Tomcat7.0源码分析——Session管理分析(上)
前言
对于广大java开发者而言,就J2EE规范中的Session应该并不陌生,我们可以使用Session管理用户的会话信息,最常见的就是拿Session来存放用户登录、身份、权限及状态等信息。对于使用Tomcat作为Web容器的大部分开发人员而言,Tomcat是如何实现Session标记用户和管理Session信息的呢?
概述
Session
Tomcat内部定义了Session和HttpSession这两个会话相关的接口,其类继承体系如图1所示。
图1
Session类继承体系图1中额外列出了Session的类继承体系,这里对他们逐个进行介绍。
Session:Tomcat中有关会话的基本接口规范,图1列出了它定义的主要方法,表1对这些方法进行介绍。
表1 Session接口说明
| 方法 | 描述 |
| getCreationTime()/setCreationTime(time : long) | 获取与设置Session的创建时间 |
| getId()/setId(id : String) | 获取与设置Session的ID |
| getThisAccessedTime() | 获取最近一次请求的开始时间 |
| getLastAccessedTime() | 获取最近一次请求的完成时间 |
| getManager()/setManager(manager : Manager) | 获取与设置Session管理器 |
| getMaxInactiveInterval()/setMaxInactiveInterval(interval : int) | 获取与设置Session的最大访问间隔 |
| getSession() | 获取HttpSession |
| isValid()/setValid(isValid : boolean) | 获取与设置Session的有效状态 |
| access()/endAccess() | 开始与结束Session的访问 |
| expire() | 设置Session过期 |
HttpSession:在HTTP客户端与HTTP服务端提供的一种会话的接口规范,图1列出了它定义的主要方法,表2对这些方法进行介绍。
表2 HttpSession接口说明
| 方法 | 描述 |
| getCreationTime() | 获取Session的创建时间 |
| getId() | 获取Session的ID |
| getLastAccessedTime() | 获取最近一次请求的完成时间 |
| getServletContext() | 获取当前Session所属的ServletContext |
| getMaxInactiveInterval()/setMaxInactiveInterval(interval : int) | 获取与设置Session的最大访问间隔 |
| getAttribute(name : String) /setAttribute(name : String, value : Object) | 获取与设置Session作用域的属性 |
| removeAttribute(name : String) | 清除Session作用域的属性 |
| invalidate() | 使Session失效并解除任何与此Session绑定的对象 |
ClusterSession:集群部署下的会话接口规范,图1列出了它的主要方法,表3对这些方法进行介绍。
表3 ClusterSession接口说明
| 方法 | 描述 |
| isPrimarySession() | 是否是集群的主Session |
| setPrimarySession(boolean primarySession) | 设置集群主Session |
StandardSession:标准的HTTP Session实现,本文将以此实现为例展开。
在部署Tomcat集群时,需要使集群中各个节点的会话状态保持同步,目前Tomcat提供了两种同步策略:
- ReplicatedSession:每次都把整个会话对象同步给集群中的其他节点,其他节点然后更新整个会话对象。这种实现比较简单方便,但会造成大量无效信息的传输。
- DeltaSession:对会话中增量修改的属性进行同步。这种方式由于是增量的,所以会大大降低网络I/O的开销,但是实现上会比较复杂因为涉及到对会话属性操作过程的管理。
Session管理器
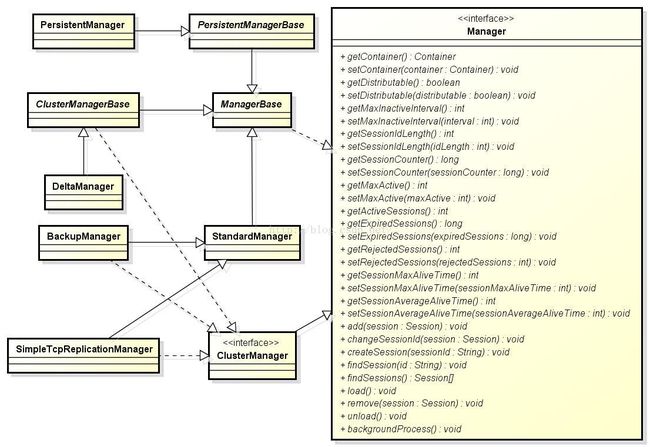
Tomcat内部定义了Manager接口用于制定Session管理器的接口规范,目前已经有很多Session管理器的实现,如图2所示。
图2 Session管理器的类继承体系
对应图2中的内容我们下面逐个描述:
Manager:Tomcat对于Session管理器定义的接口规范,图2已经列出了Manager接口中定义的主要方法,表4详细描述了这些方法的作用。
表4 Manager接口说明
| 方法 | 描述 |
| getContainer() setContainer(container : Container) |
获取或设置Session管理器关联的容器,一般为Context容器 |
| getDistributable() setDistributable(distributable : boolean) |
获取或设置Session管理器是否支持分布式 |
| getMaxInactiveInterval() setMaxInactiveInterval(interval : int) |
获取或设置Session管理器创建的Session的最大非活动时间间隔 |
| getSessionIdLength() setSessionIdLength(idLength : int) |
获取或设置Session管理器创建的Session ID的长度 |
| getSessionCounter() setSessionCounter(sessionCounter : long) |
获取或设置Session管理器创建的Session总数 |
| getMaxActive() setMaxActive(maxActive : int) |
获取或设置当前已激活Session的最大数量 |
| getActiveSessions() | 获取当前激活的所有Session |
| getExpiredSessions() setExpiredSessions(expiredSessions : long) |
获取或设置当前已过期Session的数量 |
| getRejectedSessions() setRejectedSessions(rejectedSessions : int) |
获取或设置已拒绝创建Session的数量 |
| getSessionMaxAliveTime() setSessionMaxAliveTime(sessionMaxAliveTime : int) |
获取或设置已过期Session中的最大活动时长 |
| getSessionAverageAliveTime() setSessionAverageAliveTime(sessionAverageAliveTime : int) |
获取或设置已过期Session的平均活动时长 |
| add(session : Session) remove(session : Session) |
给Session管理器增加或删除活动Session |
