对照码表进行翻译即可。
二、程序实现
流程中最关键的对Huffman树的操作在程序中主要通过两个结构体实现:Huffman_node和Huffman_code。
建立的二叉树上每个节点都以Huffman_node类型存在。节点之间的主要关系有父子、兄弟,Huffman_node中定义了指向父节点的指针*parent和指向孩子的指针*zero, *one来表述节点与节点之间的关系。除此之外,还有节点本身的属性:isLeaf、count、symbol。
而编码码字定义为了Huffman_code,本身属性包括码字占用的比特数和码字本身。
具体程序如下,部分理解在注释中给出。
Huffcode.c
/*
* huffcode - Encode/Decode files using Huffman encoding.
* http://huffman.sourceforge.net
* Copyright (C) 2003 Douglas Ryan Richardson; Gauss Interprise, Inc
*
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
*
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
*/
#include "huffman.h"
#include Huffman.c
/*
* huffman - Encode/Decode files using Huffman encoding.
* http://huffman.sourceforge.net
* Copyright (C) 2003 Douglas Ryan Richardson; Gauss Interprise, Inc
*
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
*
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
*/
#include bits[i][j] = p->bits[j];
}
else
st->numbits[i] =0;
}
return 0;
}
void output_huffman_statistics(huffman_stat *st,FILE *out_Table)
{
int i,j;
unsigned char c;
fprintf(out_Table,"symbol\t freq\t codelength\t code\n");
for(i = 0; i < MAX_SYMBOLS; ++i)
{
fprintf(out_Table,"%d\t ",i);
fprintf(out_Table,"%f\t ",st->freq[i]);
fprintf(out_Table,"%d\t ",st->numbits[i]);
if(st->numbits[i])
{
for(j = 0; j < st->numbits[i]; ++j)
{
c =get_bit(st->bits[i], j);
fprintf(out_Table,"%d",c);
}
}
fprintf(out_Table,"\n");
}
}
//end by yzhang
/*
* huffman_encode_file huffman encodes in to out.
*/
int
huffman_encode_file(FILE *in, FILE *out, FILE *out_Table) //step1:changed by yzhang for huffman statistics from (FILE *in, FILE *out) to (FILE *in, FILE *out, FILE *out_Table)
{
SymbolFrequencies sf;
SymbolEncoder *se;
huffman_node *root = NULL;
int rc;
unsigned int symbol_count;
//step2:add by yzhang for huffman statistics
huffman_stat hs;
//end by yzhang
/* Get the frequency of each symbol in the input file. */
