Python路径处理库pathlib
-
- pathlib.PurePath
- 分割路径 parts
- 驱动器 drive
- 根目录 root
- 自动判断驱动器或根目录 anchor
- 所有上级目录列表 parents
- 父目录 parent
- 完整文件名 name
- 文件后缀 suffix
- 文件后缀列表 suffixes
- 文件名 stem
- Unix 路径分隔符表示 as_posix()
- 文件 URI 表示 as_uri()
- 判断绝对路径 is_absolute()
- 拼接路径 joinpath(*other)
- 测试路径符合模式 match(pattern)
- 计算相对路径 relative_to(*other)
- 更改路径名 with_name(name)
- 更改路径后缀 with_suffix(suffix)
- pathlib.Path
- 工作目录 Path.cwd()
- 用户家目录 Path.home()
- 路径信息 stat()
- 更改路径权限 chmod(mode)
- 判断路径存在 exists()
- 展开~完整路径 expanduser()
- 过滤目录 glob(pattern)
- 用户组 group()
- 判断目录 is_dir()
- 判断文件 is_file()
- 判断符号链接 is_symlink()
- 判断套接字 is_socket()
- 判断管道 is_fifo()
- 判断块设备 is_block_device()
- 判断字符设备 is_char_device()
- 遍历目录 iterdir()
- 更改符号链接权限 lchmod(mode)
- 符号链接路径信息 lstat()
- 创建目录 mkdir()
- 打开文件 open()
- 文件拥有者 owner()
- 按字节读取 read_bytes()
- 按字符读取 read_text()
- 重命名 rename(target)
- 跨平台重命名 replace(target)
- 解析绝对路径 resolve(strict=False)
- 过滤相对路径 rglob(pattern)
- 删除空目录 rmdir()
- 判断同一文件 samefile(other_pattern)
- 创建符号链接 symlink_to()
- 创建文件 touch()
- 删除文件 unlink()
- 按字节写入 write_bytes(data)
- 按字符写入 write_text()
- pathlib.PurePath
pathlib 模块提供了文件路径对象抽象,不仅仅是替换 os.path 模块对文件的操作,可以说是路径处理的瑞士军刀。
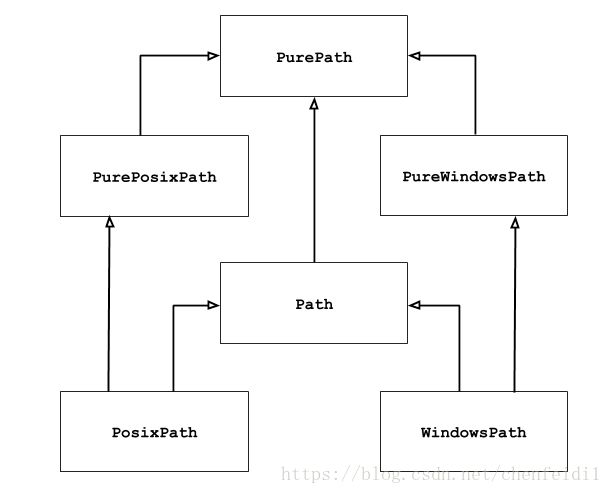
This module offers classes representing filesystem paths with semantics appropriate for different operating systems. Path classes are divided between pure paths, which provide purely computational operations without I/O, and concrete paths, which inherit from pure paths but also provide I/O operations.
