安卓中的弹窗界面介绍(AlertDialog、ProgressDialog,PopupWindow)遇到问题继续补充
AlertDialog的使用
介绍
AlertDialog可以在当前界面弹出一个对话框,这个对话框是置顶于所有的界面元素上,可以屏蔽掉其他控件的交互能力,在代码中使用灵活简单。
功能
- 基本使用(设置标题,内容,自定义内容区域)
- 让Dialog铺满屏幕
- 在自定义Dialog上弹出软键盘
- 保持Dialog不退出
- 自定义Dialog的介绍
推荐
这里推荐一个Git项目,上面提供的比较多的功能:
material-dialogs
基本使用
AlertDialog.Builder builder= new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this);
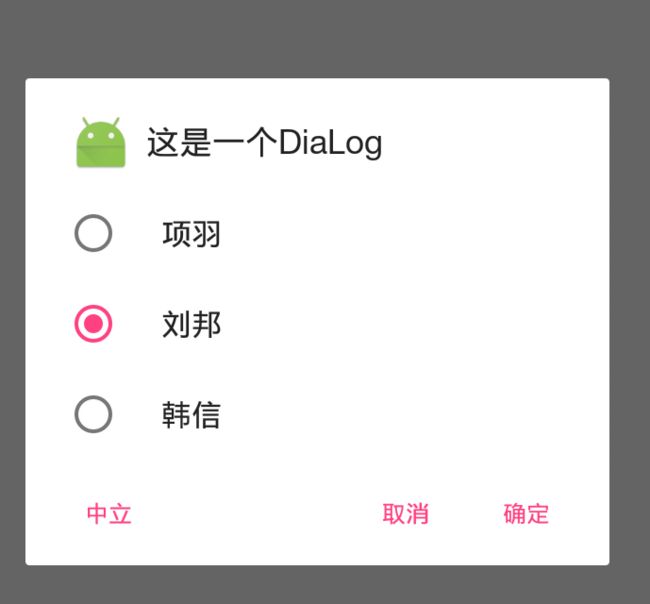
builder.setTitle("这是一个DiaLog");
//设置标题
builder.setMessage("你确定你知道了吗");
//设置内容
builder.setIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher);
//设置头像Icon
builder.show();
/**解释说明:
AlertDialog是通说Builder构建者模式来创建的,其中使用builder来创建Dialog,
通过show()方法展示*/
添加按钮
上面都是简单使用,在弹出框上还可以添加事件按钮,一共可以监听四种事件
在上面基础上添加在builder.show()之前
//添加一个确定按钮,打印log发现是 i=-1
builder.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) {
Log.d("Main","用户点击了确定按钮");
Log.d("Main","用户点击了确定按钮"+i);
}
});
//添加一个取消按钮,打印log 发现是 i=-2
builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) {
Log.d("Main","用户点击了取消按钮");
Log.d("Main","用户点击了取消按钮"+i);
}
});
//添加一个中立按钮,打印log,发现是 i=-3
builder.setNeutralButton("中立", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) {
Log.d("Main","用户点击了中立");
Log.d("Main","用户点击了中立"+i);
}
});
//这个方法是监听当用户点击了dialog窗体之外的方法,
// dialog.setCancelable(false);如果存在这句话的话,那么这个监听就无效了,
//哪怕用户按回退键
//注意的是,这个监听所指窗体之外也包括了用户按回退键这个动作
builder.setOnCancelListener(new DialogInterface.OnCancelListener() {
@Override
public void onCancel(DialogInterface dialogInterface) {
Log.d("Main","用户点击了视图外面");
}
});
/**你会发现你可以使用好多setNegativeButton,方法来设置按钮,但是最终有效果
最后添加或执行的。这样你就可以根据不同的情况来展示不同的AlertDialog界面了
另外你点了哪一个按钮,那么AlertDialog窗体就会消失*/
修改内容主题部分
当然,那就不能使用setMessage()这个方法了。
第一种:展示列表内容
builder.setItems(ss, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) {
Log.d("Main","点击了内容区域");
Log.d("Main","点击了"+i); //会发现下角标是从0、1、2开始变化的
}
});
//说明这里的ss其实: private String [] ss = {"项羽","刘邦","韩信"};
展示单选框内容
builder.setSingleChoiceItems(ss, 1, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) {
Log.d("Main","最后确定的是"+i);
//这个的特色是选中之后,dialog并不会消失,但是会确定i,用来定位的。
}
});
//这个是带有单选框的,参数二是默认选中哪一个,比如1就是默认选中1位置的
展示复选框内容
builder.setMultiChoiceItems(ss, dd, new DialogInterface.OnMultiChoiceClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i, boolean b) {
Log.d("Main",""+dialogInterface);
Log.d("Main",""+i);
Log.d("Main",""+b);
}
//这里面参数二是默认选中哪几项,是一个Boolean类型的数组
//当用户改变一个item 的条目的时候,就会走一遍监听,将改变的那一个item的位置i以及变化变化之后的
//状态true 或者 false 都可以知道
//前面的ss有多长,那么dd就应该有多长,要不然就会存在数组越界
});
//附上数组dd: private boolean []dd ={true,false,true};
使用自定义内容区域
如果上面的内容还不是能过满足你,可以使用自己定义布局样式
首先准备一个布局:
