APUE第六章学习笔记
一:口令文件的操作
/*****************************************
struct passwd成员:
struct passwd
{
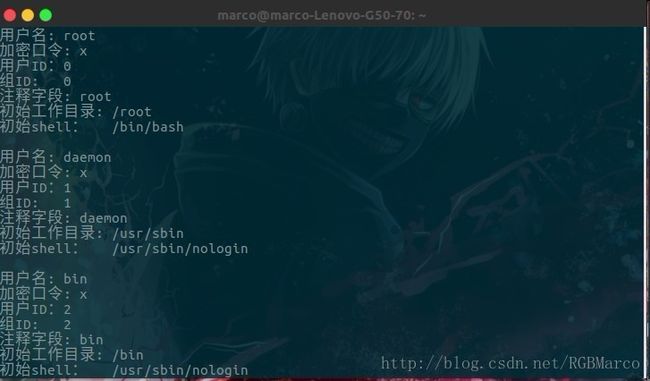
char* pw_name; // 用户名
char* pw_passwd; //加密口令
uid_t pw_uid; //数值用户ID
gid_t pw_gid; // 数值组ID
char* pw_gecos; //注释字段
char* pw_dir; //初始工作目录
char* pw_shell; //初始shell(用户程序)
/*************下列平台可能没有**************/
char* pw_class; //用户访问类
time_t pw_change; //下次更改口令时间
time_t pw_expire; //账户有效期时间
};
*****************************************//******************************************************
包含头文件: #include <pwd.h>
函数原型: struct passwd* getpwuid(uid_t uid);
函数说明: 通过用户ID获取口令文件项
返回值: 若成功,返回指针,若出错,返回NULL
*******************************************************//*******************************************************
包含头文件: #include <pwd.h>
函数原型: struct passwd* getpwuid(uid_t uid);
函数说明: 通过用户ID获取口令文件项
返回值: 若成功,返回指针,若出错,返回NULL
********************************************************//**********************************************************
包含头文件: #include <pwd.h>
函数原型: struct passwd* getpwnam(const char* name);
函数说明: 通过用户名获取口令文件项
返回值: 若成功,返回指针,若失败,返回NULL
**********************************************************/
/***********************************************************
包含头文件: #include <pwd.h>
函数原型: struct passwd* getpwent(void);
函数说明: 逐项遍历口令文件,返回当前口令文件项
返回值: 返回当前口令文件项,若到达文件尾,则返回NULL
***********************************************************//***********************************************************
包含头文件: #include <pwd.h>
函数原型: void setpwent(void);
函数说明:回绕到口令文件首项
**********************************************************/
/**********************************************************
包含头文件: #include <pwd.h>
函数原型: void endpwent(void);
函数说明: 关闭口令文件
*************************************************************/vi 6.1.c
#include \n" );
exit(0);
}
struct stat statbuf;
if (lstat(argv[1],&statbuf) < 0)
{