其中最常使用的就是 Path 类,因为它与具体系统无关。
pathlib.PurePath
分割路径 parts
类似 os.path.split(),但返回元组。
p = PurePath('/usr/bin/python3').parts # ('/', 'usr', 'bin', 'python3')
PureWindowsPath('c:/Program Files/PSF').parts # ('c:\\', 'Program Files', 'PSF')
驱动器 drive
返回驱动器名称,主要面向 Windows 系统。
PureWindowsPath('c:/Program Files/').drive # 'c:'
PureWindowsPath('/Program Files/').drive # ''
PurePosixPath('/etc').drive # ''
根目录 root
返回路径的根目录,面向 Unix/Linux 系统。
PureWindowsPath('c:/Program Files/').root # '\\'
PureWindowsPath('c:Program Files/').root # ''
PureWindowsPath('//host/share').root # '\\'
PurePosixPath('/etc').root # '/'
自动判断驱动器或根目录 anchor
PureWindowsPath('c:/Program Files/').anchor # 'c:\\'
PureWindowsPath('c:Program Files/').anchor # 'c:'
PurePosixPath('/etc').anchor # '/'
PureWindowsPath('//host/share').anchor # '\\\\host\\share\\'
所有上级目录列表 parents
返回所有上级(祖先)目录列表,[上级目录, 上上级目录, …, 根目录]
PureWindowsPath('c:/foo/bar/setup.py').parents
# [PureWindowsPath('c:/foo/bar'), PureWindowsPath('c:/foo'), PureWindowsPath('c:/')]
父目录 parent
返回父目录
PurePosixPath('/a/b/c/d').parent # PurePosixPath('/a/b/c')
注意相对路径问题:
PurePosixPath('/').parent # PurePosixPath('/')
PurePosixPath('.').parent # PurePosixPath('.')
PurePosixPath('foo/..').parent # PurePosixPath('foo')
在遇到相对路径时,在获取父目录之前调用 Path.resolve() 消除符号链接和 .. 之类表示。
完整文件名 name
返回除驱动器或根目录外完整文件名(带文件名后缀)。
PurePosixPath('my/library/setup.py').name # 'setup.py'
PureWindowsPath('//some/share/setup.py').name # 'setup.py'
PureWindowsPath('//some/share').name # ''
文件后缀 suffix
返回文件扩后缀,没有扩展名则返回空串。
PurePosixPath('my/library/setup.py').suffix # '.py'
PurePosixPath('my/library.tar.gz').suffix # '.gz'
PurePosixPath('my/library').suffix # ''
文件后缀列表 suffixes
当文件有多个后缀,返回文件所有后缀列表;没有则返回空列表。
PurePosixPath('my/library.tar.gar').suffixes # ['.tar', '.gar']
PurePosixPath('my/library.tar.gz').suffixes # ['.tar', '.gz']
PurePosixPath('my/library').suffixes # []
注意,有些软件的版本号也会被当做后缀处理,如:redis-4.0.9.tar.gz。
文件名 stem
返回不带后缀的文件名,有多个后缀则去除最后一个后缀将文件名返回。
PurePosixPath('my/library.tar.gz').stem # 'library.tar'
PurePosixPath('my/library.tar').stem # 'library'
PurePosixPath('my/library').stem # 'library'
Unix 路径分隔符表示 as_posix()
将 Windows 路径分隔符 ‘\’ 改为 Unix 样式 ‘/’。
PureWindowsPath('c:\\windows').as_posix() # 'c:/windows'
文件 URI 表示 as_uri()
返回文件 URI 表示,如果不是绝对路径抛 ValueError 异常。
PurePosixPath('/etc/passwd').as_uri() # 'file:///etc/passwd'
PureWindowsPath('c:/Windows').as_uri() # 'file:///c:/Windows'
判断绝对路径 is_absolute()
判断是否为绝对路径。
PurePosixPath('/a/b').is_absolute() # True
PurePosixPath('a/b').is_absolute() # False
PureWindowsPath('c:/a/b').is_absolute() # True
PureWindowsPath('/a/b').is_absolute() # False
PureWindowsPath('c:').is_absolute() # False
PureWindowsPath('//some/share').is_absolute() # True
拼接路径 joinpath(*other)
类似 os.path.join(),拼接路径。
PurePosixPath('/etc').joinpath('passwd') # PurePosixPath('/etc/passwd')
PurePosixPath('/etc').joinpath(PurePosixPath('passwd')) # PurePosixPath('/etc/passwd')
