C Primer Plus 第三章 课后答案
目录
复习题
1.指出下面各种数据使用的合适数据类型(有些可使用多种数据类型):
2.在什么情况下要用long类型的变量代替int类型的变量?
3.使用哪些可移植的数据类型可以获得32位有符号整数?选择的理由是什么?
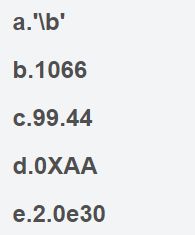
4.指出下列常量的类型和含义(如果有的话):
5.Dottie Cawm编写了一个程序,请找出程序中的错误
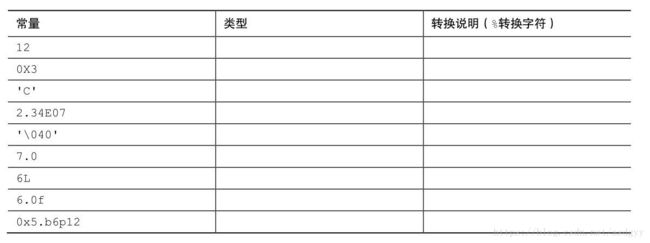
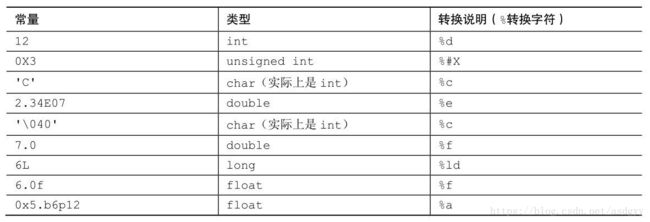
6.写出下列常量在声明中使用的数据类型和在printf()中对应的转换说明:
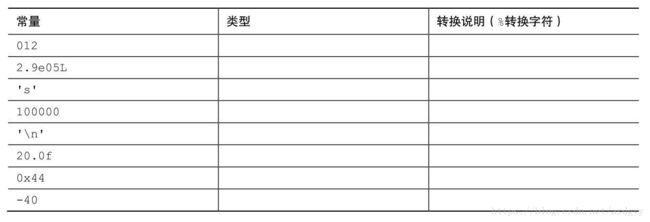
7.写出下列常量在声明中使用的数据类型和在printf()中对应的转换说明(假设int为16位):
8.假设程序的开头有下列声明:
9.假设ch是char类型的变量。分别使用转义序列、十进制值、八进制字符常量和十六进制字符常量把回车字符赋给ch(假设使用ASCII编码值)
10.修正下面的程序(在C中,/表示除以)
11.指出下列转义序列的含义:
编程练习
1.通过试验(即编写带有此类问题的程序)观察系统如何处理整数上溢、浮点数上溢和浮点数下溢的情况
2.编写一个程序,要求提示输入一个ASCII码值(如,66),然后打印输入的字符
3.编写一个程序,发出一声警报,然后打印下面的文本:
4.编写一个程序,读取一个浮点数,先打印成小数点形式,再打印成指数形式。然后,如果系统支持,再打印成p记数法(即十六进制记数法)。按以下格式输出(实际显示的指数位数因系统而异):
5.一年大约有3.156×107秒。编写一个程序,提示用户输入年龄,然后显示该年龄对应的秒数
6.1个水分子的质量约为3.0×10−23克。1夸脱水大约是950克。编写一个程序,提示用户输入水的夸脱数,并显示水分子的数量
7.1英寸相当于2.54厘米。编写一个程序,提示用户输入身高(/英寸),然后以厘米为单位显示身高
8.在美国的体积测量系统中,1品脱等于2杯,1杯等于8盎司,1盎司等于2大汤勺,1大汤勺等于3茶勺。编写一个程序,提示用户输入杯数,并以品脱、盎司、汤勺、茶勺为单位显示等价容量。思考对于该程序,为何使用浮点类型比整数类型更合适?
复习题
1.指出下面各种数据使用的合适数据类型(有些可使用多种数据类型):
a.int short unsigned short
b.float double
c.char
d.int unsigned
2.在什么情况下要用long类型的变量代替int类型的变量?
- 超出了int表示范围的整数
- 如果要处理更大的值,那么使用一种在所有系统上都保证至少是32位的类型,可以提高程序的可移植性
3.使用哪些可移植的数据类型可以获得32位有符号整数?选择的理由是什么?