其次在show()方法执行之前调用这个方法:
builder.setView(R.layout.sd);
***这里注意的是,在AlertDialog展示的内容区域,只能放一个内容,要不然就会出问题的***,
如何让dialog从底部弹出
需要注意的是,前面的都可以通过builder来完成,但是这个需要通过AlertDialog来完成,
其实,可以是在builder的基础上,新建一个AlertDialog(也就是说,你在builder.create方法之后在调用builder修改属性,对于生成的dialog是没有意义的,没有效果),因为你同时调用builder.show()还有dialog.show(),你会发现,两个窗体都会出现,谁先调用谁现出来,但是都会出来。当然了,AlertDialog 对象有许多值是不能设置的,是要builder来完成基础的搭建,并且builder也不能完成许多操作,比如调用dismiss()方法,还比如下面的,让dialog从底部弹出,这种修改窗体的。
/*介绍了这么多,其实最简单来讲:你前面构建了一个builder,然后你也得到了一个dialog对象,但是你最后在使用的时候使用builder.show(),那么最后展示出来的是builder配置的样式,和dialog配置的一点关系没有/
AlertDialog mDialog = builder.create(); //得到一个新建的AlertDialog窗体对象
Window window = mDialog.getWindow();
window.setGravity(Gravity.BOTTOM);
window.setWindowAnimations(R.style.mydialog);
mDialog.setCanceledOnTouchOutside(true);
mDialog.show();
这里引用了style格式文件,
进入时候动画,根据具体需求来写,这里只是例子罢了
退出时候动画
让Dialog和屏幕一样宽
在使用AlertDialog时候很大情况不仅需要从底部弹出,还希望的是要铺满全屏,先看几张效果图:
(1)使用 alertDialog.setView(views);

(2)alertDialog.setView(views,40,40,40,40);
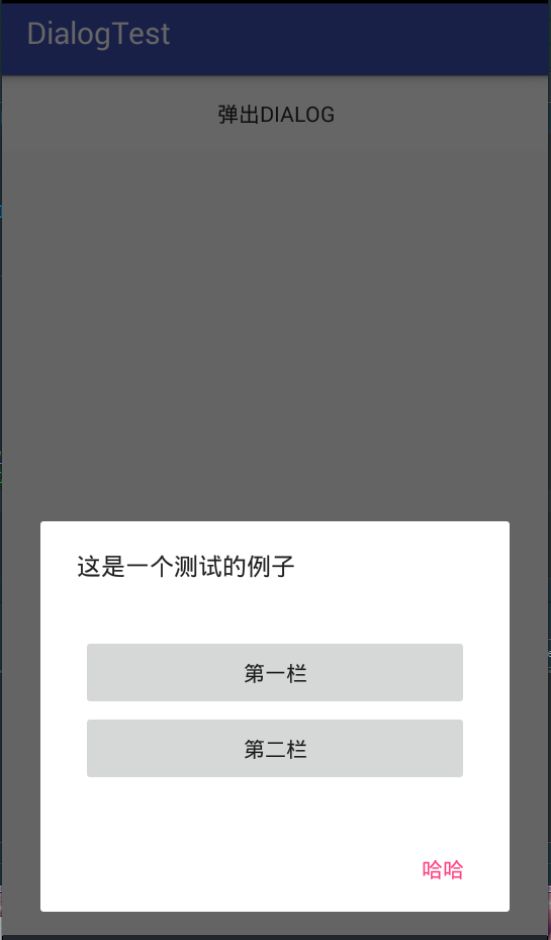
发现我在布局的时候,确实是让其match_parent了,但是展示出来却没有效果,从网上找了代码如下:
View views = LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.myitem,null,false);
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this);
builder.setMessage("这是一个测试的例子");
builder.setNegativeButton("哈哈", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"点击了哈哈",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
builder.setView(views);//也可以展示出来
AlertDialog alertDialog = builder.create();
Window window = alertDialog.getWindow();
window.setGravity(Gravity.BOTTOM);
window.setWindowAnimations(R.style.mystyle);
WindowManager.LayoutParams lp = window.getAttributes();
lp.width = WindowManager.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT;
lp.height = WindowManager.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
window.setAttributes(lp);
alertDialog.show();
运行发现,还是原样,如图一,没有达到自己想要的结果。
其实,在写代码时候:
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this,R.style.DialogTheme);
给其使用上主题就可以了,
< style name="DialogTheme" parent="@android:style/Theme.Dialog">
< item name="android:windowFrame">@null移除边框
< item name="android:windowNoTitle">true去除顶部标题栏
< item name="android:windowIsTranslucent">true窗体透明
< item name="android:background">@android:color/white背景透明
< item name="android:windowBackground">@android:color/transparent窗体背景透明
< item name="android:windowIsFloating">false窗体是否浮动
< item name="android:backgroundDimEnabled">true背景是否昏暗
< item name="android:backgroundDimAmount">0.6昏暗数量
< /style>
如果上面的还不可以,那么可以使用办法(推荐):
Window window = getWindow();
