SpringBoot学习笔记之五-Web开发Thymeleaf模板引擎
模板引擎
常用的模板引擎:JSP,Velocity,Freemarker,Thymeleaf等等
SpringBoot使用嵌入式的Tomcat,默认不支持JSP
模板引擎的作用:写一个页面模板
SpringBoot推荐Thymeleaf,语法更简单,功能更强大
用法:
(1)引入模板引擎,在pom.xml文件中添加依赖:
切换指定thymeleaf版本号:
Thymeleaf使用和语法
注意ThymeleafProperties这个配置类
只要把html页面放在类路径下的resources/templetes/文件夹下,Thymeleaf就可以自动帮我们渲染页面了
用法:
(1)导入Thymeleaf的名称空间,在html的文件头写上
lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
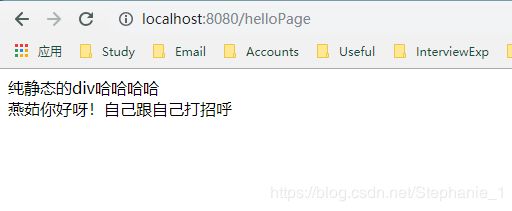
(2)显示一个纯静态的页面:
html>
lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
charset="UTF-8">
调用访问该页面的方法,在Controller中的代码:
@RequestMapping("/helloPage")
public String helloPage()
{
//访问的资源实际是:resources/templates/helloPage.html
return "helloPage";
}
(3)语法规则:
Demo:
现在Controller后台请求参数中,添加一个map,用来承载返回给客户端可访问的数据遍历,如我添加一个helloTest的变量并赋值 :
@RequestMapping("/helloPage")
public String helloPage(Map
{
map.put("helloTest", "燕茹你好呀!自己跟自己打招呼");
//访问的资源实际是:resources/templates/helloPage.html
return "helloPage";
}
然后在html页面资源使用这个变量:
html>
lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
charset="UTF-8">
运行结果,如果helloTest这个变量成功取到,div内容直接展示${}中的值内容,运行截图:
1)th:text
将div的内容设定为${}中变量的值
th:冒号后面可以跟html的任意属性!如下便签代码:
Thymeleaf支持的jsp语法:
jsp:include
c:forEach
c:if
c:set 声明变量
prepend,append:任意属性修改支持
表达式:
变量表达式: $ {...},功能:获取对象的属性,调用方法,使用内置基本对象(${#ctx的属性});
内置对象:
#ctx : the context object.
#vars: the context variables.
#locale : the context locale.
#request : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletRequest object.
#response : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletResponse object.
#session : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpSession object.
#servletContext : (only in Web Contexts) the ServletContext object.
其中ctx访问举例:其他的查找官方文档去看
#ctx : the context object. An implementation of org.thymeleaf.context.IContext or
org.thymeleaf.context.IWebContext depending on our environment (standalone or w
Note #vars and #root are synomyns for the same object, but using #ctx is recomm
/*
* ======================================================================
* See javadoc API for class org.thymeleaf.context.IContext
* ======================================================================
*/
${#ctx.locale}
${#ctx.variableNames}
/*
* ======================================================================
* See javadoc API for class org.thymeleaf.context.IWebContext
* ======================================================================
*/
${#ctx.request}
${#ctx.response}
${#ctx.session}
${#ctx.servletContext}
调用工具类啊:
#execInfo : information about the template being processed.
#messages : methods for obtaining externalized messages inside variables expressions, in the same way as they
would be obtained using #{…} syntax.
#uris : methods for escaping parts of URLs/URIs
#conversions : methods for executing the configured conversion service (if any).
#dates : methods for java.util.Date objects: formatting, component extraction, etc.
#calendars : analogous to #dates , but for java.util.Calendar objects.
#numbers : methods for formatting numeric objects.
#strings : methods for String objects: contains, startsWith, prepending/appending, etc.