| changeSessionId(session : Session) | 给Session设置新生成的随机Session ID |
| createSession(sessionId : String) | 基于Session管理器的默认属性配置创建新的Session |
| findSession(id : String) | 返回sessionId参数唯一标记的Session |
| findSessions() | 返回Session管理器管理的所有活动Session |
| load() unload() |
从持久化机制中加载Session或向持久化机制写入Session |
| backgroundProcess() | 容器接口中定义的为具体容器在后台处理相关工作的实现,Session管理器基于此机制实现了过期Session的销毁 |
ManagerBase:封装了Manager接口通用实现的抽象类,未提供对load()/unload()等方法的实现,需要具体子类去实现。所有的Session管理器都继承自ManagerBase。
ClusterManager:在Manager接口的基础上增加了集群部署下的一些接口,所有实现集群下Session管理的管理器都需要实现此接口。
PersistentManagerBase:提供了对于Session持久化的基本实现。
PersistentManager:继承自PersistentManagerBase,可以在Server.xml的元素下通过配置元素来使用。PersistentManager可以将内存中的Session信息备份到文件或数据库中。当备份一个Session对象时,该Session对象会被复制到存储器(文件或者数据库)中,而原对象仍然留在内存中。因此即便服务器宕机,仍然可以从存储器中获取活动的Session对象。如果活动的Session对象超过了上限值或者Session对象闲置了的时间过长,那么Session会被换出到存储器中以节省内存空间。
StandardManager:不用配置元素,当Tomcat正常关闭,重启或Web应用重新加载时,它会将内存中的Session序列化到Tomcat目录下的/work/Catalina/host_name/webapp_name/SESSIONS.ser文件中。当Tomcat重启或应用加载完成后,Tomcat会将文件中的Session重新还原到内存中。如果突然终止该服务器,则所有Session都将丢失,因为StandardManager没有机会实现存盘处理。
ClusterManagerBase:提供了对于Session的集群管理实现。
DeltaManager:继承自ClusterManagerBase。此Session管理器是Tomcat在集群部署下的默认管理器,当集群中的某一节点生成或修改Session后,DeltaManager将会把这些修改增量复制到其他节点。
BackupManager:没有继承ClusterManagerBase,而是直接实现了ClusterManager接口。是Tomcat在集群部署下的可选的Session管理器,集群中的所有Session都被全量复制到一个备份节点。集群中的所有节点都可以访问此备份节点,达到Session在集群下的备份效果。
为简单起见,本文以StandardManager为例讲解Session的管理。StandardManager是StandardContext的子组件,用来管理当前Context的所有Session的创建和维护。如果你已经阅读或者熟悉了《Tomcat7.0源码分析——生命周期管理》一文的内容,那么你就知道当StandardContext正式启动,也就是StandardContext的startInternal方法(见代码清单1)被调用时,StandardContext还会启动StandardManager。
代码清单1
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// 省略与Session管理无关的代码
// Acquire clustered manager
Manager contextManager = null;
if (manager == null) {
if ( (getCluster() != null) && distributable) {
try {
contextManager = getCluster().createManager(getName());
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error("standardContext.clusterFail", ex);
ok = false;
}
} else {
contextManager = new StandardManager();
}
}
// Configure default manager if none was specified
if (contextManager != null) {
setManager(contextManager);
}
if (manager!=null && (getCluster() != null) && distributable) {
//let the cluster know that there is a context that is distributable
//and that it has its own manager
getCluster().registerManager(manager);
}
// 省略与Session管理无关的代码
try {
// Start manager
if ((manager != null) && (manager instanceof Lifecycle)) {
((Lifecycle) getManager()).start();
}
// Start ContainerBackgroundProcessor thread
super.threadStart();
} catch(Exception e) {
log.error("Error manager.start()", e);
ok = false;
}
// 省略与Session管理无关的代码
}从代码清单1可以看到StandardContext的startInternal方法中涉及Session管理的执行步骤如下:
- 创建StandardManager;
- 如果Tomcat结合Apache做了分布式部署,会将当前StandardManager注册到集群中;
- 启动StandardManager;
代码清单2
@Override
public synchronized final void start() throws LifecycleException {
//省略状态校验的代码if (state.equals(LifecycleState.NEW)) {
init();
} else if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.INITIALIZED) &&
!state.equals(LifecycleState.STOPPED)) {
invalidTransition(Lifecycle.BEFORE_START_EVENT);
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP);