printf("lstat error\n");
exit(0);
}
struct passwd* pw;
if ((pw = getpwuid(statbuf.st_uid)) == NULL)
{
printf("getpwuid error\n");
exit(0);
}
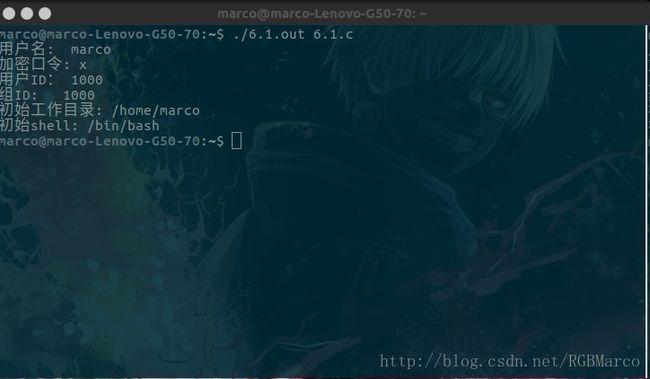
printf("用户名: %s\n",pw->pw_name);
printf("加密口令: %s\n",pw->pw_passwd);
printf("用户ID: %d\n",pw->pw_uid);
printf("组ID: %d\n",pw->pw_gid);
printf("初始工作目录: %s\n",pw->pw_dir);
printf("初始shell: %s\n",pw->pw_shell);
return 0;
}vi 6.1.1.c
#include vi 6.2.c
#include 二. 阴影口令文件
阴影口令文件项结构体
/***********************************************************
struct spwd
{
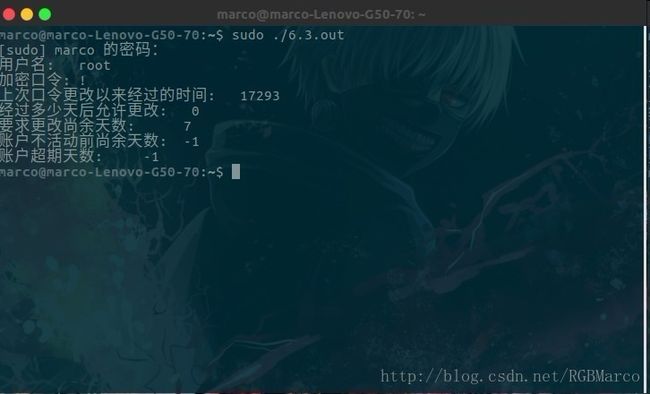
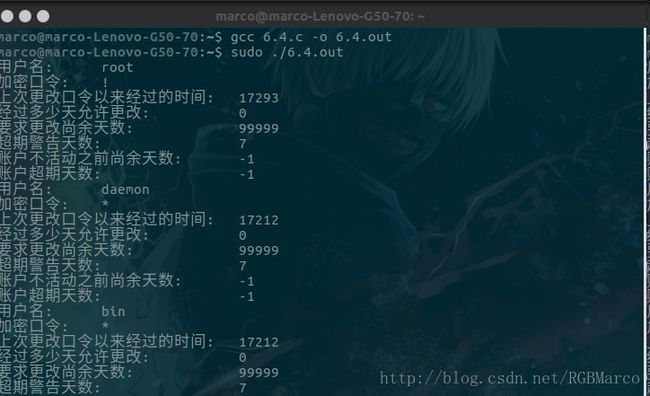
char* sp_namp; //用户登录名
char* sp_pwdp; //加密口令
int sp_lstchg; //上次更改口令以来经过的时间
int sp_min; //经多少天后允许更改
int sp_max; //要求更改尚余天数
int sp_warn; //超期警告天数
int sp_inact; //账户不活动之前尚余天数
int sp_expire; //账户超期天数
unsigned int sp_flag; //保留
}
*********************************************************/
/***********************************************************
包含头文件: #include <shadow.h>
函数原型: struct spwd* getspname(const char* name);
函数说明: 得到阴影口令文件项
返回值: 若成功,返回指针,若失败,返回NULL
**********************************************************/vi 6.3.c
#include /***********************************************************
包含头文件: #include <shadow.h>
函数原型: void setspent();
函数说明: 回绕到文件开头项
*******************************************************//*******************************************************
包含头文件: #include <shadow.h>
函数原型: struct spwd* getspent();
函数说明: 打开阴影口令文件,并返回当前阴影口令文件项
*******************************************************//********************************************************
包含头文件: #include <shadow.h>
函数原型: void endspent();
函数说明: 关闭阴影口令文件
********************************************************/vi 6.4.c
#include 三: 组文件
/**********************************************************
组文件结构体:
struct group
{
char* gr_name; //组名
char* gr_passwd; //加密口令