#objects : methods for objects in general.
#bools : methods for boolean evaluation.
#arrays : methods for arrays.
#lists : methods for lists.
#sets : methods for sets.
#maps : methods for maps.
#aggregates : methods for creating aggregates on arrays or collections.
#ids : methods for dealing with id attributes that might be repeated (for example, as a result of an iteration).
选择变量表达式: \* {...}
*{}j具体用法的demo,就是方便访问对象属性的时候:
<div th:object="${session.user}">
<p>Name: <span th:text="*{firstName}">Sebastianspan>.p>
<p>Surname: <span th:text="*{lastName}">Pepperspan>.p>
<p>Nationality: <span th:text="*{nationality}">Saturnspan>.p>
div>
对应的,如果直接使用${}的话,则用法为:
<div>
<p>Name: <span th:text="${session.user.firstName}">Sebastianspan>.p>
<p>Surname: <span th:text="${session.user.lastName}">Pepperspan>.p>
<p>Nationality: <span th:text="${session.user.nationality}">Saturnspan>.p>
div>
消息表达式: #{...}获取国际化内容
链接⽹址表达式: @ {...}
⽚段表达式: 〜{...}
需要花一定 的时间,去看完Thymeleaf的官方手册啊
最后,先整合本节学到的用法demo:包含了,如何遍历元素:
Controller中的代码返回数据时:
@RequestMapping("/helloPage")
public String helloPage(Map
{
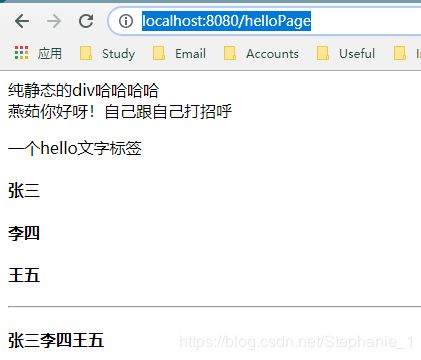
map.put("helloTest", "燕茹你好呀!自己跟自己打招呼");
map.put("hello","一个hello文字标签
");map.put("users", Arrays.asList("张三","李四","王五"));//一个数组
//访问的资源实际是:resources/templates/helloPage.html
return "helloPage";
}
页面代码:
html>
lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
charset="UTF-8">
th:text="${user}" th:each="user:${users}">
th:each="user:${users}">[[${user}]]
运行截图:
Spring Boot自动配置了SpringMVC
以下是Spring Boot 对SprinngMVC的自动配置:
The auto-configuration adds the following features on top of Spring’s defaults:
(1)Inclusion of ContentNegotiatingViewResolver and BeanNameViewResolver
beans.自动配置了ViewResolver(视图解析器:决定根据方法的返回值得到视图对象(View),视图对象决定如何渲染(是转发、还是重定向到页面)
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver :组合所有的视图解析器
如何定制:我们可以自己给容器中添加一个视图解析器,自动的将其组合进来;(我在本地测试添加自己的视图解析器的时候,没有运行成功)以下被注释的代码,启动时就会报错
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.View;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver;
import java.util.Locale;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
// @Bean //向容器中添加一个组件,添加一个自己自定义的视图解析器
// public ViewResolver myViewResolver()
// {
// return new MyViewResolver();
// }
//
// public static class MyViewResolver implements ViewResolver{
// @Override
// public View resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
// return null;
// }
// }
}
(2)Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars
(see below).
(3)Static index.html support.静态首页访问
(4)Custom Favicon support (see below).
(5) 自动注册了 Converter, GenericConverter, Formatter
beans.
