Spring系列-Spring MVC处理请求流程
上一篇文章学习了Spring MVC的加载原理,那接下来,还有其它的一些知识点需要学习。当Spring MVC初始化完之后,是如何进行工作的呢?当Http请求到了我们Web服务后,是怎么样找到对应的Controller进行处理呢,又是怎么样返回给用户页面的呢?今天这篇文章就来学习一下这个流程。
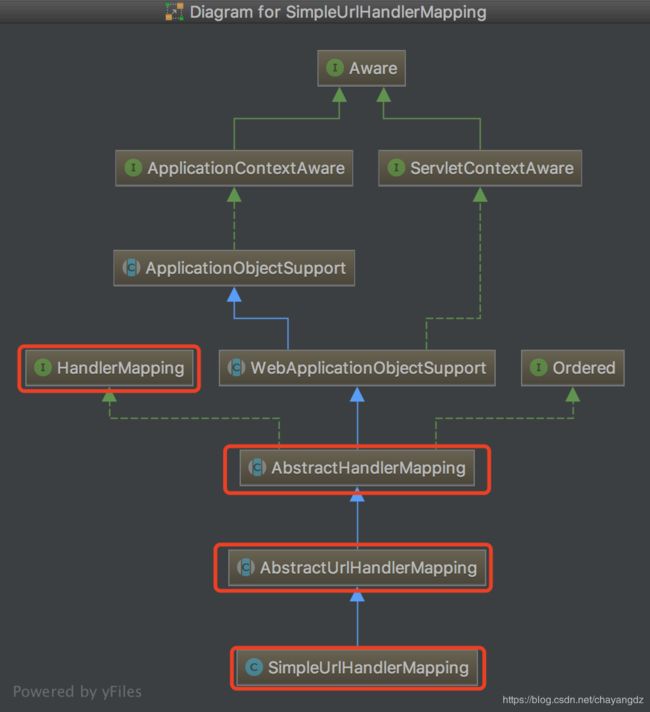
之前分析到,HandlerMapping会持有一系列URL到Controller的映射,Spring MVC提供了一系列HandlerMapping的实现,下面是继承关系:

下面就以SimpleUrlHandlerMapping为例,分析一下HandlerMapping的设计。这一条继承关系是这样的:
SimpleUrlHandlerMapping继承了AbstractUrlHandlerMapping,AbstractUrlHandlerMapping继承了AbstractHandlerMapping,AbstractHandlerMapping实现了HandlerMapping接口。
在HandlerMapping接口中,定义了一个getHandler方法,这个方法就是获取http请求对应的HandlerExecutionChain。下面看下HandlerExecutionChain的定义:
public class HandlerExecutionChain {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(HandlerExecutionChain.class);
private final Object handler;
private HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors;
private List interceptorList;
private int interceptorIndex = -1;
......
}
HandlerExecutionChain中定义了一个Object类型的handler,这个handler就是对应的Controller,还维护了一个拦截器链。
在SimpleUrlHandlerMapping中,定义了一个urlMap,存放映射关系。而且在继承关系中可以看到,实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,所以会有容器的回调,最终会调用initApplicationContext方法:
/**
* Calls the {@link #registerHandlers} method in addition to the
* superclass's initialization.
*/
@Override
public void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
super.initApplicationContext();
registerHandlers(this.urlMap);
}
/**
* Register all handlers specified in the URL map for the corresponding paths.
* @param urlMap Map with URL paths as keys and handler beans or bean names as values
* @throws BeansException if a handler couldn't be registered
* @throws IllegalStateException if there is a conflicting handler registered
*/
protected void registerHandlers(Map urlMap) throws BeansException {
if (urlMap.isEmpty()) {
logger.warn("Neither 'urlMap' nor 'mappings' set on SimpleUrlHandlerMapping");
}
else {
for (Map.Entry entry : urlMap.entrySet()) {
String url = entry.getKey();
Object handler = entry.getValue();
// Prepend with slash if not already present.
if (!url.startsWith("/")) {
url = "/" + url;
}
// Remove whitespace from handler bean name.
if (handler instanceof String) {
handler = ((String) handler).trim();
}
registerHandler(url, handler);
}
}
}
一直顺着代码跟下去,就可以看到这个流程了,SimpleUrlHandlerMapping的注册就是把url和handler作为键值对,放到handlerMap中去。
接下来看下DispatcherServlet对请求的处理,这个处理逻辑是在doService方法中:
/**
* Exposes the DispatcherServlet-specific request attributes and delegates to {@link #doDispatch}
* for the actual dispatching.
*/
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : "";
logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed +
" processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]");
}
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap();
Enumeration attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet")) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
方法会对request设置一些Attribute,然后关键是调用了doDispatch方法:
/**
* Process the actual dispatching to the handler.
* The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order.
* The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters
* to find the first that supports the handler class.
*
All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers
* themselves to decide which methods are acceptable.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure
*/
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
// 先创建一个ModelAndView,用来持有handler处理请求的结果。
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletionWithError(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, err);
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
这个doDispatch算是处理请求的核心方法了,方法一开始先创建一个ModelAndView,后面用来持有handler处理的结果。
getHandler方法,会根据当前的request请求,来决定使用哪个handler,可以看下getHandler详细的执行流程:
/**
* Return the HandlerExecutionChain for this request.
