Android 输入法框架源码分析总结(1)
1 IMF主要包含三个部分
1.InputmethodMethodManager(IMM)运行于客户端进程
- -Input Method Manager(IMM)是负责管理其他部分交互的中心,以client-side API的形式存在于每一个应用上下文中,同时和InputMethodManagerService(IMMF)进行通信,用来沟通管理所有进程间交互的全局系统服务,可以通过Context.getSystemService()来获取一个InputMethodManager的实例。
2.InputMethodService (IMS)运行于输入法进程
3.InputMethodManagerService (IMMS)运行于系统进程,负责管理系统所有输入法
获取焦点
请求绑定解绑
显示输入法
输入法框架
2 InputMethodManager 创建
每个程序都会有一个InputMethodManager 实例,IMM是程序和IMMS通信的接口,IMM实例在ViewRootImpl初始化的时候被创建 ,InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.getInstance();
// ViewRootImpl.java
public final class ViewRootImpl implements ViewParent,
View.AttachInfo.Callbacks, ThreadedRenderer.HardwareDrawCallbacks {
public ViewRootImpl(Context context, Display display) {
...
mWindowSession = WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowSession();
...
}
// WindowManagerGlobal.java
public static IWindowSession getWindowSession() {
synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) {
if (sWindowSession == null) {
try {
// 生成 InputMethodManager 实例
InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.getInstance();
IWindowManager windowManager = getWindowManagerService();
sWindowSession = windowManager.openSession(
new IWindowSessionCallback.Stub() {
@Override
public void onAnimatorScaleChanged(float scale) {
ValueAnimator.setDurationScale(scale);
}
},
imm.getClient(), imm.getInputContext());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
return sWindowSession;
}
}
// InputMethodManager.java
/**
* Retrieve the global InputMethodManager instance, creating it if it
* doesn't already exist.
* @hide
*/
public static InputMethodManager getInstance() {
synchronized (InputMethodManager.class) {
if (sInstance == null) {
try {
sInstance = new InputMethodManager(service, Looper.getMainLooper());
} cathch () {
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
}
}
return sInstance;
}
}3 程序Window获取焦点
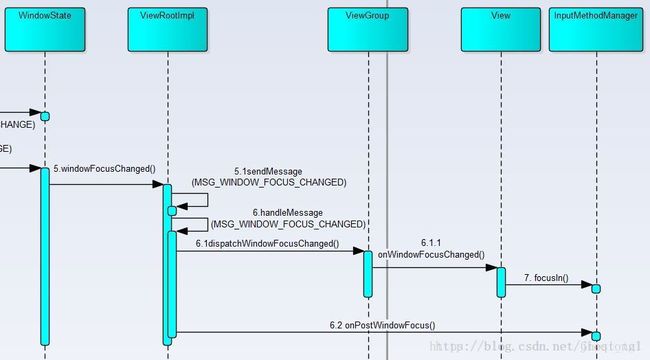
- 程序的window获得焦点的时序图如下
// **WindowManagerService.java**
private boolean updateFocusedWindowLocked(int mode, boolean updateInputWindows) {
//计算焦点window
WindowState newFocus = computeFocusedWindowLocked();
if (mCurrentFocus != newFocus) {
//焦点window发生变化,post一个message来通知程序焦点发生变化了
mH.removeMessages(H.REPORT_FOCUS_CHANGE);
mH.sendEmptyMessage(H.REPORT_FOCUS_CHANGE);
return true;
}
return false;
}
private WindowState computeFocusedWindowLocked() {
if (mAnimator.mUniverseBackground != null
&& mAnimator.mUniverseBackground.mWin.canReceiveKeys()) {
return mAnimator.mUniverseBackground.mWin;
}
final int displayCount = mDisplayContents.size();
for (int i = 0; i < displayCount; i++) {
final DisplayContent displayContent = mDisplayContents.valueAt(i);
WindowState win = findFocusedWindowLocked(displayContent);
if (win != null) {
return win;
}
}
return null;
}
//该函数就是找出最top的可以接收按键事件的window,这个window就获得焦点
private WindowState findFocusedWindowLocked(DisplayContent displayContent) {
final WindowList windows = displayContent.getWindowList();
for (int i = windows.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final WindowState win = windows.get(i);
//是否为activity的window
AppWindowToken wtoken = win.mAppToken;
//重要函数,window是否可以获取焦点
if (!win.canReceiveKeys()) {
continue;
}
// mFocusedApp是最top的activity ,下面逻辑是为了确保焦点window的app
//必须是焦点程序之上,所以这个逻辑其实并没有多大作用,只是为了检测出
//错误
if (wtoken != null && win.mAttrs.type != TYPE_APPLICATION_STARTING &&
mFocusedApp != null) {
ArrayList tasks = displayContent.getTasks();
for (int taskNdx = tasks.size() - 1; taskNdx >= 0; --taskNdx) {
AppTokenList tokens = tasks.get(taskNdx).mAppTokens;
int tokenNdx = tokens.size() - 1;
for ( ; tokenNdx >= 0; --tokenNdx) {
final AppWindowToken token = tokens.get(tokenNdx);
if (wtoken == token) {
break;
}
if (mFocusedApp == token) {
return null;
}
}
}
}
return win;
}
return null;
}
public final boolean canReceiveKeys() {
return isVisibleOrAdding()
&& (mViewVisibility == View.VISIBLE)
&& ((mAttrs.flags & WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE) == 0);
}
//由于输入法的window带有FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE, 从上可见其不可能是焦点window
//接下来系统开始通知程序端哪个window获得了焦点。
final class H extends Handler {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case REPORT_FOCUS_CHANGE: {
WindowState lastFocus;
WindowState newFocus;
synchronized(mWindowMap) {
lastFocus = mLastFocus;
newFocus = mCurrentFocus;
if (lastFocus == newFocus) {
// Focus is not changing, so nothing to do.