PurePosixPath('/etc').joinpath('init.d', 'apache2') # PurePosixPath('/etc/init.d/apache2')
测试路径符合模式 match(pattern)
测试路径是否符合 pattern。
PurePath('a/b.py').match('*.py') # True
PurePath('/a/b/c.py').match('b/*.py') # True
PurePath('/a/b/c.py').match('a/*.py') # False
如果 pattern 是绝对路径,则要求路径也是绝对路径才能匹配。
PurePath('/a.py').match('/*.py') # True
PurePath('a/b.py').match('/*.py') # False
匹配是忽略大小写的。
PureWindowsPath('b.py').match('*.PY') # True
计算相对路径 relative_to(*other)
计算两个路径的相对路径,如果不存在则抛 ValueError。
p = PurePosixPath('/etc/passwd')
p.relative_to('/') # PurePosixPath('etc/passwd')
p.relative_to('/etc') # PurePosixPath('passwd')
p.relative_to('/usr')
# Traceback (most recent call last):
# File "", line 1, in
# File "pathlib.py", line 694, in relative_to
# .format(str(self), str(formatted)))
# ValueError: '/etc/passwd' does not start with '/usr'
更改路径名 with_name(name)
返回新路径,更改最后一级路径名称,若原路径没有文件名,则抛 ValueError。
PureWindowsPath('c:/Downloads/pathlib.tar.gz').with_name('setup.py') # PureWindowsPath('c:/Downloads/setup.py')
PureWindowsPath('c:/').with_name('setup.py')
# Traceback (most recent call last):
# File "", line 1, in
# File "/home/antoine/cpython/default/Lib/pathlib.py", line 751, in with_name
# raise ValueError("%r has an empty name" % (self,))
# ValueError: PureWindowsPath('c:/') has an empty name
更改路径后缀 with_suffix(suffix)
返回新路径,更改原路径的后缀。如果原路径没有后缀,则直接添加。
PureWindowsPath('c:/Downloads/pathlib.tar.gz').with_suffix('.bz2') # PureWindowsPath('c:/Downloads/pathlib.tar.bz2')
PureWindowsPath('README').with_suffix('.txt') # PureWindowsPath('README.txt')
pathlib.Path
工作目录 Path.cwd()
@classmethod,返回当前工作目录。
Path.cwd() # PosixPath('/home/antoine/pathlib')
用户家目录 Path.home()
@classmethod,返回当前用户家目录。
Path.home() # PosixPath('/home/antoine')
路径信息 stat()
返回路径信息,类似 os.stat。
p = Path('setup.py')
p.stat().st_size # 956
p.stat().st_mtime # 1327883547.852554
更改路径权限 chmod(mode)
更改路径权限,类似 os.chmod。
p = Path('setup.py')
p.stat().st_mode # 33277
p.chmod(0o444)
p.stat().st_mode # 33060
判断路径存在 exists()
判断路径是否真实存在。
Path('.').exists() # True
Path('setup.py').exists() # True
Path('/etc').exists() # True
Path('nonexistentfile').exists() # False
如果路径指向符号链接,则判断所链接的文件或目录是否存在。
展开~完整路径 expanduser()
展开用户家目录~为绝对路径,类似 os.path.expanduser()。
PosixPath('~/films/Monty Python').expanduser() # PosixPath('/home/eric/films/Monty Python')
过滤目录 glob(pattern)
过滤目录,返回所有匹配文件的生成器。
sorted(Path('.').glob('*.py')) # [PosixPath('pathlib.py'), PosixPath('setup.py'), PosixPath('test_pathlib.py')]
sorted(Path('.').glob('*/*.py')) # [PosixPath('docs/conf.py')]
**表示任意级子目录:
sorted(Path('.').glob('**/*.py'))
# [PosixPath('build/lib/pathlib.py'),
# PosixPath('docs/conf.py'),
# PosixPath('pathlib.py'),
# PosixPath('setup.py'),
# PosixPath('test_pathlib.py')]
用户组 group()
返回路径文件用户组,若 gid 不存在则抛 KeyError。
判断目录 is_dir()
如果路径时目录,返回 True;否则返回 False,可能情况:路径为文件、路径不存在、损坏的符号链接、没有权限等。
所以返回 False 并不代表就一定是文件!