WindowManager.LayoutParams layoutParams = window.getAttributes();
layoutParams.width = WindowManager.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT;
layoutParams.horizontalMargin = 0;
window.setAttributes(layoutParams);
window.setBackgroundDrawable(new ColorDrawable(Color.TRANSPARENT));
window.getDecorView().setPadding(0,0,0,0);
window.setGravity(Gravity.BOTTOM);
如何在自定义Dialog上弹出软键盘
1、自定义主题-在使用自定义dialog的时候设置
2、自定义dialog-示例
public class MyInfoDialog extends Dialog {
private onClicker monClicker = null; //自定义接口,实现接口回调
private Context context;
public void setMonClicker(onClicker monClicker) {
this.monClicker = monClicker;
}
protected MyInfoDialog(Context context) {
super(context);
this.context = context;
}
public MyInfoDialog(Context context, int themeResId) {
super(context, themeResId);
this.context = context;
}
private EditText myEditText;
private TextView myTextView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.my_info_dialog_input);
myEditText = findViewById(R.id.editText_input_send_dialog);
myTextView = findViewById(R.id.textview_input_send_dialog);
Window window = getWindow();
WindowManager.LayoutParams layoutParams = window.getAttributes();
layoutParams.width = WindowManager.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT;
layoutParams.horizontalMargin = 0;
window.setAttributes(layoutParams);
window.setBackgroundDrawable(new ColorDrawable(Color.TRANSPARENT));
window.getDecorView().setPadding(0,0,0,0);
window.setGravity(Gravity.BOTTOM);
myTextView.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
String input = myEditText.getText().toString().trim();
if (monClicker != null){
monClicker.sendInput(input);
}
dismiss();
}
});
myEditText.setOnEditorActionListener(new TextView.OnEditorActionListener() {
@Override
public boolean onEditorAction(TextView v, int actionId, KeyEvent event) {
InputMethodManager imm = (InputMethodManager) context.getSystemService(Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE);
if (imm.isActive()) {
imm.hideSoftInputFromWindow(v.getWindowToken(), 0);
return false;
}
return false;
}
});
额外注意的是,我集成的是Dialog,并不是AlertDialog,上述代码如果使用AlertDialog,并不能弹出键盘来。
}
}
如何让让dialog不退出
前面知道dialog可以有三个按钮的监听,但是你会发现,当你点击了某一个按钮之后,它就会消失,这是因为:
这里以设置setPositiveButton为例子,
public Builder setPositiveButton(CharSequence text, final OnClickListener listener) {
P.mPositiveButtonText = text;
P.mPositiveButtonListener = listener;
return this;
}
//可以发现:设置的text赋给了mPositiveButteonText,
//设置的监听赋给了mPositiveButtonListener
关键是p:
//这个是在AlertDialog的Builder里面,这是在AlertController中定义的内部类,里面定义了大量的属性