return;
}
mLastFocus = newFocus;
}
if (newFocus != null) {
//通知新的焦点程序其获得了焦点
newFocus.reportFocusChangedSerialized(true, mInTouchMode);
notifyFocusChanged();
}
if (lastFocus != null) {
//通知老的焦点程序其获得了焦点
lastFocus.reportFocusChangedSerialized(false, mInTouchMode);
}
} break;
}
public void reportFocusChangedSerialized(boolean focused, boolean inTouchMode) {
try {
//这个就是通过Binder告知client其获得或失去了焦点
mClient.windowFocusChanged(focused, inTouchMode);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
} 4.程序变更焦点,获得焦点变更事件
- // 6.1 调用根 view的 dispatchWindowFocusChanged(),通知view程序获得焦点
– mView.dispatchWindowFocusChanged(hasWindowFocus); - // 6.2 通知 InputMethodManager 该 window 获得焦点
- –imm.onPostWindowFocus(mView, mView.findFocus(),
mWindowAttributes.softInputMode,
!mHasHadWindowFocus, mWindowAttributes.flags);
// ViewRootImpl.java
public void windowFocusChanged(boolean hasFocus, boolean inTouchMode) {
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = MSG_WINDOW_FOCUS_CHANGED;
msg.arg1 = hasFocus ? 1 : 0;
msg.arg2 = inTouchMode ? 1 : 0;
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
//程序获得焦点会通过调用mView.dispatchWindowFocusChanged和
//imm.onPostWindowFocus来通知IMMS焦点信息发生改变,需要更新输入法了
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case MSG_WINDOW_FOCUS_CHANGED: {
if (mAdded) {
boolean hasWindowFocus = msg.arg1 != 0;
mAttachInfo.mHasWindowFocus = hasWindowFocus;
profileRendering(hasWindowFocus);
if (hasWindowFocus) {
...
}
mLastWasImTarget = WindowManager.LayoutParams
.mayUseInputMethod(mWindowAttributes.flags);
InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.peekInstance();
if (imm != null && mLastWasImTarget && !isInLocalFocusMode()) {
imm.onPreWindowFocus(mView, hasWindowFocus);
}
if (mView != null) {
mAttachInfo.mKeyDispatchState.reset();
// 6.1 调用根 view的 dispatchWindowFocusChanged(),通知view程序获得焦点
mView.dispatchWindowFocusChanged(hasWindowFocus);
mAttachInfo.mTreeObserver.dispatchOnWindowFocusChange(hasWindowFocus);
}
// Note: must be done after the focus change callbacks,
// so all of the view state is set up correctly.
if (hasWindowFocus) {
if (imm != null && mLastWasImTarget && !isInLocalFocusMode()) {
// 6.2 通知 InputMethodManager 该 window 获得焦点
imm.onPostWindowFocus(mView, mView.findFocus(),
mWindowAttributes.softInputMode,
!mHasHadWindowFocus, mWindowAttributes.flags);
}
// Clear the forward bit. We can just do this directly, since
// the window manager doesn't care about it.
mWindowAttributes.softInputMode &=
~WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION;
((WindowManager.LayoutParams)mView.getLayoutParams())
.softInputMode &=
~WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION;
mHasHadWindowFocus = true;
}
}
} break;
...
}
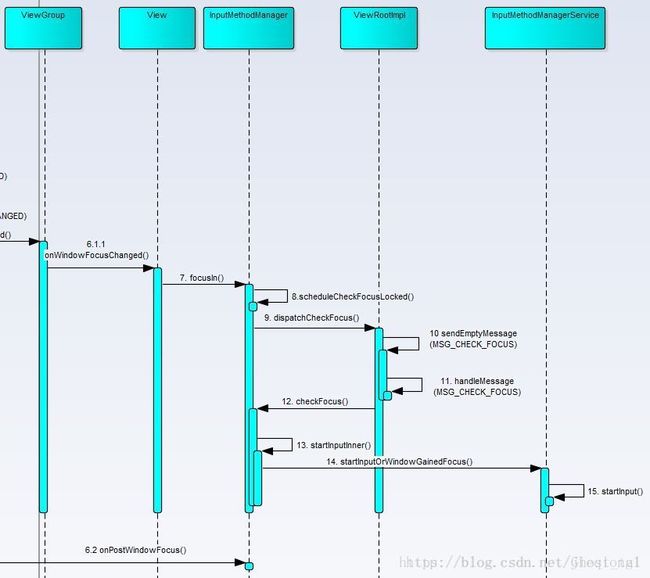
}5 焦点View向IMMS请求绑定输入法
获得焦点的 view 通过 InputMethodManager 向 Service 通知自己获得焦点
imm.focusIn(this);
6.1 之后的流程
- 创建数据通信连接接口,这个会传送到InputMethodService ,InputMethodService后面就通过这个InputConnection将输入法的字 符传递给该view
InputConnection ic = view.onCreateInputConnection(tba); - 将 InputConnection 封装为 binder 对象,这个是真正可以实现跨进程通信的封装类
servedContext = new ControlledInputConnectionWrapper(
icHandler != null ? icHandler.getLooper() : vh.getLooper(), ic, this); - view 获得焦点,IMMS将这个 view 和 输入法绑定
return startInput(startInputReason, client, inputContext, missingMethods, attribute,
controlFlags);
// ViewGroup.java
@Override
public void dispatchWindowFocusChanged(boolean hasFocus) {
super.dispatchWindowFocusChanged(hasFocus);
final int count = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
children[i].dispatchWindowFocusChanged(hasFocus);
}
}
// View.java
/**
* Called when the window containing this view gains or loses window focus.