try {
startInternal();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
setState(LifecycleState.FAILED);
throw e;
}
if (state.equals(LifecycleState.FAILED) ||
state.equals(LifecycleState.MUST_STOP)) {
stop();
} else {
// Shouldn't be necessary but acts as a check that sub-classes are
// doing what they are supposed to.
if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.STARTING)) {
invalidTransition(Lifecycle.AFTER_START_EVENT);
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTED);
}
}从代码清单2可以看出启动StandardManager的步骤如下:
- 调用init方法初始化StandardManager;
- 调用startInternal方法启动StandardManager;
StandardManager的初始化
经过上面的分析,我们知道初始化StandardManager的第一步就是调用父类LifecycleBase的init方法,关于此方法已在《Tomcat7.0源码分析——生命周期管理》一文详细介绍,所以我们只需要关心StandardManager的initInternal。StandardManager本身并没有实现initInternal方法,但是StandardManager的父类ManagerBase实现了此方法,其实现见代码清单3。
代码清单3
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
setDistributable(((Context) getContainer()).getDistributable());
// Initialize random number generation
getRandomBytes(new byte[16]);
}阅读代码清单3,我们总结下ManagerBase的initInternal方法的执行步骤:
- 将容器自身即StandardManager注册到JMX(LifecycleMBeanBase的initInternal方法的实现请参考《Tomcat7.0源码分析——生命周期管理》一文);
- 从父容器StandardContext中获取当前Tomcat是否是集群部署,并设置为ManagerBase的布尔属性distributable;
- 调用getRandomBytes方法从随机数文件/dev/urandom中获取随机数字节数组,如果不存在此文件则通过反射生成java.security.SecureRandom的实例,用它生成随机数字节数组。
代码清单4
protected void getRandomBytes(byte bytes[]) {
// Generate a byte array containing a session identifier
if (devRandomSource != null && randomIS == null) {
setRandomFile(devRandomSource);
}
if (randomIS != null) {
try {
int len = randomIS.read(bytes);
if (len == bytes.length) {
return;
}
if(log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Got " + len + " " + bytes.length );
} catch (Exception ex) {
// Ignore
}
devRandomSource = null;
try {
randomIS.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("Failed to close randomIS.");
}
randomIS = null;
}
getRandom().nextBytes(bytes);
}代码清单4中的setRandomFile方法(见代码清单5)用于从随机数文件/dev/urandom中获取随机数字节数组。
代码清单5
public void setRandomFile( String s ) {
// as a hack, you can use a static file - and generate the same
// session ids ( good for strange debugging )
if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED){
randomIS = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedSetRandomFile(s));
} else {
try{
devRandomSource=s;
File f=new File( devRandomSource );
if( ! f.exists() ) return;
randomIS= new DataInputStream( new FileInputStream(f));
randomIS.readLong();
if( log.isDebugEnabled() )
log.debug( "Opening " + devRandomSource );
} catch( IOException ex ) {
log.warn("Error reading " + devRandomSource, ex);
if (randomIS != null) {
try {
randomIS.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("Failed to close randomIS.");
}
}
devRandomSource = null;
randomIS=null;
}
}
}代码清单4中的getRandom方法(见代码清单6)通过反射生成java.security.SecureRandom的实例,并用此实例生成随机数字节数组。
代码清单6
public Random getRandom() {
if (this.random == null) {
// Calculate the new random number generator seed
long seed = System.currentTimeMillis();
long t1 = seed;
char entropy[] = getEntropy().toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < entropy.length; i++) {
long update = ((byte) entropy[i]) << ((i % 8) * 8);