int gr_gid; //数值组ID
char **gr_mem; //指向各用户名指针的数组
}
***********************************************************//*******************************************************
包含头文件: #include <grp.h>
函数原型: struct group* getgrgid(gid_t gid);
函数说明: 通过组ID获得组文件组项
返回值: 若成功,返回组文件组项指针,若失败,返回NULL
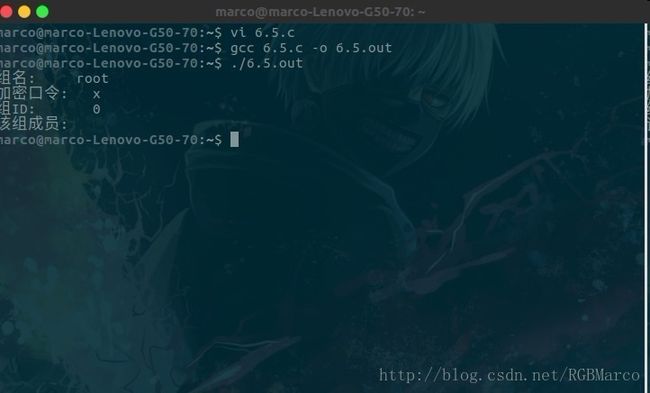
********************************************************/vi 6.5.c
#include /***********************************************************
包含头文件: #include <grp.h>
函数原型: struct group* getgrnam(const char* name);
函数说明: 通过组ID获得组文件组项指针,若失败,返回
NULL
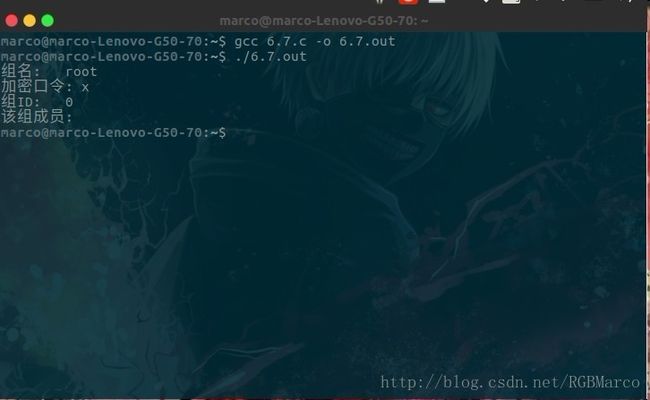
**********************************************************/#include /*********************************************************
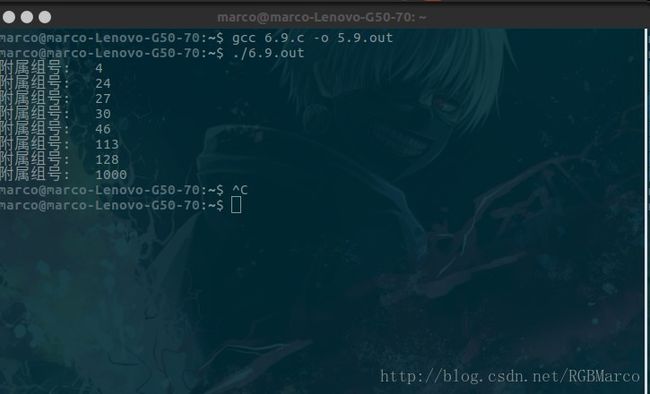
包含头文件: #include <unistd.h>
函数原型:int getgroups(int gidsetsize,gid_t grouplist[]);
函数说明: getgroups将进程所属用户的各附属组ID,填写到数组grouplist中,填写入该数组附属组ID最多为gidsize个,实际填写附属组ID数由函数返回
作为一种特殊情况,如若gidsize为0,则函数返回附属组ID数,而对数组grouplist不做修改
返回值: 若成功,返回附属组ID数量,若出错,返回-1
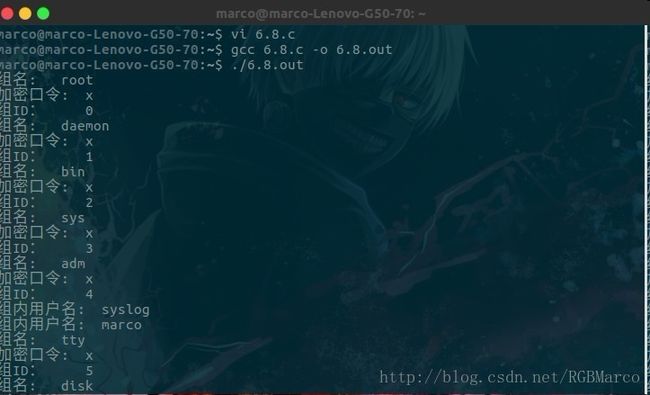
*********************************************************/vi 6.9.c
#include /***********************************************************
包含头文件: #include <grp.h> //on linux
#include // on FreeBSD,Mac Os X,
and Solaris
函数原型: int setgroups(int ngroups,const gid_t
grouplist[]);
函数说明:由超级用户调用以便为调用进程设置附属组ID表
返回值: 若成功,返回0,若出错,返回-1
*******************************************************//*********************************************************
包含头文件:#include <grp.h> // on linux and Solaris
#include // on FreeBSD and Mac Os X
函数原型: int initgroups(const char* username,gid_t basegid);
函数说明: 为用户初始化附属组ID表
返回值: 若成功,返回0,若失败,返回-1
****************************************************//**********************************************************
struct utsname
{
char sysname[]; //操作系统名称
char nodename[]; //网络上的名称