* Tries all handler mappings in order.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @return the HandlerExecutionChain, or {@code null} if no handler could be found
*/
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
"Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Look up a handler for the given request, falling back to the default
* handler if no specific one is found.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @return the corresponding handler instance, or the default handler
* @see #getHandlerInternal
*/
@Override
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.corsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
@Override
protected Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
Object handler = lookupHandler(lookupPath, request);
if (handler == null) {
// We need to care for the default handler directly, since we need to
// expose the PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE for it as well.
Object rawHandler = null;
if ("/".equals(lookupPath)) {
rawHandler = getRootHandler();
}
if (rawHandler == null) {
rawHandler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (rawHandler != null) {
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (rawHandler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) rawHandler;
rawHandler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
validateHandler(rawHandler, request);
handler = buildPathExposingHandler(rawHandler, lookupPath, lookupPath, null);
}
}
if (handler != null && logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Mapping [" + lookupPath + "] to " + handler);
}
else if (handler == null && logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No handler mapping found for [" + lookupPath + "]");
}
return handler;
}
getHandler方法中会遍历handlerMappings列表,然后调用每个HandlerMapping的getHandler方法,获取HandlerExecutionChain,如果当前的HandlerMapping获取成功,则直接返回。HandlerMapping的getHandler入参是个HttpServletRequest,会先调用getHandlerInternal方法获取handler,如果获取到的为空,则返回默认的handler。
还是回到doDispatch方法中继续看,通过getHandler获得handler之后,还会通过getHandlerAdapter方法,获得HandlerAdapter,后面会调用HandlerAdapter的handle方法,这个方法会真正触发对Controller中方法的调用,比如,可以看下SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter中这个方法的实现:
@Override
public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return ((Controller) handler).handleRequest(request, response);
}
@Override
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws Exception {
// Delegate to WebContentGenerator for checking and preparing.
checkRequest(request);
prepareResponse(response);
// Execute handleRequestInternal in synchronized block if required.
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
return handleRequestInternal(request, response);
}
}
}
return handleRequestInternal(request, response);
}
还是回到doDispatch的逻辑中,仔细观察下,其实在调用HandlerAdapter的handle方法之前和之后,还有两个方法的调用,applyPreHandle和applyPostHandle,这两个方法就是执行拦截器中的方法。
之后,会调用processDispatchResult方法,进行结果的处理:
/**
* Handle the result of handler selection and handler invocation, which is
* either a ModelAndView or an Exception to be resolved to a ModelAndView.
*/
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, ModelAndView mv, Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling");
}
}
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
}
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}
这个方法中,关键的是render方法,这个方法是对ModelAndView对象进行处理的。
/**
* Render the given ModelAndView.
* This is the last stage in handling a request. It may involve resolving the view by name.
* @param mv the ModelAndView to render
* @param request current HTTP servlet request
* @param response current HTTP servlet response
* @throws ServletException if view is missing or cannot be resolved
* @throws Exception if there's a problem rendering the view
*/
protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Determine locale for request and apply it to the response.
Locale locale = this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request);
response.setLocale(locale);
View view;
if (mv.isReference()) {
// We need to resolve the view name.
view = resolveViewName(mv.getViewName(), mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() +
"' in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
else {
// No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object.
view = mv.getView();
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " +
"View object in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
// Delegate to the View object for rendering.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
try {
view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" +
getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
在这个方法中,会获取到View视图对象,调用视图对象的render方法,进行视图的呈现。在获取视图对象的时候,会判断如果当前的ModelAndView是个引用的话,就调用resolveViewName方法,对视图名进行解析。
protected View resolveViewName(String viewName, Map model, Locale locale,
HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
for (ViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) {
View view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale);
if (view != null) {
return view;
}
}
return null;
}
接下来再看下视图对象的render方法:
@Override
public void render(Map model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Rendering view with name '" + this.beanName + "' with model " + model +
" and static attributes " + this.staticAttributes);
}
Map mergedModel = createMergedOutputModel(model, request, response);
prepareResponse(request, response);
renderMergedOutputModel(mergedModel, getRequestToExpose(request), response);
}
方法入参包含一个model参数,这个就是我们在业务逻辑中,设置到ModelAndView中去的,render方法会把所有的信息设置到一个Map中,然后通过response,把视图呈现给http客户端。
/**
* Creates a combined output Map (never {@code null}) that includes dynamic values and static attributes.
* Dynamic values take precedence over static attributes.
*/
protected Map createMergedOutputModel(Map model, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Map pathVars = (this.exposePathVariables ?
(Map) request.getAttribute(View.PATH_VARIABLES) : null);
// Consolidate static and dynamic model attributes.
int size = this.staticAttributes.size();
size += (model != null ? model.size() : 0);
size += (pathVars != null ? pathVars.size() : 0);
Map mergedModel = new LinkedHashMap(size);
mergedModel.putAll(this.staticAttributes);
if (pathVars != null) {
mergedModel.putAll(pathVars);
}
if (model != null) {
mergedModel.putAll(model);
}
// Expose RequestContext?
if (this.requestContextAttribute != null) {
mergedModel.put(this.requestContextAttribute, createRequestContext(request, response, mergedModel));
}
return mergedModel;
}
到这里,流程就基本上完成了,其实renderMergedOutputModel还有一些内容,这里就不再分析了。
总结一下,http请求过来时,先到DispatcherServlet的doService方法,然后调用doDispatch方法,doDispatch里面会根据request的请求url,返回对应的handler,然后根据handler获取HandlerAdapter,调用HandlerAdapter的handle方法,处理请求。之后对返回的ModelAndView处理,获取view对象,调用view的render对视图处理,返回到页面。
参考资料:
1.《Spring技术内幕》 计文柯 著