面试准备笔记
-
- 网络相关
- 关于TCP/IP3次握手在socket中的实现方式
- 深度学习相关
- 1. differences between avg pool and max pool?
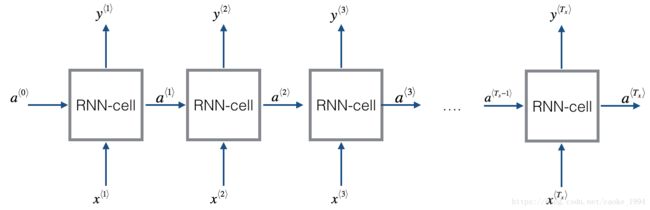
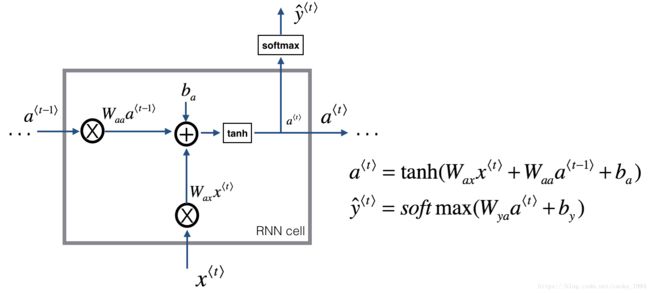
- 2. RNN structrue
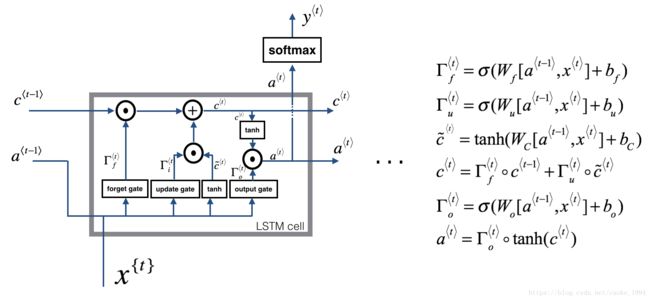
- 3. LSTM structure
- 4. differences between RNN and LSTM
- 5. GAN
- 6. DCGAN
- 7. tensorflow kernel default initializer
- 8. tensorflow conv padding
- 网络相关
网络相关
关于TCP/IP3次握手在socket中的实现方式
- 服务器 bind b i n d -> listen l i s t e n
- 客户端尝试 connect c o n n e c t ,进入阻塞状态,等待服务器返回(第一次握手,客户端发送SYN i 包)
- 服务器 accept a c c e p t 进入阻塞状态,等待客户端状态返回(第二次握手,服务器发送 ACK i+1 和SYN j包)
- 客户端 connect c o n n e c t 返回,(第三次握手,客户端发送ACK j+1 包)
- 服务器accept返回,(此时连接已建立)
深度学习相关
1. differences between avg pool and max pool?
First, we perform pooling to reduce variance, reduce computation complexity(reduces 75% data), extract low level features from neighbourhood.
Max pooling extracts the most important features like edges whereas, average pooling extracts features so smoothly.For image data, I think max pooling is better for extracting the extreme features.
From experience, average pooling prevents the network from learning the image structures such as edges and textures.
In other way, average pooling does not reject all of data and retains more information.
2. RNN structrue
3. LSTM structure
- Update gate i
- Update cell g
- Output gate o
总之,简写便是
4. differences between RNN and LSTM
All RNNs have feedback loops in the recurrent layer. This lets them maintain information in ‘memory’ over time. But, it can be difficult to train standard RNNs to solve problems that require learning long-term temporal dependencies. This is because the gradient of the loss function decays exponentially with time (called the vanishing gradient problem). LSTM networks are a type of RNN that uses special units in addition to standard units. LSTM units include a ‘memory cell’ that can maintain information in memory for long periods of time. A set of gates is used to control when information enters the memory, when it’s output, and when it’s forgotten. This architecture lets them learn longer-term dependencies. GRUs are similar to LSTMs, but use a simplified structure. They also use a set of gates to control the flow of information, but they don’t use separate memory cells, and they use fewer gates.
5. GAN
Generative Adversarial Networks(GAN), with two different neural network.
First network is a traditional neural network called the discriminator to classify the images.
The other called generator, will take random noise as input and transform it using neural network to produce images
strategy
where x∼Pdata x ∼ P d a t a ,are samples from the input data, z∼P(z) z ∼ P ( z ) are the random noise samples
In the original, update G to min the prob of D making the correct choice while update D to max the prob of D making the correct choice
in practice, update G to max the prob of D making the incorrect choice instead;
this trick helps to alleviate problems with the G gradient vanishing when the D is confident;
so, here are two steps:
1. update the G to maximize the prob of D making the incorrect choice on generated data:
2. update the D to maximize the prob of the D making the correct choice on real and generated data:
均匀分布噪声
def sample_noise(batch_size, dim):
"""Generate random uniform noise from -1 to 1.