private final AlertController.AlertParams P;
在AlertParams 中有一个方法:
public void apply(AlertController dialog) {
if (mCustomTitleView != null) {
dialog.setCustomTitle(mCustomTitleView);
} else {
if (mTitle != null) {
dialog.setTitle(mTitle);
}
if (mIcon != null) {
dialog.setIcon(mIcon);
}
if (mIconId != 0) {
dialog.setIcon(mIconId);
}
if (mIconAttrId != 0) {
dialog.setIcon(dialog.getIconAttributeResId(mIconAttrId));
}
}
if (mMessage != null) {
dialog.setMessage(mMessage);
}
if (mPositiveButtonText != null) {
dialog.setButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_POSITIVE, mPositiveButtonText, mPositiveButtonListener, null);
}
if (mNegativeButtonText != null) {
dialog.setButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_NEGATIVE, mNegativeButtonText,mNegativeButtonListener, null);
}
if (mNeutralButtonText != null) {
dialog.setButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_NEUTRAL, mNeutralButtonText,mNeutralButtonListener, null);
}
// For a list, the client can either supply an array of items or an
// adapter or a cursor
if ((mItems != null) || (mCursor != null) || (mAdapter != null)) {
createListView(dialog);
}
if (mView != null) {
if (mViewSpacingSpecified) {
dialog.setView(mView, mViewSpacingLeft, mViewSpacingTop, mViewSpacingRight,
mViewSpacingBottom);
} else {
dialog.setView(mView);
}
} else if (mViewLayoutResId != 0) {
dialog.setView(mViewLayoutResId);
}
}
//可以发现,在这个名为应用的方法中,有如下代码
//dialog.setButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_POSITIVE, //mPositiveButtonText, mPositiveButtonListener, null);
//而setButton方法是AlertController中定义的方法,如下:
public void setButton(int whichButton, CharSequence text, DialogInterface.OnClickListener listener, Message msg) {
if (msg == null && listener != null) {
msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(whichButton, listener);
}//如果msg不为空,并且存在听者,可以得到相对应的msg
switch (whichButton) {
//针对与各种不同的按钮whichButton,通过前面的调用,可以发现,
//whichButton就是一些int数值,下面完成赋值操作
case DialogInterface.BUTTON_POSITIVE:
mButtonPositiveText = text;
mButtonPositiveMessage = msg;
break;
case DialogInterface.BUTTON_NEGATIVE:
mButtonNegativeText = text;
mButtonNegativeMessage = msg;
break;
case DialogInterface.BUTTON_NEUTRAL:
mButtonNeutralText = text;
mButtonNeutralMessage = msg;
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Button does not exist");
}
}
上述表示,设置完监听的底层操作,用于接下来的点击事件。
在AlertDialog类中的onCreate方法中,存在:
mAlert.installContent();
在AlertController类中找到这个方法,里面调用了,
setupView();
里面存在:
setupButtons(buttonPanel);
在这个方法中会发现:
mButtonPositive.setOnClickListener(mButtonHandler);
然后,会发现mButtonHandler参数