Converter:转换器,public String hello(User user);类型转换使用Converter
Formatter:格式化器,2019-1-6 Date
这个格式化的配置相关,最新的Spring Boot已经跟视频对不上了。
添加格式化器的函数:(WebMvcAutoConfiguration自动配置类中)
@Override
public void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {
for (Converter, ?> converter : getBeansOfType(Converter.class)) {
registry.addConverter(converter);
}
for (GenericConverter converter : getBeansOfType(GenericConverter.class)) {
registry.addConverter(converter);
}
for (Formatter formatter : getBeansOfType(Formatter.class)) {
registry.addFormatter(formatter);
}
}
(6)Support for HttpMessageConverters (see below).
HttpMessageConverters :SpringMVC用于转换Http请求和响应的。User->Json
HttpMessageConverters:是从容器中确定,获取所有的HttpMessageConverters
自己给容器中添加HttpMessageConverters,只需要将自己的组件注册到容器中
(7)Automatic registration of MessageCodesResolver (see below).定义错误代码生成规则
(8)Automatic use of a ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer bean (see
below).
我们可以创建一个ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer来替换默认的(添加到容器)
步骤:
初始化WebDataBinder
请求数据===JavaBean
Web的所有自动场景,都在下面的这个包里面
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web
如何修改Spring Boot的默认配置:
模式:
(1)Spring Boot在自动配置很多组件的时候
先看容器中有没有用户自己配置的(@Bean,@Component)如果有就用用户配置的,如果没有,才自动配置;如果有的组件可以有多个(ViewResolver)将用户配置的和自己配置的组合起来;
(2)扩展SpringMVC
如下是一个原先普通的springmvc.xml配置文件:
文件位置:
xml配置文件内容:
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<mvc:view-controller path="/helloTest" view-name="helloPage" />
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/hello"/>
mvc:interceptor>
mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
(1)编写一个配置类(@Configuration),是WebMvcConfigurerAdapter类型;不能标注@EnableWebMvc注解
以下为一个配置类,实现修改视图解析器的效果:
既保留了所有的自动配置,也能用我们扩展的配置:
package com.example.demo.config;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ViewControllerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter;
//使用 WebMvcConfigurerAdapter 可以用来扩展SprinngMVC的功能,
//但是目测在当前新版本的SpringBoot这个抽象类已经被丢弃了,找到了新的继承类?
@Configuration//标注这是一个配置类
public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
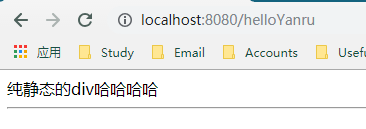
//浏览器发送 /helloYanru,跳转到helloPage页面
registry.addViewController("/helloYanru").setViewName("helloPage");
}
}
运行效果:在浏览器请求localhost:8080/helloYanru,就可以跳转到helloPage.html
这个跟原先的请求接口没有冲突,相当于,请求helloPage和helloYanru都能跳转到这个页面
@RequestMapping("/helloPage")
public String helloPage(Map
{
map.put("helloTest", "燕茹你好呀!自己跟自己打招呼");
map.put("hello","一个hello文字标签
");map.put("users", Arrays.asList("张三","李四","王五"));//一个数组
//访问的资源实际是:resources/templates/helloPage.html
return "helloPage";
}
(2)在做其他自动配置时,会导入@Import(EnableWebMvcAutoConfiguration.class)
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class,
TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class, ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
}
(3)容器中所有的WebMvcConfigure都会起作用
(4)我们的配置类也会被调用
效果:SpringMVC的自动配置和我们的扩展配置都会起作用
全面接管SpringMVC
SpringBoot对SpringMVC的自动配置不要了,所有都是我们自己配:需要在配置类中添加@EnableWebMvc,MyMvcConfig我自己的配置类添加了这个注解之后,结果就是所有的自动配置全都失效了。。一般来说是不需要这么用的!!!(但是这个注解在我的机器和Spring版本上,环境中并没有生效,如果生效了,则用户是无法直接访问原先的静态资源目录的!)
@EnableWebMvc这个注解是见WebMvcConfigurationSupport的组件导入进来,导入的只是SpringBoot的最基本的组件;
简单的登录页demo开始!