* ViewGroups should override to route to their children.
*
* @param hasFocus True if the window containing this view now has focus,
* false otherwise.
*/
public void dispatchWindowFocusChanged(boolean hasFocus) {
onWindowFocusChanged(hasFocus);
}
/**
* Called when the window containing this view gains or loses focus. Note
* that this is separate from view focus: to receive key events, both
* your view and its window must have focus. If a window is displayed
* on top of yours that takes input focus, then your own window will lose
* focus but the view focus will remain unchanged.
*
* @param hasWindowFocus True if the window containing this view now has
* focus, false otherwise.
*/
public void onWindowFocusChanged(boolean hasWindowFocus) {
InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.peekInstance();
if (!hasWindowFocus) {
if (isPressed()) {
setPressed(false);
}
if (imm != null && (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FOCUSED) != 0) {
imm.focusOut(this);
}
removeLongPressCallback();
removeTapCallback();
onFocusLost();
} else if (imm != null && (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FOCUSED) != 0) {
// 获得焦点的 view 通过 InputMethodManager 向 Service 通知自己获得焦点
imm.focusIn(this);
}
refreshDrawableState();
}
// InputMethodManager.java
/**
* Call this when a view receives focus.
* @hide
*/
public void focusIn(View view) {
synchronized (mH) {
focusInLocked(view);
}
}
// InputMethodManager.java
/**
* Call this when a view receives focus.
* @hide
*/
public void focusIn(View view) {
synchronized (mH) {
focusInLocked(view);
}
}
void focusInLocked(View view) {
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "focusIn: " + dumpViewInfo(view));
if (view != null && view.isTemporarilyDetached()) {
// This is a request from a view that is temporarily detached from a window.
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Temporarily detached view, ignoring");
return;
}
if (mCurRootView != view.getRootView()) {
// This is a request from a window that isn't in the window with
// IME focus, so ignore it.
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Not IME target window, ignoring");
return;
}
mNextServedView = view;// 保存焦点view的变量
scheduleCheckFocusLocked(view);
}
static void scheduleCheckFocusLocked(View view) {
ViewRootImpl viewRootImpl = view.getViewRootImpl();
if (viewRootImpl != null) {
viewRootImpl.dispatchCheckFocus();
}
}
// ViewRootImpl.java
public void dispatchCheckFocus() {
if (!mHandler.hasMessages(MSG_CHECK_FOCUS)) {
// This will result in a call to checkFocus() below.
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MSG_CHECK_FOCUS);
}
}
case MSG_CHECK_FOCUS: {
InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.peekInstance();
if (imm != null) {
imm.checkFocus();
}
} break;
// InputMethodManager.java
/**
* @hide
*/
public void checkFocus() {
// 确认当前 focused view 是否已经调用过 startInputInner() 来绑定输入法,
// 因为前面 mView.dispatchWindowFocusChanged() 已经完成了 focused view 的绑定,
// 大部分情况下,该函数返回 false , 不会再次调用 startInputInner()
if (checkFocusNoStartInput(false)) {
startInputInner(InputMethodClient.START_INPUT_REASON_CHECK_FOCUS, null, 0, 0, 0);
}
}
private boolean checkFocusNoStartInput(boolean forceNewFocus) {
// This is called a lot, so short-circuit before locking.
if (mServedView == mNextServedView && !forceNewFocus) {
return false;
}
final ControlledInputConnectionWrapper ic;
synchronized (mH) {
if (mServedView == mNextServedView && !forceNewFocus) {
return false;
}
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "checkFocus: view=" + mServedView
+ " next=" + mNextServedView
+ " forceNewFocus=" + forceNewFocus
+ " package="
+ (mServedView != null ? mServedView.getContext().getPackageName() : "" ));
if (mNextServedView == null) {
finishInputLocked();
// In this case, we used to have a focused view on the window,
// but no longer do. We should make sure the input method is
// no longer shown, since it serves no purpose.
closeCurrentInput();
return false;
}
ic = mServedInputConnectionWrapper;
mServedView = mNextServedView;
mCurrentTextBoxAttribute = null;
mCompletions = null;
mServedConnecting = true;
}
if (ic != null) {
ic.finishComposingText();
}
return true;
}
boolean startInputInner(@InputMethodClient.StartInputReason final int startInputReason,
IBinder windowGainingFocus, int controlFlags, int softInputMode,
int windowFlags) {
final View view;
synchronized (mH) {
// 获得上面的焦点view
view = mServedView;
// Make sure we have a window token for the served view.
if (DEBUG) {
Log.v(TAG, "Starting input: view=" + dumpViewInfo(view) +
" reason=" + InputMethodClient.getStartInputReason(startInputReason));
}
if (view == null) {
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "ABORT input: no served view!");
return false;
}
}
// Now we need to get an input connection from the served view.
// This is complicated in a couple ways: we can't be holding our lock
// when calling out to the view, and we need to make sure we call into
// the view on the same thread that is driving its view hierarchy.
Handler vh = view.getHandler();
if (vh == null) {
// If the view doesn't have a handler, something has changed out
// from under us, so just close the current input.
// If we don't close the current input, the current input method can remain on the
// screen without a connection.
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "ABORT input: no handler for view! Close current input.");
closeCurrentInput();
return false;
}
if (vh.getLooper() != Looper.myLooper()) {
// The view is running on a different thread than our own, so
// we need to reschedule our work for over there.