seed ^= update;
}
try {
// Construct and seed a new random number generator
Class clazz = Class.forName(randomClass);
this.random = (Random) clazz.newInstance();
this.random.setSeed(seed);
} catch (Exception e) {
// Fall back to the simple case
log.error(sm.getString("managerBase.random", randomClass),
e);
this.random = new java.util.Random();
this.random.setSeed(seed);
}
if(log.isDebugEnabled()) {
long t2=System.currentTimeMillis();
if( (t2-t1) > 100 )
log.debug(sm.getString("managerBase.seeding", randomClass) + " " + (t2-t1));
}
}
return (this.random);
}根据以上的分析,StandardManager的初始化主要就是执行了ManagerBase的initInternal方法。
StandardManager的启动
调用StandardManager的startInternal方法用于启动StandardManager,见代码清单7。
代码清单7
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Force initialization of the random number generator
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Force random number initialization starting");
generateSessionId();
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Force random number initialization completed");
// Load unloaded sessions, if any
try {
load();
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardManager.managerLoad"), t);
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
}从代码清单7可以看出启动StandardManager的步骤如下:
步骤一 调用generateSessionId方法(见代码清单8)强制初始化随机数生成器;
注意:此处调用generateSessionId方法的目的不是为了生成Session ID,而是为了强制初始化随机数生成器。
代码清单8
protected synchronized String generateSessionId() {
byte random[] = new byte[16];
String jvmRoute = getJvmRoute();
String result = null;
// Render the result as a String of hexadecimal digits
StringBuilder buffer = new StringBuilder();
do {
int resultLenBytes = 0;
if (result != null) {
buffer = new StringBuilder();
duplicates++;
}
while (resultLenBytes < this.sessionIdLength) {
getRandomBytes(random);
random = getDigest().digest(random);
for (int j = 0;
j < random.length && resultLenBytes < this.sessionIdLength;
j++) {
byte b1 = (byte) ((random[j] & 0xf0) >> 4);
byte b2 = (byte) (random[j] & 0x0f);
if (b1 < 10)
buffer.append((char) ('0' + b1));
else
buffer.append((char) ('A' + (b1 - 10)));
if (b2 < 10)
buffer.append((char) ('0' + b2));
else
buffer.append((char) ('A' + (b2 - 10)));
resultLenBytes++;
}
}
if (jvmRoute != null) {
buffer.append('.').append(jvmRoute);
}
result = buffer.toString();
} while (sessions.containsKey(result));
return (result);
}步骤二 加载持久化的Session信息。为什么Session需要持久化?由于在StandardManager中,所有的Session都维护在一个ConcurrentHashMap中,因此服务器重启或者宕机会造成这些Session信息丢失或失效,为了解决这个问题,Tomcat将这些Session通过持久化的方式来保证不会丢失。下面我们来看看StandardManager的load方法的实现,见代码清单9所示。
代码清单9
public void load() throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException {
if (SecurityUtil.isPackageProtectionEnabled()){
try{
AccessController.doPrivileged( new PrivilegedDoLoad() );
} catch (PrivilegedActionException ex){
Exception exception = ex.getException();
if (exception instanceof ClassNotFoundException){
throw (ClassNotFoundException)exception;
} else if (exception instanceof IOException){
throw (IOException)exception;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Unreported exception in load() "
+ exception);
}
} else {
doLoad();
}
}如果需要安全机制是打开的并且包保护模式打开,会通过创建PrivilegedDoLoad来加载持久化的Session,其实现如代码清单10所示。
代码清单10
private class PrivilegedDoLoad
implements PrivilegedExceptionAction {