char release[]; //当前发布级别
char version[]; //当前发布版本
char machine[]; //当前硬件体系类型
}
**********************************************************//***********************************************************
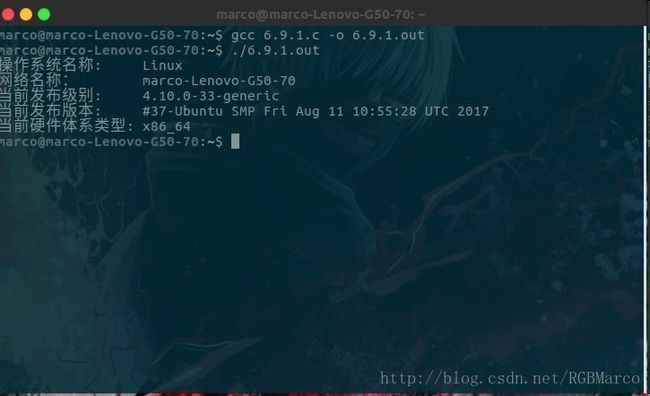
包含头文件: #include <sys/utsname.h>
函数原型: int uname(struct utsname* name);
函数说明: 得到主机和操作系统有关信息
返回值: 若成功,返回非负值,若失败,返回-1
**********************************************************/vi 6.9.1.c
#include vi 6.9.2.c
/***********************************************************
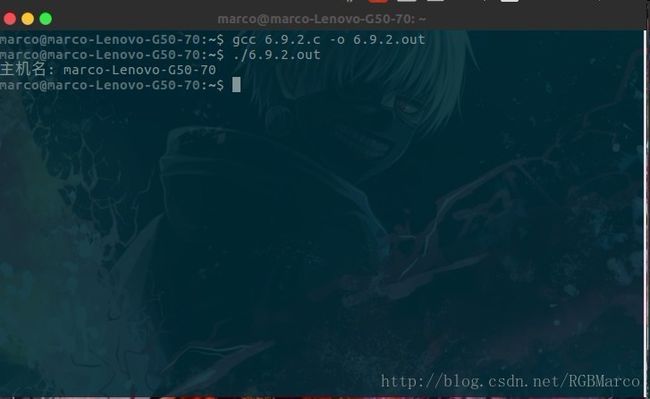
包含头文件: #include <unistd.h>
函数原型: int gethostname(char* name,int namelen);
函数说明: 得到主机名, 该主机名通常为TCP/IP网络主机的名字
返回值: 若成功,返回0,若失败,返回-1
**********************************************************/#include 四: 时间和例程
/*************************************************************
包含头文件: #include <time.h>
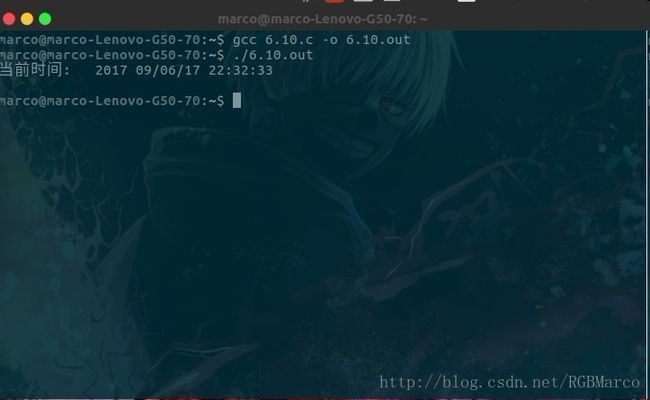
函数原型: time_t time(time_t *calptr);
函数说明: 返回当前时间和日期
时间值作为函数值返回,如果参数非空,则时间值也存放
在由calptr指向的单元内
返回值: 若成功,返回时间值,若出错,返回-1
*************************************************************/vi 6.10.c
#include /*************************************************************
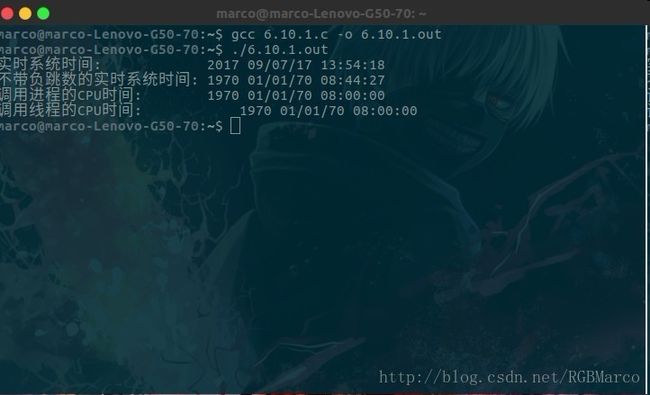
时钟通过clockid_t类型标识:
标识符 选项 说明
CLOCK_REALTIME 实时系统时间
CLOCK_MONTONIC _ POSIX_MONOTONIC_CLOCK 不带负跳数的实时系统时间
CLOCK_PROCESS_CPUTIME_ID POSIXCPUTIME 调用进程的CPU时间
CLOCK_THREAD_CPUTIME_ID POSIXTHREAD_CPUTIME 调用线程的CPU时间
***********************************************************//*********************************************************
包含头文件: #include <sys/time.h>
函数原型: int colck_gettime(clockid_t clock_id,
struct timespec *tsp);
函数说明: 获取指定时钟的时间
返回值: 若成功,返回0,若失败,返回-1
*********************************************************/vi 6.10.1.c
#include /*********************************************************
包含头文件: #include <sys/time.h>
函数原型: int clock_getres(clockid_t clock_id,struct timespec *tsp);
