Spring Cloud系列(十九) Hystrix仪表盘(Finchley.RC2版本)
在之前关于Hystrix的介绍中,多次提到了关于请求命令的度量指标的判断。这些度量指标都是HystrixCommand和HystrixObservableCommand实例在执行过程中记录的重要信息,它们除了在Hystrix断路器实现中使用之外,对于系统运维也有非常大的帮助。这些指标信息会以“滚动时间窗”和“桶”结合的方式进行汇总,并在内存中驻留一段时间,以供内部或外部进行查询使用,Hystrix仪表盘就是这些指标信息的消费者之一。
Spring Cloud 已经整合了Hystrix Dashboard,在Spring Cloud构建一个Hystrix Dashboard很简单,需要四步:
第一步,创建一个标准Spring Boot工程,命令hystrix-dashboard-vFinchley.Rc2。选择依赖
创建项目后的pom.xml
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-actuator
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix-dashboard
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
第二步,为应用主类添加注解@EnableHystrixDashboard,启用Hystrix Dashboard功能。
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableHystrixDashboard
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
第三步,修改配置文件,比如添加端口等,此步非必须。
spring:
application:
name: hystrix-dashboard
server:
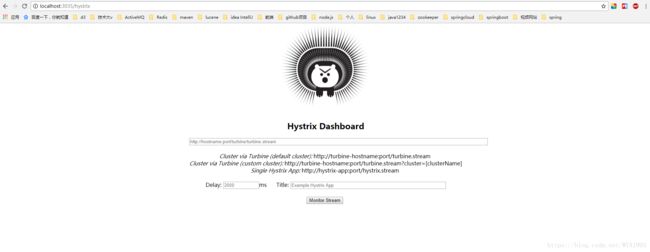
port: 3035到此已经完成了基本配置,启动应用,访问:localhost:3035/hystrix可以看到如下页面。
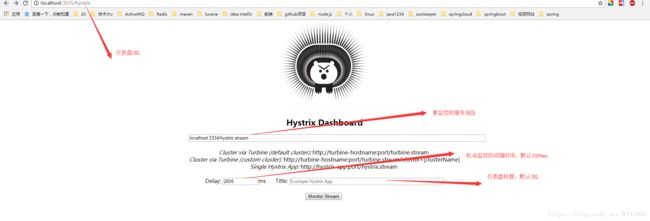
这是Hystrix Dashboard 的监控首页,该页面中并没有具体的监控信息。从页面的文字内容我们可以知道,Hystrix Dashboard 共支持三种不同的监控方式:
- 默认的集群监控:通过URL http://turbine-hostname:port/turine.stream开启,实现对默认集群的监控。
- 指定的集群监控:通过URL http://turbine-hostname:port/turine.stream?cluster=[clusterName]开启,实现对clusterName集群的监控。
- 单体应用的监控:通过URL http://hystrix-app:port/hystrix.stream开启,实现对具体某个服务实例的监控。
前两者需要整合Turbine才能实现对集群的监控,最后一个是对单个服务实例的监控。
对单个服务实例的监控
既然Hystrix Dashboard监控单实例节点需要通过访问实例的/hystrix.stream接口来实现,我们自然需要为服务实例添加这个端点。
第一步:为服务实例添加actuator监控模块依赖和断路器依赖并配置actuator让端点暴露,这里我还是用我之前的项目hystrix-vFinchley.Rc2
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-actuator
#应用名称
spring:
application:
name: hystrix #为服务命名
server:
port: 3334
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:1111/eureka/ #指定服务注册中心位置
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true
instance-id: ${spring.cloud.client.ip-address}:${server.port}
hystrix:
command:
default:
execution:
isolation:
thread:
timeoutInMilliseconds: 2000 #修改Hystrix默认超时时间
第二步,确保在服务实例的主类中已经使用@EnableCircuitBreaker或者@SpringCloudApplication注解开启了断路器功能。
现在重启hystrix-vFinchley.Rc2的实例,输入要监控的服务实例URL
进入页面发现报错
且hystrix-dashboard控制台报404错误
Failed opening connection to http://localhost:3334/hystrix.stream?delay=2000 : 404 : HTTP/1.1 404
Hystrix Dashboard 监控单实例节点需要通过访问实例的/actuator/hystrix.stream接口来实现,自然我们需要为服务实例(被监控服务)添加这个 endpoint,修改服务实例的配置文件,添加对actuator的配置
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: hystrix.stream # 或者'*'此时再次重启,不好意思还是报404错误,需要在服务实例(被监控服务)主类添加代码:
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean hystrixMetricsStreamServlet() {
ServletRegistrationBean registration = new ServletRegistrationBean(new HystrixMetricsStreamServlet());
registration.addUrlMappings("/hystrix.stream");
return registration;
}重新启动服务实例后再次访问,页面变成了Loading,是因为需要有调用任意hysrix接口,不然没有hystrix调用,访问hystrix.stream会一直ping,hystrix监控界面就会一直loading。现在调用hello Api和findById Api 和 hello1 API后
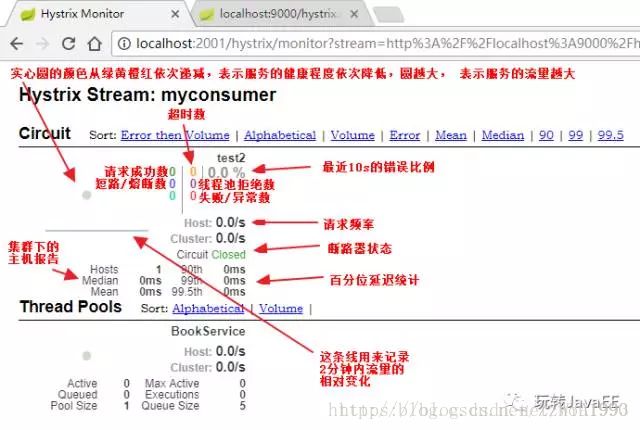
如图,userServiceCommand和hello和UserCommand是命令名。
在监控信息左上部可以看到两个重要的图形信息:一个实心圆和一条曲线。
- 实心圆:其有两种含义。通过颜色的变化代表了实例的监控程度,它的健康度从绿色、黄色、橙色、红色递减。该实心圆的大小会根据实例的请求流量发生变化,流量越大实心圆越大,通过实心圆我们可以在大量的实例中快速发现故障实例和高压力实例。
- 曲线:用来记录2分钟内流量的相对变化,可以通过它来观察流量的上升和下降趋势。
关于其他参数的解释这里盗个图
这里就对单体服务的监控介绍完了。但是在分布式系统中往往有很多服务需要监控,所以下一篇会介绍Turbine和Hystrix Dashboard配合实现对集群的监控。
注意:当使用Hystrix Dashboard监控Spring Cloud Zuul构建的API网关时,ThreadPool信息会一直处于Loading状态,这是由于Zuul默认使用信号量来实现隔离,只有通过Hystrix配置把隔离机制改为线程池的方式才能得以展示。