YOLOv1 目标检测 训练及训练中存在的问题
下载的版本为:https://github.com/pjreddie/darknet.git
根据官网教程下载VOC数据集及权重:https://pjreddie.com/darknet/yolov1/
训练
1. 对cfg/yolov1.cfg做修改:
注释掉Testing的部分,使用Training部分,batch=64,subdivisions=8,否则会出现大量-nan,以及loss不收敛情况
[net]
# Testing
# batch=1
# subdivisions=1
# Training // 使用training部分
batch=64
subdivisions=8
height=448
width=448
channels=3
momentum=0.9
decay=0.0005
saturation=1.5
exposure=1.5
hue=.1batch=1,-nan情况:
2. 对examples/yolo.c做修改:
相比较yolov2和yolov3,yolov1还没有采用类似 voc.data 的配置文件,故需要在源代码里,修改trainset的路径
void train_yolo(char *cfgfile, char *weightfile)
{
char *train_images = "/data/voc/train.txt"; //修改为train.txt对应路径
char *backup_directory = "/home/pjreddie/backup/"; //训练后得到的权重(weights)的存放地
srand(time(0));
char *base = basecfg(cfgfile);
printf("%s\n", base);
float avg_loss = -1;
network *net = load_network(cfgfile, weightfile, 0);
printf("Learning Rate: %g, Momentum: %g, Decay: %g\n", net->learning_rate, net->momentum, net->decay);
int imgs = net->batch*net->subdivisions;
int i = *net->seen/imgs;
data train, buffer;3. 开始训练:
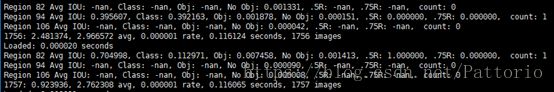
./darknet yolo train cfg/yolov1/yolo.train.cfg extraction.conv.weights使用GPU,CUDA,显卡为GeForce GTX 1080,在VOC数据集完成了对YOLOv1的训练(iter = 40000),IOU普遍在0.69以上,且loss从一开始的15收敛到了2.7左右(忘记保存训练过程了),得到最终权重yolov1_final_weight.weight,训练时间差不多25小时。
训练log(末期):
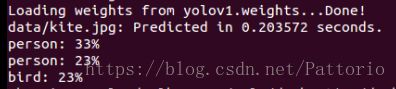
最终得到的权重进行单张图片检测的精确度不如作者在官网上给的权重高
作者所给权重:
训练所得权重:
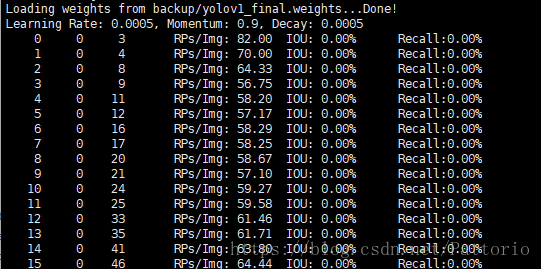
Valid和Recall
在进行测试的时候,遇到了 validate_yolo 能够检测到边框并且边框位置和ground truth相近然而validate_yolo_racall函数测得recall为0的问题:
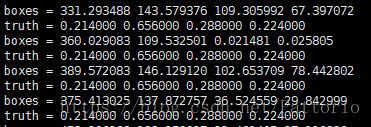
尝试着输出了一下用于IOU比较的gt和detection box的值,发现了问题:
ground truth是相对大小,而detection box是绝对大小,我们看一下调用的yolo.c中的recall函数可以看出问题:
void validate_yolo_recall(char *cfg, char *weights)
{
network *net = load_network(cfg, weights, 0);
set_batch_network(net, 1);
fprintf(stderr, "Learning Rate: %g, Momentum: %g, Decay: %g\n", net->learning_rate, net->momentum, net->decay);
srand(time(0));
char *base = "results/comp4_det_test_";
list *plist = get_paths("data/voc.2007.test");
char **paths = (char **)list_to_array(plist);
layer l = net->layers[net->n-1];
int classes = l.classes;
int side = l.side;
int j, k;
/* 冗余部分,我删掉了
// eliminate
// it opens the detection result in results file.