Inputs:
- batch_size: integer giving the batch size of noise to generate
- dim: integer giving the dimension of the the noise to generate
Returns:
TensorFlow Tensor containing uniform noise in [-1, 1] with shape [batch_size, dim]
"""
random_noise = tf.random_uniform(maxval=1,minval=-1,shape=[batch_size, dim])
return random_noise鉴别网络D
def discriminator(x):
"""Compute discriminator score for a batch of input images.
Inputs:
- x: TensorFlow Tensor of flattened input images, shape [batch_size, 784]
Returns:
TensorFlow Tensor with shape [batch_size, 1], containing the score
for an image being real for each input image.
"""
with tf.variable_scope("discriminator"):
fc1 = tf.layers.dense(inputs=x, units=256, activation=leaky_relu)
fc2 = tf.layers.dense(inputs=fc1, units=256, activation=leaky_relu)
logits = tf.layers.dense(inputs=fc2, units=1)
return logits生成网络G
def generator(z):
"""Generate images from a random noise vector.
Inputs:
- z: TensorFlow Tensor of random noise with shape [batch_size, noise_dim]
Returns:
TensorFlow Tensor of generated images, with shape [batch_size, 784].
"""
with tf.variable_scope("generator"):
fc1 = tf.layers.dense(inputs=z, units=1024, activation=tf.nn.relu)
fc2 = tf.layers.dense(inputs=fc1, units=1024, activation=tf.nn.relu)
# TanH (To restrict the output to be [-1,1])
img = tf.layers.dense(inputs=fc2, units=784, activation=tf.nn.tanh)
return img定义损失函数(极大似然函数)
def gan_loss(logits_real, logits_fake):
"""Compute the GAN loss.
Inputs:
- logits_real: Tensor, shape [batch_size, 1], output of discriminator
Log probability that the image is real for each real image
- logits_fake: Tensor, shape[batch_size, 1], output of discriminator
Log probability that the image is real for each fake image
Returns:
- D_loss: discriminator loss scalar
- G_loss: generator loss scalar
"""
true_labels = tf.ones_like(logits_fake)
# DISCRIMINATOR loss has 2 parts: how well it classifies real images and how well it
# classifies fake images.
real_image_loss = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits_real, labels=true_labels)
fake_image_loss = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits_fake, labels=1-true_labels)
# Combine and average losses over the batch
D_loss = real_image_loss + fake_image_loss
D_loss = tf.reduce_mean(D_loss)
# GENERATOR is trying to make the discriminator output 1 for all its images.
# So we use our target label vector of ones for computing generator loss.
G_loss = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits_fake, labels=true_labels)
# Average generator loss over the batch.
G_loss = tf.reduce_mean(G_loss)
return D_loss, G_loss优化函数 optimization o p t i m i z a t i o n
def get_solvers(learning_rate=1e-3, beta1=0.5):
"""Create solvers for GAN training.
Inputs:
- learning_rate: learning rate to use for both solvers
- beta1: beta1 parameter for both solvers (first moment decay)
Returns:
- D_solver: instance of tf.train.AdamOptimizer with correct learning_rate and beta1
- G_solver: instance of tf.train.AdamOptimizer with correct learning_rate and beta1
"""
D_solver = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate, beta1=beta1)
G_solver = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate, beta1=beta1)
return D_solver, G_solvercomposing the generator and discriminator
tf.reset_default_graph()
# number of images for each batch
batch_size = 128
# our noise dimension
noise_dim = 96
# placeholder for images from the training dataset
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784])
# random noise fed into our generator
z = sample_noise(batch_size, noise_dim)
# generated images
G_sample = generator(z)
with tf.variable_scope("") as scope:
#scale images to be -1 to 1
logits_real = discriminator(preprocess_img(x))
# Re-use discriminator weights on new inputs
scope.reuse_variables()
logits_fake = discriminator(G_sample)
# Get the list of variables for the discriminator and generator
D_vars = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, 'discriminator')
G_vars = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, 'generator')
# get our solver
D_solver, G_solver = get_solvers()
# get our loss
D_loss, G_loss = gan_loss(logits_real, logits_fake)
# setup training steps
# G_var in D_solver won't update while D_var in D_solver update
D_train_step = D_solver.minimize(D_loss, var_list=D_vars)
G_train_step = G_solver.minimize(G_loss, var_list=G_vars)
D_extra_step = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS, 'discriminator')
G_extra_step = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS, 'generator')trianing the gan
def run_a_gan(sess, G_train_step, G_loss, D_train_step, D_loss, G_extra_step, D_extra_step,\
show_every=250, print_every=50, batch_size=128, num_epoch=10):
"""Train a GAN for a certain number of epochs.