private final View.OnClickListener mButtonHandler = new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
final Message m;
if (v == mButtonPositive && mButtonPositiveMessage != null) {
m = Message.obtain(mButtonPositiveMessage);
} else if (v == mButtonNegative && mButtonNegativeMessage != null) {
m = Message.obtain(mButtonNegativeMessage);
} else if (v == mButtonNeutral && mButtonNeutralMessage != null) {
m = Message.obtain(mButtonNeutralMessage);
} else {
m = null;
}
if (m != null) {
m.sendToTarget();
} mHandler.obtainMessage(ButtonHandler.MSG_DISMISS_DIALOG, mDialog).sendToTarget();
}
};
//会对于前面准备的相对应的msgt进行判断,然后,要是存在的话,就会调用sendToTarget()方法。异步的方式通知Handler的handleMessage方法执行我们最开始设置的监听器中的onClick()方法。通过发送MSG_DISMISS_DIALOG消息,在Handler的handleMessage()方法中调用dismiss()方法退出dialog,这就是为什么点击按钮之后对话框无条件退出的原因。
总结:dialog的时候一般会调用setPositiveButton()方法传入我们自己的监听器,然后在create()(show会首先执行create)的时候该监听器会被赋值给dialog内部AlertParams对象的mPositiveButtonListener属性,然后该对象的apply()方法将该赋值后的mPositiveButtonListener封装在一个message对象中,
//上述是准备工作,下述是刺激事件,
在按钮被点击之后,就会获取我们先前message对象中封装的监听器,进而调用该监听器的onClick()方法执行我们在setPositiveButton()中传入的监听器逻辑,同时发送消息调用dismiss()方法让对话框消失。
解决办法:
用户输入不满意的话就通过反射修改mShowing的值为false,再手动调用dismiss(),由于mShowing为false,对话框就不会消失
mBuilder.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) {
Field field = null;
try {
field = dialogInterface.getClass().getSuperclass().getSuperclass().getDeclaredField("mShowing");
field.setAccessible(true);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (is != 3) {
try {
field.set(dialogInterface, false);
dialogInterface.dismiss();
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "还不够,现在是" + is, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
is++;
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "还不够,现在是" + is, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
try {
field.set(dialogInterface,true);
dialogInterface.dismiss();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
通过上述就可以不退出了
注意:
(1)setView和setContentView()两者的区别:
setView()覆盖AlertDialog的Title和Button之间的部分,而setContentView()全部覆盖。
如果不注意这点的话,很容易在使用自定义样式的时候,出现黑框。
自定义AlertDialog,建议这样用,比较简单直接
public class YinSiDialog extends AlertDialog {
public YinSiDialog(Context context) {
super(context);
}
private TextView butongyiText;
private TextView tongyiText;
private WebSettings webSettings;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.dialog_yin_si);
//和Activity一样用
butongyiText = findViewById(R.id.textView_yin_si_butongyi);
tongyiText = findViewById(R.id.textView_yin_si_tongyi);
Window window = getWindow();