注意:
配置文件修改指定项目名称:
#配置项目的名称,以后访问该项目的资源就不是直接IP:端口/页面关键字了,而是得带上项目名称
server.servlet.context-path=/yanru
运行效果,此后请求地址就不能直接请求页面了,要在端口号后面添加项目名称:
页面国际化
国际化实现步骤:
(1)编辑国际化配置文件
(2)使用ResourceBundleMessageSource管理国际化资源文件
(3)在页面使用fmt:message取出国际化内容
在Spring Boot中的步骤:
(1)编写国际化配置文件,抽取页面需需要显示的国际化消息
可以在编辑视图编辑多语言关键字,如图:
也可以直接以普通的属性文件方式编辑,如下是login_zh_CN.properties
login.btn=登录
login.password=密码
login.tip=请登录
login.username=用户名
(2)SpringBoot自动配置好了国家化的组件,在MessageSourceAutoConfiguration配置类:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = MessageSource.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@Conditional(ResourceBundleCondition.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties
public class MessageSourceAutoConfiguration {
//yanru备注:我们的配置文件,可以放在类路径下的message.properties
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.messages")
public MessageSourceProperties messageSourceProperties() {
return new MessageSourceProperties();
}
@Bean
public MessageSource messageSource(MessageSourceProperties properties) {
ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource();
if (StringUtils.hasText(properties.getBasename())) {
messageSource.setBasenames(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(
StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(properties.getBasename())));
}
if (properties.getEncoding() != null) {
messageSource.setDefaultEncoding(properties.getEncoding().name());
}
messageSource.setFallbackToSystemLocale(properties.isFallbackToSystemLocale());
Duration cacheDuration = properties.getCacheDuration();
if (cacheDuration != null) {
messageSource.setCacheMillis(cacheDuration.toMillis());
}
messageSource.setAlwaysUseMessageFormat(properties.isAlwaysUseMessageFormat());
messageSource.setUseCodeAsDefaultMessage(properties.isUseCodeAsDefaultMessage());
return messageSource;
}
}
(3)配置application.properties指定使用哪个多语言文件:
#指定多语言相关,指定页面使用哪个多语言配置文件
spring.messages.basename=language.login
注意:在使用配置文件涉及中文的时候,要对file编码进行设置,设置本项目的编码方式:
对IDEA全局文件进行设置,不然上图的设置只是针对当前项目的:
File->Other Setting-> Settings for New Projects 中的File Encodings
(4)在html页面取值并使用。取值方式,例如:#{login.btn}取登陆按钮的文本,然后Web运行环境去取用哪种翻译,取决于当前浏览器设置的默认语言。这样
页面取值demo:
href="javascript: showLoginForm();" th:text="#{login.btn}">
基本原理:
国际化Locale(区域信息对象):LocaleResolver(获取区域信息)
具体见配置类WebMvcAutoConfiguration:
默认的区域信息解析器:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc", name = "locale")
public LocaleResolver localeResolver() {
if (this.mvcProperties
.getLocaleResolver() == WebMvcProperties.LocaleResolver.FIXED) {
return new FixedLocaleResolver(this.mvcProperties.getLocale());
}
AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver localeResolver = new AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver();
localeResolver.setDefaultLocale(this.mvcProperties.getLocale());
return localeResolver;
}
默认的区域信息解析,就是根据请求头携带的信息,确定要用什么多语言去做
(5)编写自己的多语言解析器,提供接口让用户自己去编辑修改语言
package component;
import com.sun.corba.se.spi.resolver.LocalResolver;
import org.apache.tomcat.jni.Local;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver;
import org.thymeleaf.util.StringUtils;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.util.Locale;
/**
* 自己的区域信息解析,用来做多语言翻译的
*/
public class MyLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver {
@Override
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request)
{
String l = request.getParameter("l");
Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(l))
{
String [] split = l.split("_");
locale = new Locale(split[0], split[1]);
}
return locale;
}
@Override
public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale)
{
}
}
(6)最后将自己写的语言解析器组件添加到容器中去:
在我自己的MyMvcConfig配置类中添加:
//向容器中添加我的多语言解析器