symbol_count = get_symbol_frequencies(&sf, in); //演示扫描完一遍文件后,SF指针数组的每个元素的构成
//step3:add by yzhang for huffman statistics,... get the frequency of each symbol
huffST_getSymFrequencies(&sf,&hs,symbol_count);
//end by yzhang
/* Build an optimal table from the symbolCount. */
se = calculate_huffman_codes(&sf);
root = sf[0];
//step3:add by yzhang for huffman statistics... output the statistics to file
huffST_getcodeword(se, &hs);
output_huffman_statistics(&hs,out_Table);
//end by yzhang
/* Scan the file again and, using the table
previously built, encode it into the output file. */
rewind(in);
rc = write_code_table(out, se, symbol_count);
if(rc == 0)
rc = do_file_encode(in, out, se);
/* Free the Huffman tree. */
free_huffman_tree(root);
free_encoder(se);
return rc;
}
int
huffman_decode_file(FILE *in, FILE *out)
{
huffman_node *root, *p;
int c;
unsigned int data_count;
/* Read the Huffman code table. */
root = read_code_table(in, &data_count);
if(!root)
return 1;
/* Decode the file. */
p = root;
while(data_count > 0 && (c = fgetc(in)) != EOF)
{
unsigned char byte = (unsigned char)c;
unsigned char mask = 1;
while(data_count > 0 && mask)
{
p = byte & mask ? p->one : p->zero;
mask <<= 1;
if(p->isLeaf)
{
fputc(p->symbol, out);
p = root;
--data_count;
}
}
}
free_huffman_tree(root);
return 0;
}
#define CACHE_SIZE 1024
int huffman_encode_memory(const unsigned char *bufin,
unsigned int bufinlen,
unsigned char **pbufout,
unsigned int *pbufoutlen)
{
SymbolFrequencies sf;
SymbolEncoder *se;
huffman_node *root = NULL;
int rc;
unsigned int symbol_count;
buf_cache cache;
/* Ensure the arguments are valid. */
if(!pbufout || !pbufoutlen)
return 1;
if(init_cache(&cache, CACHE_SIZE, pbufout, pbufoutlen))
return 1;
/* Get the frequency of each symbol in the input memory. */
symbol_count = get_symbol_frequencies_from_memory(&sf, bufin, bufinlen);
/* Build an optimal table from the symbolCount. */