PrivilegedDoLoad() {
// NOOP
}
public Void run() throws Exception{
doLoad();
return null;
}
} 从代码清单10看到实际负责加载的方法是doLoad,根据代码清单9知道默认情况下,加载Session信息的方法也是doLoad。所以一起来看看doLoad的实现,见代码清单11。代码清单11
protected void doLoad() throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Start: Loading persisted sessions");
// Initialize our internal data structures
sessions.clear();
// Open an input stream to the specified pathname, if any
File file = file();
if (file == null)
return;
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(sm.getString("standardManager.loading", pathname));
FileInputStream fis = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
Loader loader = null;
ClassLoader classLoader = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(file.getAbsolutePath());
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
if (container != null)
loader = container.getLoader();
if (loader != null)
classLoader = loader.getClassLoader();
if (classLoader != null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Creating custom object input stream for class loader ");
ois = new CustomObjectInputStream(bis, classLoader);
} else {
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Creating standard object input stream");
ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("No persisted data file found");
return;
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardManager.loading.ioe", e), e);
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException f) {
// Ignore
}
}
if (bis != null) {
try {
bis.close();
} catch (IOException f) {
// Ignore
}
}
throw e;
}
// Load the previously unloaded active sessions
synchronized (sessions) {
try {
Integer count = (Integer) ois.readObject();
int n = count.intValue();
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Loading " + n + " persisted sessions");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
StandardSession session = getNewSession();
session.readObjectData(ois);
session.setManager(this);
sessions.put(session.getIdInternal(), session);
session.activate();
if (!session.isValidInternal()) {
// If session is already invalid,
// expire session to prevent memory leak.
session.setValid(true);
session.expire();
}
sessionCounter++;
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardManager.loading.cnfe", e), e);
try {
ois.close();
} catch (IOException f) {
// Ignore
}
throw e;
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardManager.loading.ioe", e), e);
try {
ois.close();
} catch (IOException f) {
// Ignore
}
throw e;
} finally {
// Close the input stream
try {
ois.close();
} catch (IOException f) {
// ignored
}
// Delete the persistent storage file
if (file.exists() )
file.delete();
}
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Finish: Loading persisted sessions");
}从代码清单11看到StandardManager的doLoad方法的执行步骤如下:
- 清空sessions缓存维护的Session信息;
- 调用file方法返回当前Context下的Session持久化文件,比如:D:\workspace\Tomcat7.0\work\Catalina\localhost\host-manager\SESSIONS.ser;
- 打开Session持久化文件的输入流,并封装为CustomObjectInputStream;
- 从Session持久化文件读入持久化的Session的数量,然后逐个读取Session信息并放入sessions缓存中。
后记:个人总结整理的《深入理解Spark:核心思想与源码分析》一书现在已经正式出版上市,目前京东、当当、天猫等网站均有销售,欢迎感兴趣的同学购买。
京东:http://item.jd.com/11846120.html
当当:http://product.dangdang.com/23838168.html