判断文件 is_file()
如果路径是文件返回 True,否则返回 False,情况和 is_dir() 类似。
判断符号链接 is_symlink()
False 情况类似 is_dir()。
判断套接字 is_socket()
False 情况类似 is_dir()。
判断管道 is_fifo()
False 情况类似 is_dir()。
判断块设备 is_block_device()
False 情况类似 is_dir()。
判断字符设备 is_char_device()
False 情况类似 is_dir()。
遍历目录 iterdir()
当路径为目录时,遍历目录。
p = Path('docs')
for child in p.iterdir(): child
# PosixPath('docs/conf.py')
# PosixPath('docs/_templates')
# PosixPath('docs/make.bat')
# PosixPath('docs/index.rst')
# PosixPath('docs/_build')
# PosixPath('docs/_static')
# PosixPath('docs/Makefile')
更改符号链接权限 lchmod(mode)
类似 chmod(),但当路径是符号链接时,更改的是链接的权限,而不是所指向文件的权限。
符号链接路径信息 lstat()
类似 stat(),但当路径是符号链接时,返回的是链接的信息,而不是所指向文件的信息。
创建目录 mkdir()
mkdir(mode=0o777, parents=False, exist_ok=False)
如果设置
mode,则根据进程的 umask 值决定文件的权限。如果创建的目录父目录不存在,则需要设置
parents=True,效果类似mkdir -p,否则抛FileNotFoundError。如果目录已存在,抛
FileExistsError,可以设置exist_ok=True忽略异常。
打开文件 open()
open(mode='r', buffering=-1, encoding=None, errors=None, newline=None),类似内置 open() 方法。
p = Path('setup.py')
with p.open() as f:
f.readline() # '#!/usr/bin/env python3\n'
文件拥有者 owner()
返回文件拥有者,如果 uid 未找到,则抛 KeyError。
按字节读取 read_bytes()
p = Path('my_binary_file')
p.write_bytes(b'Binary file contents') # 20
p.read_bytes() # b'Binary file contents'
按字符读取 read_text()
read_text(encoding=None, errors=None)
p = Path('my_text_file')
p.write_text('Text file contents') # 18
p.read_text() # 'Text file contents'
重命名 rename(target)
Unix 下重命名文件或目录,target 可以是字符串或 path 对象。如果是文件,重命名后内容还是原文件内容。
p = Path('foo')
p.open('w').write('some text') # 9
target = Path('bar')
p.rename(target)
target.open().read() # 'some text'
跨平台重命名 replace(target)
跨平台重命名文件或目录。不同于 rename 只在 Unix 下可用。
解析绝对路径 resolve(strict=False)
返回绝对路径,符号链接和相对路径都会被解析。如果路径不存在且 strict=True,则抛 FileNotFoundError。
p = Path() # PosixPath('.')
p.resolve() # PosixPath('/home/antoine/pathlib')
Path('docs/../setup.py').resolve() # PosixPath('/home/antoine/pathlib/setup.py')
过滤相对路径 rglob(pattern)
类似 glob(),但在 pattern 前添加 **。
sorted(Path().rglob("*.py"))
# [PosixPath('build/lib/pathlib.py'),
# PosixPath('docs/conf.py'),
# PosixPath('pathlib.py'),
# PosixPath('setup.py'),
# PosixPath('test_pathlib.py')]
删除空目录 rmdir()
删除目录,要求目录为空。若非空可使用 shutil.rmtree()。
判断同一文件 samefile(other_pattern)
判断两路径是否执行同一个文件,可以传入字符串或者 path 对象。类似 os.path.samefile() 和 os.path.samestat()。
p = Path('spam')
q = Path('eggs')
p.samefile(q) # False
p.samefile('spam') # True
创建符号链接 symlink_to()
symlink_to(target, target_is_directory=False),如果要链接目标是目录,在 Windows 下必须设置 target_is_directory=True;Unix 下忽略该选项。
p = Path('mylink')
p.symlink_to('setup.py')
p.resolve() # PosixPath('/home/antoine/pathlib/setup.py')
p.stat().st_size # 956
p.lstat().st_size # 8
创建文件 touch()
touch(mode=0o666, exist_ok=True),创建文件,如果文件已存在且 exist_ok=False,则抛 FileExistsError,设置为 True 则忽略(文件修改时间更新到当前时间)。
删除文件 unlink()
只用于删除文件和符号链接,若路径指向目录,请改用调用 rmdir() 或 shutil.rmtree()。
按字节写入 write_bytes(data)
p = Path('my_binary_file')
p.write_bytes(b'Binary file contents') # 20
p.read_bytes() # b'Binary file contents'
按字符写入 write_text()
write_text(data, encoding=None, errors=None)
p = Path('my_text_file')
p.write_text('Text file contents') # 18
p.read_text() # 'Text file contents'
https://docs.python.org/3.6/library/pathlib.html?highlight=path#module-pathlib
https://www.cnblogs.com/sigai/p/8074329.html