系统已经定义了情况下:
正好32位:int_32t
至少32位:int_least32_t
运算最快的32位:int_fast32_t
4.指出下列常量的类型和含义(如果有的话):
a.字符型型常量
b.整型常量
c.浮点型常量
d.十六进制整形常量
e.浮点型常量
5.Dottie Cawm编写了一个程序,请找出程序中的错误
include
main
(
float g; h;
float tax, rate;
g = e21;
tax = rate*g;
) #include
int main
{
float g, h;
float tax, rate;
g = 1e21;
tax = rate*g;
return 0;
} 6.写出下列常量在声明中使用的数据类型和在printf()中对应的转换说明:
7.写出下列常量在声明中使用的数据类型和在printf()中对应的转换说明(假设int为16位):
8.假设程序的开头有下列声明:
printf("The odds against the %d were %ld to 1.\n", imate, shot);
printf("A score of %f is not an %c grade.\n", log, grade);
9.假设ch是char类型的变量。分别使用转义序列、十进制值、八进制字符常量和十六进制字符常量把回车字符赋给ch(假设使用ASCII编码值)
ch = '\r'
ch = 13
ch = '015'
ch = '\0xd'
10.修正下面的程序(在C中,/表示除以)
void main(int) / this program is perfect /
{
cows, legs integer;
printf("How many cow legs did you count?\n);
scanf("%c", legs);
cows = legs / 4;
printf("That implies there are %f cows.\n", cows)
}int main(void) / this program is perfect /
{
int cows, legs integer;
printf("How many cow legs did you count?\n);
scanf("%d", legs);
cows = legs / 4;
printf("That implies there are %d cows.\n", cows)
}11.指出下列转义序列的含义:
a.换行符
b.反斜杠
c.双引号
d.制表符
编程练习
1.通过试验(即编写带有此类问题的程序)观察系统如何处理整数上溢、浮点数上溢和浮点数下溢的情况
#include
#include
int main()
{
int UpInt = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
UpInt *= 2;
printf("%d\n", UpInt);
}
float UpFloat = 1e64 * 1e2;
float DownFloat = 1e-64* 1e-2;
printf("%d\n", UpInt);
printf("%f\n", UpFloat);
printf("%f\n", DownFloat);
return 0;
}
//int型上溢为0
//float上溢为#INF
//float下溢为0.000000 2.编写一个程序,要求提示输入一个ASCII码值(如,66),然后打印输入的字符
#include
#include
int main()
{
char input;
printf("Input66: ");
scanf("%d", &input);
printf("%c\n", input);
}
3.编写一个程序,发出一声警报,然后打印下面的文本:
#include
#include
int main()
{
printf("\aStartled by the sudden sound, Sally shouted,\n\"By the Great Pumpkin, what was that!\"");
} 4.编写一个程序,读取一个浮点数,先打印成小数点形式,再打印成指数形式。然后,如果系统支持,再打印成p记数法(即十六进制记数法)。按以下格式输出(实际显示的指数位数因系统而异):
#include
#include
int main()
{
float n;
printf("Enter a floating-point value: ");
scanf("%f", &n);
printf("fixed-point notation:%.6f\n", n);
printf("exponential notation:%.6e\n", n);
printf("p notation:%a\n", n);
} 5.一年大约有3.156×107秒。编写一个程序,提示用户输入年龄,然后显示该年龄对应的秒数
#include
#include
int main()
{
const float t = 3.156e7;
int age;
printf("%e\n", age * t);
} 6.1个水分子的质量约为3.0×10−23克。1夸脱水大约是950克。编写一个程序,提示用户输入水的夸脱数,并显示水分子的数量
#include
#include
int main()
{
const float t = 3e-23;
int n;
printf("Input n:");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("%e\n", n * 950 / t);
}
7.1英寸相当于2.54厘米。编写一个程序,提示用户输入身高(/英寸),然后以厘米为单位显示身高
#include
#include
int main()
{
const float t = 2.54;
float n;
printf("Input n:");
scanf("%f", &n);
printf("%f\n", n / t);
} 8.在美国的体积测量系统中,1品脱等于2杯,1杯等于8盎司,1盎司等于2大汤勺,1大汤勺等于3茶勺。编写一个程序,提示用户输入杯数,并以品脱、盎司、汤勺、茶勺为单位显示等价容量。思考对于该程序,为何使用浮点类型比整数类型更合适?
#include
#include
int main()
{
const float pt = 0.5;
const float gs = 8.0;
const float ts = gs * 2;
const float cs = ts * 3;
printf("Input n:");
float n;
scanf("%f", &n);
printf("pt:%f\n", pt * n);
printf("gs:%f\n", gs * n);
printf("ts:%f\n", ts * n);
printf("cs:%f\n", cs * n);
}