window.setBackgroundDrawable(new ColorDrawable(Color.TRANSPARENT));//关键代码,要不然无法全部用你的背景
//上面两句是你自定义布局展示出来的关键,没有这句话的话,你的dialog的宽度就是系统默认的,你在布局中设置的宽度,
只是改变内容区域,
initWebView();
setCancelable(false);
butongyiText.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (butongyiInfo != null){
butongyiInfo.clickBtn();
}
dismiss();
}
});
tongyiText.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (tongyiInfo != null){
tongyiInfo.clickBtn();
}
dismiss();
}
});
}
//自定义接口,用来完成接口回调功能
private InfoDialogInterface butongyiInfo;
private InfoDialogInterface tongyiInfo;
public void setButongyiInfo(InfoDialogInterface butongyiInfo) {
this.butongyiInfo = butongyiInfo;
}
public void setTongyiInfo(InfoDialogInterface tongyiInfo) {
this.tongyiInfo = tongyiInfo;
}
}
ProgressDialog的使用
介绍
与AlertDialog类似,都是可以在界面上弹出一个对话框,都能够屏蔽掉其他空间爱你的交互能力。
基本使用
progressDialog = new ProgressDialog(MainActivity.this);
//这是创建方式之一,还有一种,是需要两个参数,参数二是主题,int theme;
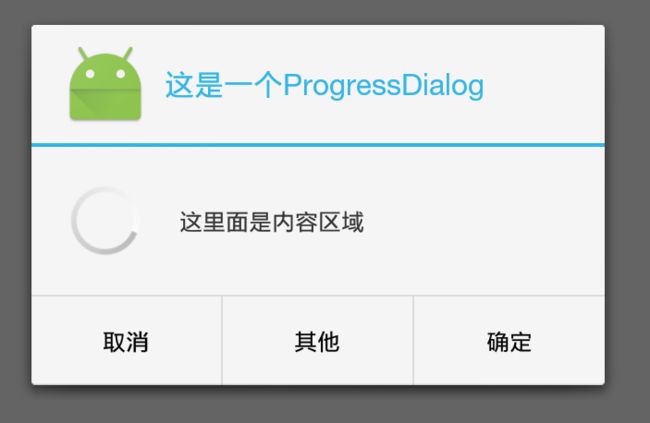
progressDialog.setTitle("这是一个ProgressDialog");
//设置题目
progressDialog.setMessage("这里面是内容区域");
//设置内容区域
progressDialog.setIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher);
//设置Icon
progressDialog.show();
添加按钮
与AlertDialog类似,也是提供了三个按钮的操作,一共可以有四个监听事件
progressDialog.setButton(ProgressDialog.BUTTON_NEGATIVE, "取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) {
Log.d("Main",""+i);//-2
}
});
progressDialog.setButton(ProgressDialog.BUTTON_POSITIVE, "确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) {
Log.d("Main",""+i);//-1
}
});
progressDialog.setButton(ProgressDialog.BUTTON_NEUTRAL, "其他", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) {
Log.d("Main",""+i);//-3
}
});
progressDialog.setOnCancelListener(new DialogInterface.OnCancelListener() {
@Override
public void onCancel(DialogInterface dialogInterface) {
Log.d("Main","点击了空白区域");
}
});
//上述四个动作一点,progressDialog也是消失
//除非设置progressDialog.setCancelable(false);当然设置这个属性,表示的是
//针对于点击空白处和回退键处无效了,那么点击三个按钮还是一样会隐藏dialog窗体
改变中间显示内容
可以根据不同的style确定不同的style
progressDialog.setProgressStyle(ProgressDialog.STYLE_HORIZONTAL);
//会展示一个条形状
progressDialog.setProgressStyle(ProgressDialog.STYLE_SPINNER);
//就是默认的,不断转圈的样式()就是图一的样式
看看ProgressDialog.SYTLE_HORIZONTAL是什么??
通过上面,你会发现,类似于下载的那个progress,
在show()方法之前,可以
progressDialog.setIndeterminate(false);
//这样就可以保证可以修改进度了
在show方法之后可以调用:
progressDialog.setProgress(10);
//改变进度条的样式
// 通过下面方法可以改变进度条的颜色。progressDialog.setProgressDrawable(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.ss));
PopupWindow的使用
介绍
其实AlertDialog使用起来已经比较方便了,但是其 有一个致命的缺点,就是不能随意的设置弹出位置,当然,你也可以通过设置弹出的某些属性完成,但肯定不方便,所以PopupWindow推出使用.