函数说明:把参数tsp指向的timespec结构初始化为与
clock_id参数对应的时钟精度
***********************************************************//***********************************************************
包含头文件: #include <sys/time.h>
函数原型:int clock_settime(clockid_t clock_id,const
struct timespec *tsp);
函数说明:对特定的时钟设置时间
返回值:若成功,返回0,若出错,返回-1
***********************************************************//**********************************************************
包含头文件: #include <sys/time.h>
函数原型: int gettimeofday(struct timeval* restrict tp,void * restrict tzp);
函数说明: tzp唯一合法值是NULL,其他值将产生不确定的结果(某些平台支持用tzp说明时区)
gettimeofday函数以距特定时间的秒数的方式将时间存放于tp指向的timeval结构
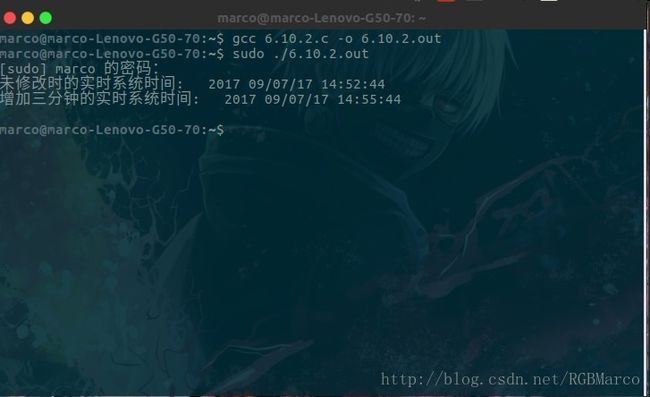
**********************************************************/vi 6.10.2
#include /**********************************************************
结构体 struct tm
{
int tm_sec; //秒
int tm_min; //分
int tm_hour; //时
int tm_mday; //日 of 月
int tm_mon; //月
int tm_year; //年
int tm_wday; //日 of 周
int tm_yady; //日 of 年
int tm_isdst; //夏令时标识符 若为正,开启标识符,
若为0,关闭夏令时,若为负,未知
}
********************************************************//**********************************************************
包含头文件: #include <time.h>
函数原型: struct tm* localtime(const time_t *calptr);
函数说明: 将日历时间转换为本地时间
返回值: 若成功,返回结构体tm指针,若出错,返回NULL
**********************************************************//**********************************************************
包含头文件: #include <time.h>
函数原型: struct tm* gmtime(const time_t* calptr);
函数说明:将日历时间转化为协调统一时间
返回值: 若成功,返回结构体tm指针,若失败,返回NULL
***********************************************************//*************************************************************
包含头文件: #include <time.h>
函数原型: time_t mktime(struct tm* tmptr);
函数说明: 将tm结构体指针分解成time_t并返回
返回值: 若成功,返回日历时间,若失败,返回-1
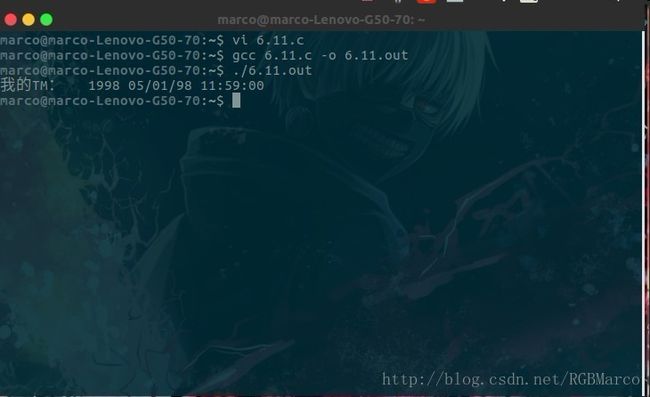
************************************************************/vi 6.11.c
#include