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Starting input: reschedule to view thread");
vh.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
startInputInner(startInputReason, null, 0, 0, 0);
}
});
return false;
}
// Okay we are now ready to call into the served view and have it
// do its stuff.
// Life is good: let's hook everything up!
EditorInfo tba = new EditorInfo();
// Note: Use Context#getOpPackageName() rather than Context#getPackageName() so that the
// system can verify the consistency between the uid of this process and package name passed
// from here. See comment of Context#getOpPackageName() for details.
tba.packageName = view.getContext().getOpPackageName();
tba.fieldId = view.getId();
// 创建数据通信连接接口 InputConnection,这个会传送到InputMethodService
// InputMethodService 后面就是通过这个connection将输入法的字符传给该view
InputConnection ic = view.onCreateInputConnection(tba);
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Starting input: tba=" + tba + " ic=" + ic);
synchronized (mH) {
// Now that we are locked again, validate that our state hasn't
// changed.
if (mServedView != view || !mServedConnecting) {
// Something else happened, so abort.
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG,
"Starting input: finished by someone else. view=" + dumpViewInfo(view)
+ " mServedView=" + dumpViewInfo(mServedView)
+ " mServedConnecting=" + mServedConnecting);
return false;
}
// If we already have a text box, then this view is already
// connected so we want to restart it.
if (mCurrentTextBoxAttribute == null) {
controlFlags |= CONTROL_START_INITIAL;
}
// Hook 'em up and let 'er rip.
mCurrentTextBoxAttribute = tba;
mServedConnecting = false;
if (mServedInputConnectionWrapper != null) {
mServedInputConnectionWrapper.deactivate();
mServedInputConnectionWrapper = null;
}
ControlledInputConnectionWrapper servedContext;
final int missingMethodFlags;
if (ic != null) {
mCursorSelStart = tba.initialSelStart;
mCursorSelEnd = tba.initialSelEnd;
mCursorCandStart = -1;
mCursorCandEnd = -1;
mCursorRect.setEmpty();
mCursorAnchorInfo = null;
final Handler icHandler;
missingMethodFlags = InputConnectionInspector.getMissingMethodFlags(ic);
if ((missingMethodFlags & InputConnectionInspector.MissingMethodFlags.GET_HANDLER)!= 0) {
// InputConnection#getHandler() is not implemented.
icHandler = null;
} else {
icHandler = ic.getHandler();
}
// 将 InputConnection 封装为 binder 对象,这个是真正可以实现跨进程通信的封装类
servedContext = new ControlledInputConnectionWrapper(
icHandler != null ? icHandler.getLooper() : vh.getLooper(), ic, this);
} else {
servedContext = null;
missingMethodFlags = 0;
}
mServedInputConnectionWrapper = servedContext;
try {
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "START INPUT: view=" + dumpViewInfo(view) + " ic="
+ ic + " tba=" + tba + " controlFlags=#"
+ Integer.toHexString(controlFlags));
final InputBindResult res = mService.startInputOrWindowGainedFocus(
startInputReason, mClient, windowGainingFocus, controlFlags, softInputMode,
windowFlags, tba, servedContext, missingMethodFlags);
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Starting input: Bind result=" + res);
if (res != null) {
if (res.id != null) {
setInputChannelLocked(res.channel);
mBindSequence = res.sequence;
// 获得输入法的通信接口
mCurMethod = res.method;
mCurId = res.id;
mNextUserActionNotificationSequenceNumber =
res.userActionNotificationSequenceNumber;
if (mServedInputConnectionWrapper != null) {
mServedInputConnectionWrapper.setInputMethodId(mCurId);
}
} else {
if (res.channel != null && res.channel != mCurChannel) {
res.channel.dispose();
}
if (mCurMethod == null) {
// This means there is no input method available.
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "ABORT input: no input method!");
return true;
}
}
} else {
if (startInputReason
== InputMethodClient.START_INPUT_REASON_WINDOW_FOCUS_GAIN) {
// We are here probably because of an obsolete window-focus-in message sent
// to windowGainingFocus. Since IMMS determines whether a Window can have
// IME focus or not by using the latest window focus state maintained in the
// WMS, this kind of race condition cannot be avoided. One obvious example
// would be that we have already received a window-focus-out message but the
// UI thread is still handling previous window-focus-in message here.
// TODO: InputBindResult should have the error code.
if (DEBUG) Log.w(TAG, "startInputOrWindowGainedFocus failed. "
+ "Window focus may have already been lost. "
+ "win=" + windowGainingFocus + " view=" + dumpViewInfo(view));
if (!mActive) {
// mHasBeenInactive is a latch switch to forcefully refresh IME focus
// state when an inactive (mActive == false) client is gaining window
// focus. In case we have unnecessary disable the latch due to this
// spurious wakeup, we re-enable the latch here.
// TODO: Come up with more robust solution.