创建PopupWindow
一共有四种方法创建PopUpWindow
//方法一:
public PopupWindow (Context context)
//方法二:
public PopupWindow(View contentView)
//方法三:
public PopupWindow(View contentView, int width, int height)
//方法四:
public PopupWindow(View contentView, int width, int height, boolean focusable)
---------------------
作者:启舰
来源:CSDN
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/harvic880925/article/details/49272285
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!
系统提供四种方法,官产方法四,其参数最全,表明PopupWindow在使用过程中最关键的四部分
contentView 你要设置给PopupWindow使其显示的内容
width 与 height 必须设置的,要不然PopupWindow无法显示
focusable 是否可以接受点击
用法
PopupWindow popupWindow = new PopupWindow(MainActivity.this);
//填充出弹出的View
View pop_view = getLayoutInflater().inflate(R.layout.pop_up_view,null);
//设置给popupwindow
popupWindow.setContentView(pop_view);
//必须给popupwindow设置大小
popupWindow.setWidth(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT); // 可以设置大小,也可以用这样设定
popupWindow.setHeight(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
//进行展示
popupWindow.showAsDropDown(textView);
//展示出来,参数一是锚点,就是相对于哪一个View来展示,另外你还可以选择三个参数的该方法,
可以通过设置x,y设置偏移量
结果如图一
R.layout.pop_up_view就是设置给PopupWindow的布局,你希望展示什么,就怎么布局

你会发现挺丑的,背景还是黑色的,那么尝试给自己的布局文件:R.layout.pop_up_view ,在根哪里设置
android:background="#FFFFFF",运行效果如下图二

这样就好看多了
如果进行下面配置 popupWindow.setHeight(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
另一种展示出来方式showAtLocation
popupWindow.showAtLocation(textView,Gravity.BOTTOM,0,0);
虽然设置给textview,但是其自动找父布局进行展示,结果如下
注意,上面的popupwindow点击外部不能取消,必须进行下面操作才可以
//但是有一点需要注意的是,你都不能点击外部取消,所以必须进行下面的操作
popupWindow.setBackgroundDrawable(new ColorDrawable(Color.TRANSPARENT));
//设置背景色为透明
//如果你的布局文件设置背景颜色了,那么还是会展示布局的背景颜色,就不再是透明的了
popupWindow.setOutsideTouchable(true);
如果你的布局文件里面没有设置根背景,那么就是透明的,效果如下:

给内容区域添加点击事件
//添加点击事件
TextView textView = pop_view.findViewById(R.id.first_textView);
textView.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"点击了第一个条目",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
popupWindow.dismiss();
}
});
你会发现,添加了popupWindow.dismiss(),因为你点击了相应的控件之后,PopupWindow不会主动dismiss

给PopUpWindows添加动画
1 先定义两个动画,一个是进来动画,一个是出去动画
进来动画
出去动画
写一个主题文件
给PopUpWindows使用
mPopupWindow.setAnimationStyle(R.style.pop_anim);
这样PopUpWindow就可以带有动画了.
给PopupWindows释放内存
可以在Activity的onDestroy中,调用:
if(popUpWindow != null ){
popUpWindow.dismiss();
popUpWindw = null;
}
这样可以避免内存的回收.
##给PopUpWinddows添加遮罩
使用PopupWindows你会发现,只是弹出一个框,但是和Dialog不一样,dialog出了内容区域都是灰色的,所以需要给popUpwindows添加遮罩,完成出了popup内容之外区域的灰色化。
在弹出popup时候,设置当前Window的窗口的灰度,然后popup再铺在上面,完成这个效果,取消popup时候,
也需要在重置回来:
WindowManager.LayoutParams lp = ((Activity)context).getWindow().getAttributes();
lp.alpha = alpha;// 0.0-1.0
((Activity)context).getWindow().setAttributes(lp);
此方法可以用于别的情况下的窗口灰度处理,
方法二:
针对于特殊情况,有一个当前可视区域的全屏View,
可以设置当前view的透明度来实现效果呢!