// it will clear all the result in existed file.
FILE **fps = calloc(classes, sizeof(FILE *));
for(j = 0; j < classes; ++j){
char buff[1024];
snprintf(buff, 1024, "%s%s.txt", base, voc_names[j]);
fps[j] = fopen(buff, "w");
}
*/
int m = plist->size;
int i=0;
float thresh = .001;
float iou_thresh = .5;
float nms = 0;
int total = 0;
int correct = 0;
int proposals = 0;
float avg_iou = 0;
for(i = 0; i < m; ++i){
char *path = paths[i];
image orig = load_image_color(path, 0, 0);
image sized = resize_image(orig, net->w, net->h);
char *id = basecfg(path);
network_predict(net, sized.data);
// get_network_boxes函数用来求detection boxes的各项参数,保存在dets中
int nboxes = 0;
detection *dets = get_network_boxes(net, orig.w, orig.h, thresh, 0, 0, 1, &nboxes);
if (nms) do_nms_obj(dets, side*side*l.n, 1, nms);
// ground truth,是利用voc_label.py生成的相对位置
char labelpath[4096];
find_replace(path, "images", "labels", labelpath);
find_replace(labelpath, "JPEGImages", "labels", labelpath);
find_replace(labelpath, ".jpg", ".txt", labelpath);
find_replace(labelpath, ".JPEG", ".txt", labelpath);
int num_labels = 0;
box_label *truth = read_boxes(labelpath, &num_labels);
for(k = 0; k < side*side*l.n; ++k){
if(dets[k].objectness > thresh){
++proposals;
}
}
for (j = 0; j < num_labels; ++j) {
++total;
box t = {truth[j].x, truth[j].y, truth[j].w, truth[j].h};
float best_iou = 0;
for(k = 0; k < side*side*l.n; ++k){ // 每个detection box和ground truth比较IOU
float iou = box_iou(dets[k].bbox, t);
if(dets[k].objectness > thresh && iou > best_iou){
best_iou = iou;
}
}
avg_iou += best_iou;
if(best_iou > iou_thresh){
++correct;
}
}
fprintf(stderr, "%5d %5d %5d\tRPs/Img: %.2f\tIOU: %.2f%%\tRecall:%.2f%%\n", i, correct, total, (float)proposals/(i+1), avg_iou*100/total, 100.*correct/total);
free_detections(dets, nboxes);
free(id);
free_image(orig);
free_image(sized);
}
}
求detection box用的是get_detection_boxes这个函数,我们再来看下这个函数,这个函数在src/network.c中:
detection *get_network_boxes(network *net, int w, int h, float thresh, float hier, int *map, int relative, int *num)
{
detection *dets = make_network_boxes(net, thresh, num);
fill_network_boxes(net, w, h, thresh, hier, map, relative, dets);
return dets;
}跳转到fill_network_boxes函数:
void fill_network_boxes(network *net, int w, int h, float thresh, float hier, int *map, int relative, detection *dets)
{
int j;
for(j = 0; j < net->n; ++j){
layer l = net->layers[j];
if(l.type == YOLO){
int count = get_yolo_detections(l, w, h, net->w, net->h, thresh, map, relative, dets);
dets += count;
}
if(l.type == REGION){
get_region_detections(l, w, h, net->w, net->h, thresh, map, hier, relative, dets);
dets += l.w*l.h*l.n;
}
if(l.type == DETECTION){
get_detection_detections(l, w, h, thresh, dets);
dets += l.w*l.h*l.n;
}
}
}这里的l.type是根据yolov1.cfg文件来定义的([detection]),在yolov3中为yolo,在yolov2中检测层为region,在yolov1中为detection,我们再进入get_detection_detections函数里看一下,该函数在src/detection_layer.c中:
void get_detection_detections(layer l, int w, int h, float thresh, detection *dets)
{
int i,j,n;
float *predictions = l.output;
//int per_cell = 5*num+classes;
for (i = 0; i < l.side*l.side; ++i){
int row = i / l.side;
int col = i % l.side;
for(n = 0; n < l.n; ++n){
int index = i*l.n + n;
int p_index = l.side*l.side*l.classes + i*l.n + n;
float scale = predictions[p_index];
int box_index = l.side*l.side*(l.classes + l.n) + (i*l.n + n)*4;
box b;
b.x = (predictions[box_index + 0] + col) / l.side * w;
b.y = (predictions[box_index + 1] + row) / l.side * h;
b.w = pow(predictions[box_index + 2], (l.sqrt?2:1)) * w;
b.h = pow(predictions[box_index + 3], (l.sqrt?2:1)) * h;
dets[index].bbox = b;
dets[index].objectness = scale;
for(j = 0; j < l.classes; ++j){
int class_index = i*l.classes;
float prob = scale*predictions[class_index+j];
dets[index].prob[j] = (prob > thresh) ? prob : 0;
}
}
}
} // 求box边框
b.x = (predictions[box_index + 0] + col) / l.side * w;
b.y = (predictions[box_index + 1] + row) / l.side * h;
b.w = pow(predictions[box_index + 2], (l.sqrt?2:1)) * w;
b.h = pow(predictions[box_index + 3], (l.sqrt?2:1)) * h;可以看到,求得得边框值是绝对大小(因为乘上了原图的w,h),而ground truth是一个相对位置,所以我们需要在这里动动手脚,即:
b.x = (predictions[box_index + 0] + col) / l.side;
b.y = (predictions[box_index + 1] + row) / l.side;
b.w = pow(predictions[box_index + 2], (l.sqrt?2:1));
b.h = pow(predictions[box_index + 3], (l.sqrt?2:1));这样就可以得到边框的相对大小了。但!仅仅这样还不够!因为在validate_yolo函数里,也调用了这个get_detection_boxes函数,如果只改这里,求得的valid_results是会出问题的。
运行一下./darknet yolo valid cfg/yolov1.cfg weights,可以得到对valid set的检测结果,这些结果是一个绝对值,保存在results文件夹中,如果我们像上述更改了get_detection_boxes,会使得保存的检测结果也是一个相对值(看你要如何后续处理数据,如果像要绝对值的话,就需要再改动一个地方)
validate_yolo函数会调用:
detection *dets = get_network_boxes(net, w, h, thresh, 0, 0, 0, &nboxes); //得到检测框
if (nms) do_nms_sort(dets, l.side*l.side*l.n, classes, iou_thresh);
// write real size into result
print_yolo_detections(fps, id, l.side*l.side*l.n, classes, w, h, dets); //将检测结果写入文件我们需要在将检测结果写入文件的时候再动动手脚(注释掉的部分是源码)
void print_yolo_detections(FILE **fps, char *id, int total, int classes, int w, int h, detection *dets)
{
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i < total; ++i){
// get its real size (not relative size)
float xmin = dets[i].bbox.x * w - dets[i].bbox.w * w /2.;
float xmax = dets[i].bbox.x * w + dets[i].bbox.w * w /2.;
float ymin = dets[i].bbox.y * h - dets[i].bbox.h * h /2.;
float ymax = dets[i].bbox.y * h + dets[i].bbox.h * h /2.;
/*
// change
float xmin = dets[i].bbox.x - dets[i].bbox.w/2.;
float xmax = dets[i].bbox.x + dets[i].bbox.w/2.;
float ymin = dets[i].bbox.y - dets[i].bbox.h/2.;
float ymax = dets[i].bbox.y + dets[i].bbox.h/2.;
// change
*/
if (xmin < 0) xmin = 0;
if (ymin < 0) ymin = 0;
if (xmax > w) xmax = w;
if (ymax > h) ymax = h;
for(j = 0; j < classes; ++j){
if (dets[i].prob[j]) fprintf(fps[j], "%s %f %f %f %f %f\n", id, dets[i].prob[j],
xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax);
}
}
}