mHasBeenInactive = true;
}
}
}
if (mCurMethod != null && mCompletions != null) {
try {
mCurMethod.displayCompletions(mCompletions);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "IME died: " + mCurId, e);
}
}
return true;
}
// InputMethodManagerService.java
@Override
public InputBindResult startInputOrWindowGainedFocus(
/* @InputMethodClient.StartInputReason */ final int startInputReason,
IInputMethodClient client, IBinder windowToken, int controlFlags, int softInputMode,
int windowFlags, @Nullable EditorInfo attribute, IInputContext inputContext,
/* @InputConnectionInspector.missingMethods */ final int missingMethods) {
if (windowToken != null) {
// focusIn 不走该分支
return windowGainedFocus(startInputReason, client, windowToken, controlFlags,
softInputMode, windowFlags, attribute, inputContext, missingMethods);
} else {
//通知InputMethodManagerService,该程序的view获得焦点,IMMS将这个 view 和 输入法绑定
return startInput(startInputReason, client, inputContext, missingMethods, attribute,
controlFlags);
}
}6 IMMS处理View绑定输入法事件
为了讲解整个绑定过程,我们假设此时输入法service还没启动,这个情况下的输入法绑定是最长的,整个过程经历过如下过程:
1) 启动输入法service
2) 绑定输入法window的token
3) 请求输入法为焦点程序创建一个连接会话-
4) 将输入法的接口传递回程序client端
5) 绑定输入法和焦点view
1-4是和程序相关的,而5是和view相关的。所以你可以说1~4是用来绑定程序window和输入法,而5是用来绑定程序view和输入法。
输入法还没启动时,弹出输入法会经过1~5,输入法已经启动,但是焦点window发生变化时会经历3~5,焦点window没有变化,只是改变了焦点view,则只会经历5。
6.1启动输入法service
// InputMethodManagerService.java
@Override
public InputBindResult startInputOrWindowGainedFocus(
/* @InputMethodClient.StartInputReason */ final int startInputReason,
IInputMethodClient client, IBinder windowToken, int controlFlags, int softInputMode,
int windowFlags, @Nullable EditorInfo attribute, IInputContext inputContext,
/* @InputConnectionInspector.missingMethods */ final int missingMethods) {
if (windowToken != null) {
// focusIn 不走该分支
return windowGainedFocus(startInputReason, client, windowToken, controlFlags,
softInputMode, windowFlags, attribute, inputContext, missingMethods);
} else {
// view 获得焦点,IMMS将这个 view 和 输入法绑定
return startInput(startInputReason, client, inputContext, missingMethods, attribute,
controlFlags);
}
}
private InputBindResult startInput(
/* @InputMethodClient.StartInputReason */ final int startInputReason,
IInputMethodClient client, IInputContext inputContext,
/* @InputConnectionInspector.missingMethods */ final int missingMethods,
@Nullable EditorInfo attribute, int controlFlags) {
if (!calledFromValidUser()) {
return null;
}
synchronized (mMethodMap) {
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.v(TAG, "startInput: reason="
+ InputMethodClient.getStartInputReason(startInputReason)
+ " client = " + client.asBinder()
+ " inputContext=" + inputContext
+ " missingMethods="
+ InputConnectionInspector.getMissingMethodFlagsAsString(missingMethods)
+ " attribute=" + attribute
+ " controlFlags=#" + Integer.toHexString(controlFlags));
}
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
return startInputLocked(startInputReason, client, inputContext, missingMethods,
attribute, controlFlags);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(ident);
}
}
}
InputBindResult startInputLocked(
/* @InputMethodClient.StartInputReason */ final int startInputReason,
IInputMethodClient client, IInputContext inputContext,
/* @InputConnectionInspector.missingMethods */ final int missingMethods,
@Nullable EditorInfo attribute, int controlFlags) {
// If no method is currently selected, do nothing.
if (mCurMethodId == null) {
return mNoBinding;
}
// 程序在 Service 端 对应的数据结构
ClientState cs = mClients.get(client.asBinder());
...
return startInputUncheckedLocked(cs, inputContext, missingMethods, attribute,
controlFlags);
}
InputBindResult startInputUncheckedLocked(@NonNull ClientState cs, IInputContext inputContext,
/* @InputConnectionInspector.missingMethods */ final int missingMethods,
@NonNull EditorInfo attribute, int controlFlags) {
// If no method is currently selected, do nothing.
if (mCurMethodId == null) {
return mNoBinding;
}
if (!InputMethodUtils.checkIfPackageBelongsToUid(mAppOpsManager, cs.uid,
attribute.packageName)) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Rejecting this client as it reported an invalid package name."
+ " uid=" + cs.uid + " package=" + attribute.packageName);
return mNoBinding;
}
if (mCurClient != cs) {
// 如果新程序和当前活动的程序不同,取消当前活动程序与输入法的绑定
// Was the keyguard locked when switching over to the new client?
mCurClientInKeyguard = isKeyguardLocked();
// If the client is changing, we need to switch over to the new
// one.
unbindCurrentClientLocked(InputMethodClient.UNBIND_REASON_SWITCH_CLIENT);
if (DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "switching to client: client="
+ cs.client.asBinder() + " keyguard=" + mCurClientInKeyguard);
// If the screen is on, inform the new client it is active
if (mIsInteractive) {
executeOrSendMessage(cs.client, mCaller.obtainMessageIO(
MSG_SET_ACTIVE, mIsInteractive ? 1 : 0, cs));
}
}
// Bump up the sequence for this client and attach it.
mCurSeq++;
if (mCurSeq <= 0) mCurSeq = 1;
// 将新程序设置为当前活动的程序
mCurClient = cs;
mCurInputContext = inputContext;
mCurInputContextMissingMethods = missingMethods;
mCurAttribute = attribute;
// Check if the input method is changing.
if (mCurId != null && mCurId.equals(mCurMethodId)) {
if (cs.curSession != null) {
// Fast case: if we are already connected to the input method,
// then just return it.