Inputs:
- sess: A tf.Session that we want to use to run our data
- G_train_step: A training step for the Generator
- G_loss: Generator loss
- D_train_step: A training step for the Generator
- D_loss: Discriminator loss
- G_extra_step: A collection of tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS for generator
- D_extra_step: A collection of tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS for discriminator
Returns:
Nothing
"""
# compute the number of iterations we need
max_iter = int(mnist.train.num_examples*num_epoch/batch_size)
for it in range(max_iter):
# every show often, show a sample result
if it % show_every == 0:
samples = sess.run(G_sample)
fig = show_images(samples[:16])
plt.show()
print()
# run a batch of data through the network
minibatch,minbatch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
_, D_loss_curr = sess.run([D_train_step, D_loss], feed_dict={x: minibatch})
_, G_loss_curr = sess.run([G_train_step, G_loss])
# print loss every so often.
# We want to make sure D_loss doesn't go to 0
if it % print_every == 0:
print('Iter: {}, D: {:.4}, G:{:.4}'.format(it,D_loss_curr,G_loss_curr))
print('Final images')
samples = sess.run(G_sample)
fig = show_images(samples[:16])
plt.show()create session
def get_session():
config = tf.ConfigProto()
config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
session = tf.Session(config=config)
return session
with get_session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
run_a_gan(sess,G_train_step,G_loss,D_train_step,D_loss,G_extra_step,D_extra_step)6. DCGAN
Deep Convolution GANs
Discriminator
def discriminator(x):
"""Compute discriminator score for a batch of input images.
Inputs:
- x: TensorFlow Tensor of flattened input images, shape [batch_size, 784]
Returns:
TensorFlow Tensor with shape [batch_size, 1], containing the score
for an image being real for each input image.
"""
with tf.variable_scope("discriminator"):
unflatten = tf.reshape(x, shape=[-1, 28, 28, 1])
conv1 = tf.layers.conv2d(inputs=unflatten, kernel_size=5, strides=1, filters=32 ,activation=leaky_relu)
maxpool1 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=conv1, pool_size=2, strides=2)
conv2 = tf.layers.conv2d(inputs=maxpool1, kernel_size=5, strides=1, filters=64,activation=leaky_relu)
maxpool2 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=conv2, pool_size=2, strides=2)
flatten = tf.reshape(maxpool2, shape=[-1, 1024])
fc1 = tf.layers.dense(inputs=flatten, units=1024, activation=leaky_relu)
logits = tf.layers.dense(inputs=fc1, units=1)
return logitsGenerator
def generator(z):
"""Generate images from a random noise vector.
Inputs:
- z: TensorFlow Tensor of random noise with shape [batch_size, noise_dim]
Returns:
TensorFlow Tensor of generated images, with shape [batch_size, 784].
"""
with tf.variable_scope("generator"):
fc1 = tf.layers.dense(inputs=z, units=1024, activation=tf.nn.relu)
bn1 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(inputs=fc1, training=True)
fc2 = tf.layers.dense(inputs=bn1, units=7*7*128, activation=tf.nn.relu)
bn2 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(inputs=fc2, training=True)
reshaped = tf.reshape(bn2, shape=[-1, 7, 7, 128])
conv_transpose1 = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(inputs=reshaped, filters=64, kernel_size=4, strides=2, activation=tf.nn.relu,
padding='same')
bn3 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(inputs=conv_transpose1, training=True)
conv_transpose2 = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(inputs=bn3, filters=1, kernel_size=4, strides=2, activation=tf.nn.tanh,
padding='same')
img = tf.reshape(conv_transpose2, shape=[-1, 784])
return img7. tensorflow kernel default initializer
The Glorot uniform initializer, also called Xavier uniform initializer. It draws samples from a uniform distribution within [−limit,limit] [ − l i m i t , l i m i t ] where limit=6(fanin+fanout−−−−−−−−−√ l i m i t = 6 ( f a n i n + f a n o u t where fanin f a n i n is the number of input units in the weight tensor and fanout f a n o u t is the number of output units in the weight tensor. Reference: http://jmlr.org/proceedings/papers/v9/glorot10a/glorot10a.pdf
8. tensorflow conv padding
for conv2d
output = (input - filter + stride) // stride # VALID
output = (input + stride - 1) // stride # SAME
for conv2d_transpose
逆向计算,上式output 为输入的x,input shape 为指定的 output_shape 参数