se = calculate_huffman_codes(&sf);
root = sf[0];
/* Scan the memory again and, using the table
previously built, encode it into the output memory. */
rc = write_code_table_to_memory(&cache, se, symbol_count);
if(rc == 0)
rc = do_memory_encode(&cache, bufin, bufinlen, se);
/* Flush the cache. */
flush_cache(&cache);
/* Free the Huffman tree. */
free_huffman_tree(root);
free_encoder(se);
free_cache(&cache);
return rc;
}
int huffman_decode_memory(const unsigned char *bufin,
unsigned int bufinlen,
unsigned char **pbufout,
unsigned int *pbufoutlen)
{
huffman_node *root, *p;
unsigned int data_count;
unsigned int i = 0;
unsigned char *buf;
unsigned int bufcur = 0;
/* Ensure the arguments are valid. */
if(!pbufout || !pbufoutlen)
return 1;
/* Read the Huffman code table. */
root = read_code_table_from_memory(bufin, bufinlen, &i, &data_count);
if(!root)
return 1;
buf = (unsigned char*)malloc(data_count);
/* Decode the memory. */
p = root;
for(; i < bufinlen && data_count > 0; ++i)
{
unsigned char byte = bufin[i];
unsigned char mask = 1;
while(data_count > 0 && mask)
{
p = byte & mask ? p->one : p->zero;
mask <<= 1;
if(p->isLeaf)
{
buf[bufcur++] = p->symbol;
p = root;
--data_count;
}
}
}
free_huffman_tree(root);
*pbufout = buf;
*pbufoutlen = bufcur;
return 0;
}
三、结果分析
实验选取了10中文件类型进行Huffman编码,分别为bmp、doc、exe、pdf、png、ppt、rar、wav、xls、yuv。对编码后的文件进行分析,得到以下结果图表:
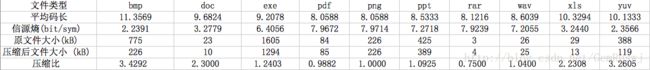
可以看到,进行Huffman编码后,大多数文件都变小了,压缩比在1到4之间。但也有rar这样经过编码后不小反大的文件。
再观察每个文件的字符概率分布情况:
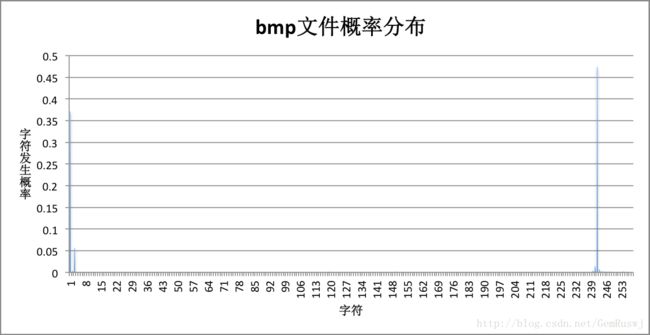
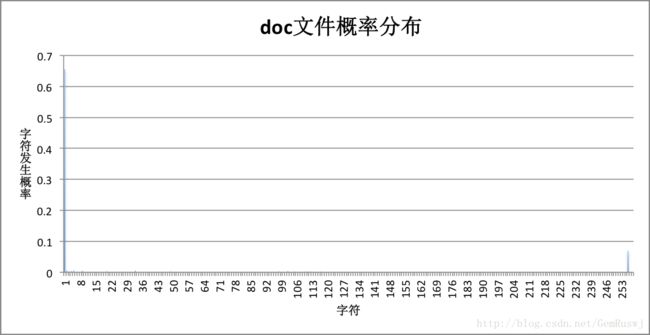
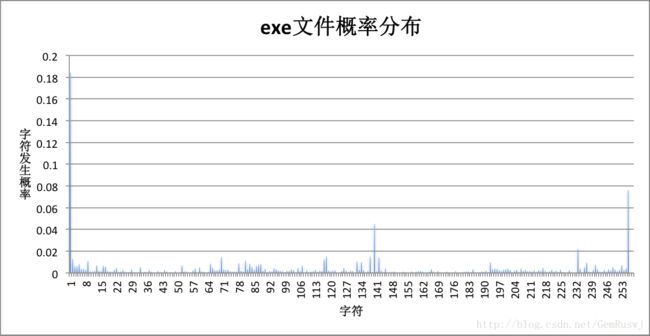
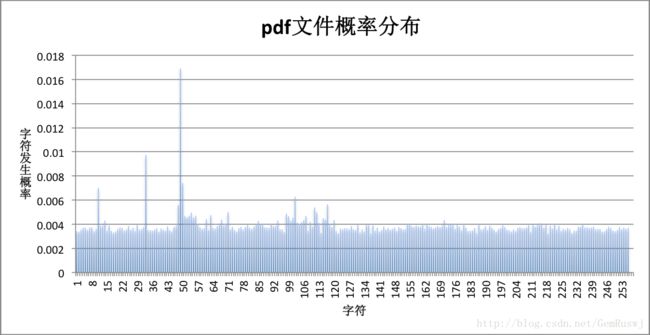
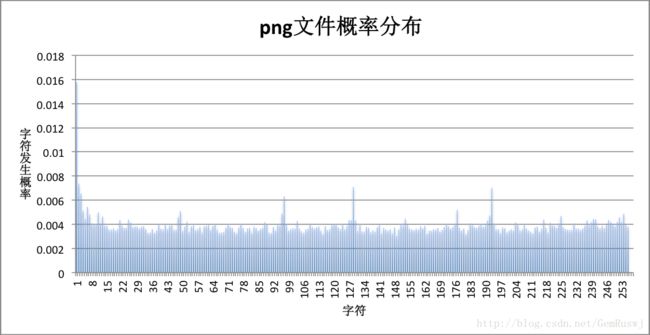
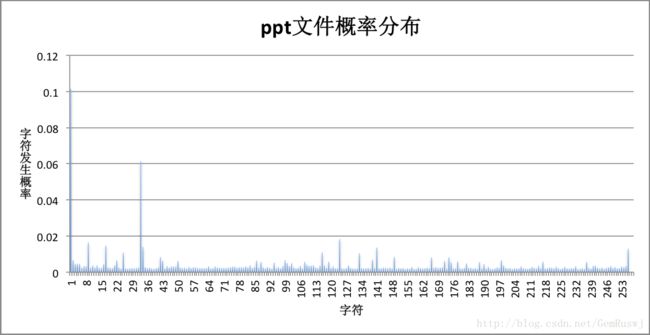
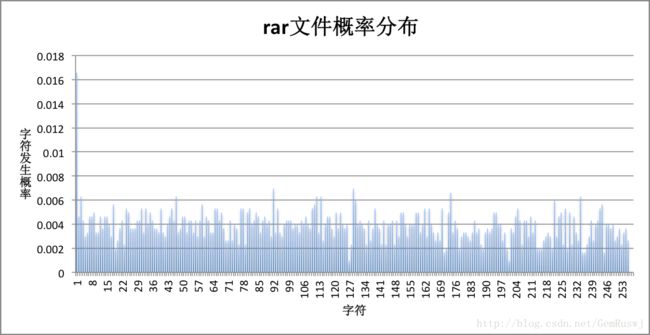
对比联合图表可以发现,压缩比是由概率分布决定的。相比于实验选用的bmp、doc等字符概率比较集中的文件,字符概率分布平均分散的文件(如rar、png、pdf),压缩比更小,信源熵更大。