// 连接已经建立,开始绑定
return attachNewInputLocked(
(controlFlags&InputMethodManager.CONTROL_START_INITIAL) != 0);
}
if (mHaveConnection) {
if (mCurMethod != null) {
// 如果 输入法的连接 已经创建,直接传递给程序 client 端
// Return to client, and we will get back with it when
// we have had a session made for it.
requestClientSessionLocked(cs);
return new InputBindResult(null, null, mCurId, mCurSeq,
mCurUserActionNotificationSequenceNumber);
} else if (SystemClock.uptimeMillis()
< (mLastBindTime+TIME_TO_RECONNECT)) {
// In this case we have connected to the service, but
// don't yet have its interface. If it hasn't been too
// long since we did the connection, we'll return to
// the client and wait to get the service interface so
// we can report back. If it has been too long, we want
// to fall through so we can try a disconnect/reconnect
// to see if we can get back in touch with the service.
return new InputBindResult(null, null, mCurId, mCurSeq,
mCurUserActionNotificationSequenceNumber);
} else {
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.IMF_FORCE_RECONNECT_IME,
mCurMethodId, SystemClock.uptimeMillis()-mLastBindTime, 0);
}
}
}
// 启动输入法并建立连接
return startInputInnerLocked();
}
InputBindResult startInputInnerLocked() {
if (mCurMethodId == null) {
return mNoBinding;
}
if (!mSystemReady) {
// If the system is not yet ready, we shouldn't be running third
// party code.
return new InputBindResult(null, null, mCurMethodId, mCurSeq,
mCurUserActionNotificationSequenceNumber);
}
InputMethodInfo info = mMethodMap.get(mCurMethodId);
if (info == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown id: " + mCurMethodId);
}
unbindCurrentMethodLocked(true);
// 启动输入法Service
mCurIntent = new Intent(InputMethod.SERVICE_INTERFACE);
mCurIntent.setComponent(info.getComponent());
mCurIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_CLIENT_LABEL,
com.android.internal.R.string.input_method_binding_label);
mCurIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_CLIENT_INTENT, PendingIntent.getActivity(
mContext, 0, new Intent(Settings.ACTION_INPUT_METHOD_SETTINGS), 0));
if (bindCurrentInputMethodService(mCurIntent, this, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE
| Context.BIND_NOT_VISIBLE | Context.BIND_NOT_FOREGROUND
| Context.BIND_SHOWING_UI)) {
mLastBindTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
mHaveConnection = true;
mCurId = info.getId();
// mCurToken 是给输入法Service 来绑定输入法window的
// 通过 mCurToken ,InputMethodManagerService 直接管理 输入法window
mCurToken = new Binder();
try {
if (true || DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "Adding window token: " + mCurToken);
mIWindowManager.addWindowToken(mCurToken,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_INPUT_METHOD);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
return new InputBindResult(null, null, mCurId, mCurSeq,
mCurUserActionNotificationSequenceNumber);
} else {
mCurIntent = null;
Slog.w(TAG, "Failure connecting to input method service: "
+ mCurIntent);
}
return null;
}
private boolean bindCurrentInputMethodService(
Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags) {
if (service == null || conn == null) {
Slog.e(TAG, "--- bind failed: service = " + service + ", conn = " + conn);
return false;
}
return mContext.bindServiceAsUser(service, conn, flags,
new UserHandle(mSettings.getCurrentUserId()));
}
// AbstractInputMethodService.java
//输入法启动完成后就在函数onBind 传回一个binder接口
@Override
final public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
if (mInputMethod == null) {
mInputMethod = onCreateInputMethodInterface();
}
// IInputMethodWrapper 将 IMMS的调用转化为 message,
// 然后在 message 线程调用 mInputMethod 对应的接口,
// 实现输入法的异步处理
return new IInputMethodWrapper(this, mInputMethod);
}
// InputMethodService.java
/**
* Implement to return our standard {@link InputMethodImpl}. Subclasses
* can override to provide their own customized version.
*/
@Override
public AbstractInputMethodImpl onCreateInputMethodInterface() {
return new InputMethodImpl();
}
// 由于IMMS是以bindService的方式启动输入法service,所以当输入法service启动完
// 成后它就会回调IMMS的onServiceConnected
// InputMethodManagerService.java
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
synchronized (mMethodMap) {
if (mCurIntent != null && name.equals(mCurIntent.getComponent())) {
// 保存输入法Service 传递过来的 通信接口IInputMethod
mCurMethod = IInputMethod.Stub.asInterface(service);
if (mCurToken == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Service connected without a token!");
unbindCurrentMethodLocked(false);
return;
}
if (DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "Initiating attach with token: " + mCurToken);
// 将刚刚创建的window token传递给输入法service,然后输入用这个token
// 创建window,这样IMMS可以用根据这个token找到输入法在IMMS里
// 的数据及输入法window在WMS里的数据
executeOrSendMessage(mCurMethod, mCaller.obtainMessageOO(
MSG_ATTACH_TOKEN, mCurMethod, mCurToken));
if (mCurClient != null) {
clearClientSessionLocked(mCurClient);
// 请求为程序和输入法建立一个连接会话,这样client就可以直接和
// 输入法通信了
requestClientSessionLocked(mCurClient);
}
}
}
}
case MSG_ATTACH_TOKEN:
args = (SomeArgs)msg.obj;
try {
if (DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "Sending attach of token: " + args.arg2);
// 和输入法通信
((IInputMethod)args.arg1).attachToken((IBinder)args.arg2);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
args.recycle();
return true;6.2-1输入法Window token的绑定及使用分析
输入法Window token绑定
IMMS在输入法启动完成并回调onServiceConnected时会将一个Window token传递给输入法。
// InputMethodManagerService.java
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
synchronized (mMethodMap) {