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver()
{
return new MyLocaleResolver();
}
(7)运行项目,在登陆页面的地址中添加参数l=??来指定语言,如:
http://localhost:8080/yanru/login?l=en_US指定当前语言是英文,如果login?l=zh_CN,则请求页面将会用中文展示
登陆开发Demo
开发期间使用目标引擎修改页面以后,需要实时生效:
(1)禁用目标引擎的缓存
#禁用模板引擎的缓存
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
(2)页面修改以后Ctrl+F9,重新编译
(3)拦截器登陆检查
步骤:
第一步:编写自己的拦截器组件:
package component;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* function:一个登录的拦截器,用来进行登录检查
* date:2019-1-10 21:21:03
*/
public class LoginHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
//模板方法执行之前
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws ServletException, IOException {
Object user = request.getSession().getAttribute("loginUser");
System.out.println("用户登录了么 user="+user+"@");
if(user == null) //没有登录,返回登录页面
{
request.setAttribute("message", "没有权限请先登录!");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/login.html").forward(request,response); //跳转回登录页面
return false;
}
else //已登录
{
return true;
}
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler,
@Nullable ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, @Nullable Exception ex) throws Exception {
}
}
第二步:将拦拦截器组件添加到容器中:
package com.example.demo.config;
import component.LoginHandlerInterceptor;
import component.MyLocaleResolver;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ViewControllerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter;
//使用 WebMvcConfigurerAdapter 可以用来扩展SprinngMVC的功能,
//但是目测在当前新版本的SpringBoot这个抽象类已经被丢弃了,找到了新的继承类?
@Configuration//标注这是一个配置类
//@EnableWebMvc //标注这是一个SpringMVC的配置类
public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
//浏览器发送 /helloYanru,跳转到helloPage页面
registry.addViewController("/helloYanru").setViewName("helloPage");
}
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurerAdapter webMvcConfigurerAdapter()
{
WebMvcConfigurerAdapter adapter = new WebMvcConfigurerAdapter(){
@Override //现在添加这个注解会编译报错的
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry)
{
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("templates/login");
registry.addViewController("/login.html").setViewName("templates/login");
}
//2019-1-10注册拦截器
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry)
{
//除了登录页面以外的请求都忽略,使得保证用户必须是登录状态才能访问其他页面
//静态资源,已经做好了静态资源映射,不用单独处理拦截,也可以正常访问静态资源
registry.addInterceptor(new LoginHandlerInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**").excludePathPatterns("/login.html","/","/user/login");
}
};
return adapter;
}
//向容器中添加我的多语言解析器
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver()
{
return new MyLocaleResolver();
}
}
第三步:此后用户访问除了登陆以外的页面,都要验证 用户是否已登陆,否则就跳转到登陆页面让他登陆
最后LoginController的实现接手登陆请求:
package com.example.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.thymeleaf.util.StringUtils;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 登录的请求
*/
@Controller
public class LoginController {
//上面这个写法也可以
// @PostMapping(value = "/user/login")
@RequestMapping(value = "/userLogin", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username, @RequestParam("password") String password, Map
{
System.out.println("收到的数据 username="+username+",password="+password+"@");
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(username) && !StringUtils.isEmpty(password))
{
//模拟登录成功
map.put("message", "登录成功!");
session.setAttribute("loginUser", username);
return "redirect:mainPage.html";//redirect防止表单重复提交这句话是重定向到mainPage页面,具体实现能访问mainPage是在 MyMvcConfig的addViewControllers()方法中
}
else
{
map.put("message", "用户名密码错误");
return "login";
}
}
// @RequestMapping(value = "/mainPage")
// public String
}
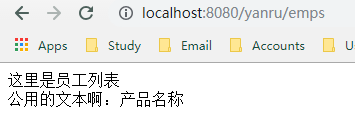
(4)DEMO:开发员工列表
什么是RestfulCRUD:CRUD满足Rest风格
什么是Rest风格?