if (mCurIntent != null && name.equals(mCurIntent.getComponent())) {
mCurMethod = IInputMethod.Stub.asInterface(service);
executeOrSendMessage(mCurMethod, mCaller.obtainMessageOO(
MSG_ATTACH_TOKEN, mCurMethod, mCurToken));
if (mCurClient != null) {
clearClientSessionLocked(mCurClient);
requestClientSessionLocked(mCurClient);
}
}
}
}
case MSG_ATTACH_TOKEN:
args = (SomeArgs)msg.obj;
try {
//和输入法通信
((IInputMethod)args.arg1).attachToken((IBinder)args.arg2);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
args.recycle();
public class InputMethodService extends AbstractInputMethodService {
public class InputMethodImpl extends AbstractInputMethodImpl {
public void attachToken(IBinder token) {
if (mToken == null) {
//保存token
mToken = token;
//这样输入法的window就绑定这个window token
mWindow.setToken(token);
}
}
} 6.2-2输入法Window token使用
由于系统存在多个输入法,所以输入法要和IMMS通信,必须要个机制来标示自己是哪个输入法,这个就是通过上面的输入法Window token来实现的,比如输入法自己关闭自己:
//InputMethodService.java输入法接口
public void requestHideSelf(int flags) {
//mToken就是上面提到的过程----IMMS传递给输入法的
mImm.hideSoftInputFromInputMethod(mToken, flags);
}
//InputMethodManager.java
public void hideSoftInputFromInputMethod(IBinder token, int flags) {
try {
mService.hideMySoftInput(token, flags);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//IMMS
@Override
public void hideMySoftInput(IBinder token, int flags) {
if (!calledFromValidUser()) {
return;
}
synchronized (mMethodMap) {
if (token == null || mCurToken != token) {
if (DEBUG) Slog.w(TAG, "Ignoring hideInputMethod of uid "
+ Binder.getCallingUid() + " token: " + token);
return;
}
long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
hideCurrentInputLocked(flags, null);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(ident);
}
}
} 6.3输入法连接会话创建
到此程序和输入法的session就建立了
// InputMethodManagerService.java
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
synchronized (mMethodMap) {
if (mCurIntent != null && name.equals(mCurIntent.getComponent())) {
// 保存输入法Service 传递过来的 通信接口IInputMethod
mCurMethod = IInputMethod.Stub.asInterface(service);
if (mCurToken == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Service connected without a token!");
unbindCurrentMethodLocked(false);
return;
}
if (DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "Initiating attach with token: " + mCurToken);
// 将刚刚创建的window token传递给输入法service,然后输入用这个token
// 创建window,这样IMMS可以用根据这个token找到输入法在IMMS里
// 的数据及输入法window在WMS里的数据
executeOrSendMessage(mCurMethod, mCaller.obtainMessageOO(
MSG_ATTACH_TOKEN, mCurMethod, mCurToken));
if (mCurClient != null) {
clearClientSessionLocked(mCurClient);
// 请求为程序和输入法建立一个连接会话,这样client就可以直接和
// 输入法通信了
requestClientSessionLocked(mCurClient);
}
}
}
}
case MSG_ATTACH_TOKEN:
args = (SomeArgs)msg.obj;
try {
if (DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "Sending attach of token: " + args.arg2);
// 和输入法通信
((IInputMethod)args.arg1).attachToken((IBinder)args.arg2);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
args.recycle();
return true;
// InputMethodService.java
/**
* Concrete implementation of
* {@link AbstractInputMethodService.AbstractInputMethodImpl} that provides
* all of the standard behavior for an input method.
*/
public class InputMethodImpl extends AbstractInputMethodImpl {
/**
* Take care of attaching the given window token provided by the system.
*/
public void attachToken(IBinder token) {
if (mToken == null) {
// 保存token
mToken = token;
// 这样输入法的window就绑定这个window token
mWindow.setToken(token);
}
}
}
// InputMethodManagerService.java
void requestClientSessionLocked(ClientState cs) {
if (!cs.sessionRequested) {
if (DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating new session for client " + cs);
// 这里又出现了InputChannel对,很面熟吧,在前面几篇文章已经详细分析过
// 了,可见它已经成为一种通用的跨平台的数据通信接口了
InputChannel[] channels = InputChannel.openInputChannelPair(cs.toString());
cs.sessionRequested = true;
executeOrSendMessage(mCurMethod, mCaller.obtainMessageOOO(
MSG_CREATE_SESSION, mCurMethod, channels[1],
new MethodCallback(this, mCurMethod, channels[0])));
}
}
case MSG_CREATE_SESSION: {
args = (SomeArgs)msg.obj;
IInputMethod method = (IInputMethod)args.arg1;
InputChannel channel = (InputChannel)args.arg2;
try {
method.createSession(channel, (IInputSessionCallback)args.arg3);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
} finally {
// Dispose the channel if the input method is not local to this process
// because the remote proxy will get its own copy when unparceled.
if (channel != null && Binder.isProxy(method)) {
channel.dispose();
}
}
args.recycle();
return true;
}
//上面是IMMS端,下面就看IMS输入法端的处理
// IInputMethodWrapper.java
@Override
public void createSession(InputChannel channel, IInputSessionCallback callback) {
mCaller.executeOrSendMessage(mCaller.obtainMessageOO(DO_CREATE_SESSION,
channel, callback));
}
case DO_CREATE_SESSION: {
SomeArgs args = (SomeArgs)msg.obj;
inputMethod.createSession(new InputMethodSessionCallbackWrapper(
mContext, (InputChannel)args.arg1,
(IInputSessionCallback)args.arg2));
args.recycle();
return;
}
// AbstractInputMethodService.java
/**
* Base class for derived classes to implement their {@link InputMethod}
* interface. This takes care of basic maintenance of the input method,
* but most behavior must be implemented in a derived class.
*/
public abstract class AbstractInputMethodImpl implements InputMethod {
/**
* Instantiate a new client session for the input method, by calling
* back to {@link AbstractInputMethodService#onCreateInputMethodSessionInterface()
* AbstractInputMethodService.onCreateInputMethodSessionInterface()}.
*/
public void createSession(SessionCallback callback) {
callback.sessionCreated(onCreateInputMethodSessionInterface());
}
}
// InputMethodManagerService.java
@Override
public void sessionCreated(IInputMethodSession session) {
long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
mParentIMMS.onSessionCreated(mMethod, session, mChannel);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(ident);
}
}
}
6.5传递输入法接口给程序client端
// InputMethodManagerService.java
void onSessionCreated(IInputMethod method, IInputMethodSession session,
InputChannel channel) {
synchronized (mMethodMap) {
if (mCurMethod != null && method != null
&& mCurMethod.asBinder() == method.asBinder()) {
if (mCurClient != null) {
clearClientSessionLocked(mCurClient);
mCurClient.curSession = new SessionState(mCurClient,
method, session, channel);
InputBindResult res = attachNewInputLocked(true);
if (res.method != null) {
executeOrSendMessage(mCurClient.client, mCaller.obtainMessageOO(
MSG_BIND_CLIENT, mCurClient.client, res));
}
return;
}
}
}
// Session abandoned. Close its associated input channel.
channel.dispose();
}6.5绑定输入法和焦点view
// 输入法和view绑定
InputBindResult attachNewInputLocked(boolean initial) {
if (!mBoundToMethod) {
executeOrSendMessage(mCurMethod, mCaller.obtainMessageOO(
MSG_BIND_INPUT, mCurMethod, mCurClient.binding));
mBoundToMethod = true;
}
final SessionState session = mCurClient.curSession;
if (initial) {
executeOrSendMessage(session.method, mCaller.obtainMessageIOOO(
MSG_START_INPUT, mCurInputContextMissingMethods, session, mCurInputContext,
mCurAttribute));
} else {
executeOrSendMessage(session.method, mCaller.obtainMessageIOOO(
MSG_RESTART_INPUT, mCurInputContextMissingMethods, session, mCurInputContext,
mCurAttribute));
}
if (mShowRequested) {
if (DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "Attach new input asks to show input");
showCurrentInputLocked(getAppShowFlags(), null);
}
return new InputBindResult(session.session,
(session.channel != null ? session.channel.dup() : null),
mCurId, mCurSeq, mCurUserActionNotificationSequenceNumber);
}
case MSG_BIND_INPUT:
args = (SomeArgs)msg.obj;
try {
((IInputMethod)args.arg1).bindInput((InputBinding)args.arg2);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
args.recycle();
return true;
case MSG_START_INPUT: {
int missingMethods = msg.arg1;
args = (SomeArgs) msg.obj;
try {
SessionState session = (SessionState) args.arg1;
setEnabledSessionInMainThread(session);
session.method.startInput((IInputContext) args.arg2, missingMethods,
(EditorInfo) args.arg3);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
args.recycle();
return true;
}
case MSG_BIND_CLIENT: {
args = (SomeArgs)msg.obj;
IInputMethodClient client = (IInputMethodClient)args.arg1;
InputBindResult res = (InputBindResult)args.arg2;
try {
// 调回到程序端,InputMethodManager.onBindMethod()
client.onBindMethod(res);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Client died receiving input method " + args.arg2);
} finally {
// Dispose the channel if the input method is not local to this process
// because the remote proxy will get its own copy when unparceled.
if (res.channel != null && Binder.isProxy(client)) {
res.channel.dispose();
}
}
args.recycle();
return true;
}
// IInputMethodWrapper.java
@Override
public void startInput(IInputContext inputContext,
@InputConnectionInspector.MissingMethodFlags final int missingMethods,
EditorInfo attribute) {
mCaller.executeOrSendMessage(mCaller.obtainMessageIOO(DO_START_INPUT,
missingMethods, inputContext, attribute));
}
case DO_START_INPUT: {
SomeArgs args = (SomeArgs)msg.obj;
int missingMethods = msg.arg1;
// IInputContext就是输入法和文本输入view的通信接口
// 通过这个接口,输入法能够获取view的信息,也能够直接将文本传送给view
IInputContext inputContext = (IInputContext)args.arg1;
InputConnection ic = inputContext != null
? new InputConnectionWrapper(inputContext, missingMethods) : null;
EditorInfo info = (EditorInfo)args.arg2;
info.makeCompatible(mTargetSdkVersion);
inputMethod.startInput(ic, info);
args.recycle();
return;
}
// InputMethodService.java
public void startInput(InputConnection ic, EditorInfo attribute) {
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "startInput(): editor=" + attribute);
doStartInput(ic, attribute, false);
}
void doStartInput(InputConnection ic, EditorInfo attribute, boolean restarting) {
if (!restarting) {
doFinishInput();
}
mInputStarted = true;
mStartedInputConnection = ic;
mInputEditorInfo = attribute;
initialize();
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "CALL: onStartInput");
onStartInput(attribute, restarting);
if (mWindowVisible) {
if (mShowInputRequested) {
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "CALL: onStartInputView");
mInputViewStarted = true;
onStartInputView(mInputEditorInfo, restarting);
startExtractingText(true);
} else if (mCandidatesVisibility == View.VISIBLE) {
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "CALL: onStartCandidatesView");
mCandidatesViewStarted = true;
onStartCandidatesView(mInputEditorInfo, restarting);
}
}
}到此焦点view已经通过调用IMMS的startInput和输入法绑定了,但是此时输入法还没有显示。但是系统紧接着会调用windowGainFocus来显示输入法
未完待续。。。。
- 参考文档
- https://blog.csdn.net/huangyabin001/article/details/28434989
- https://blog.csdn.net/huangyabin001/article/details/28435093#comments
- https://blog.csdn.net/jieqiong1/article/details/71262987