REST是一种软件架构风格,或者说是一种规范,其强调HTTP应当以资源为中心,并且规范了URI的风格;规范了HTTP请求动作(GET/PUT/POST/DELETE/HEAD/OPTIONS)的使用,具有对应的语义。
分析第一步:URI:/资源名称/资源标识,HTTP请求方式区分对资源CRUD操作
|
|
普通CRUD(URI来区分操作) |
RestfulCRUD |
| 查询 |
getEmp |
emp-GET |
| 添加 |
addEmp?xxx |
emp-POST |
| 修改 |
updateEmp?id=xxx&xx=xxxx |
emp/{id}-PUT |
| 删除 |
deleteEmp?id=1 |
emp/{id}-DELETE |
分析第二步:实验demo的请求架构:
|
|
请求URI |
请求方式 |
| 查询所有员工 |
emps |
GET |
| 查询某个员工 |
emp/{id} |
GET |
| 来到添加页面 |
emp |
GET |
| 添加员工 |
emp |
POST |
| 来到修改页面(查出员工并回显) |
emp/{id} |
GET |
| 修改员工 |
emp |
PUT |
| 删除员工 |
emp/123,123表示员工id |
DELETE |
分析第三步:实现跳转到员工列表
thymeleaf公共页面元素抽取:
抽取公共片段:
引入公共片段:
<div th:insert="~{footer :: copy}">div>
~{template:selector} 模板名,选择器
~{template:fragmentname} 模板名,片段名
实现:
第一步:先定义一个想要公用的片段:
第二步:在另外一个页面,想要复用这个div时定义使用:
运行效果:
其他引入公共片段的方法:
如下总共使用的代码:
...
各自分别的运行效果,是各自的结果div层级效果:
<body>
...
<div>
<footer>
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
footer>
div>
<footer>
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
footer>
<div>
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
div>
body>
总结:
th:insert 将公共片段整个插入到声明引入的元素中
th:replace 将声明引入的元素替换为公共片段
th:include 将被引入的片段内容包含进这个标签中
#############################################################################
后续
PS:
关于Maven常用资源依赖的学习:
什么是WebJars
WebJars以jar包的形式来使用前端的各种框架、组件,如jquery、bootstrap
WebJars将客户端(浏览器)资源(JavaScript,Css等)打成jar包文件,以对资源进行统一依赖管理。WebJars的jar包部署在Maven中央仓库上。
引用webjar资源的方法:
如下,我想引用bootstrap的资源
配置pom.xml文件:
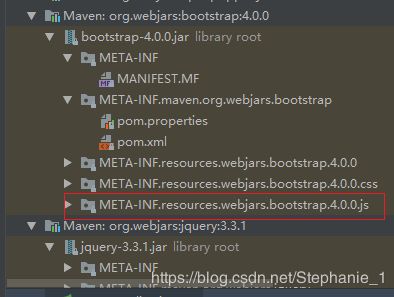
导入成功之后,项目的maven引用资源如图:
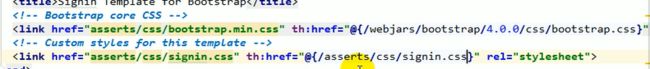
在.html页面引用资源的写法,比如像引用上图红色框的bootstrap4.0.0的js,则写法:
如果既要引用bootstrap样式又要使用自己的样式,写法:
PS:
IDEA快捷键:
搜索类:Ctrl+Shift+Alt+N
查看当前类的父类所有的方法,当子类准备重写一个方法时:Ctrl+O列出所有的父类的方法