java.util.Map接口是JDK1.2开始提供的一个基于键值对的散列表接口,其设计的初衷是为了替换JDK1.0中的java.util.Dictionary抽象类。Dictionary是JDK最初的键值对类,它不可以存储null作为key和value,目前这个类早已不被使用了。目前都是在使用Map接口,它是可以存储null值作为key和value,但Map的key是不可以重复的。其常用的实现类主要有HashMap,TreeMap,ConcurrentHashMap等
HashMap源码解读
目前JDK已经发布到JDK12,主流的JDK版本是JDK8, 但是如果阅读HashMap的源码建议先看JDK7的源码。JDK7和JDK8的源码中HashMap的实现原理大体相同,只不过是在JDK8中做了部分优化。但是JDK8的源码可读性非常差。
HashMap 是一个存储键值对(key-value)映射的散列表,继承于AbstractMap,实现了Map、Cloneable、java.io.Serializable接口,HashMap是线程不安全的,它存储的映射也是无序的。
HashMap的底层主要是基于数组和链表来实现的(JDK8之后又引入了红黑树),数据存储时会通过对key进行哈希操作取到哈希值,然后将哈希值对数组长度取模,得到的值就是该键值对在数组中的索引index值,如果数组该位置没有值则直接将该键值对放在该位置,如果该位置已经有值则将其插入相应链表的位置,JDK8开始为优化链表长度过长导致的性能问题从而引入了红黑树,当链表的长度大于8时会自动将链表转成红黑树。
JDK7中HashMap的源码解读
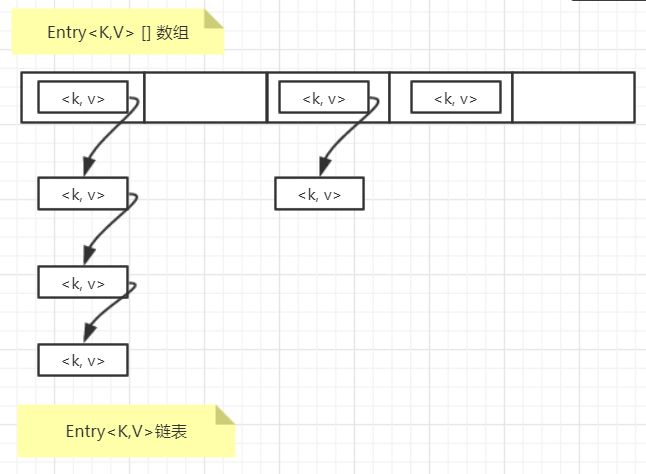
JDK7中HashMap采用Entry数组来存储键值对,每一个键值对组成了一个Entry实体,Entry类实际上是一个单向的链表结构,它具有Next指针,可以连接下一个Entry实体组成链表。
JDK7中HashMap源码中的主要字段
// 数组默认的大小
// 1 << 4,表示1,左移4位,变成10000,即16,以二进制形式运行,效率更高
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;
// 数组最大值
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// 默认的负载因子
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
// 真正存放数据的数组
transient Entry[] table = (Entry[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
HashMap中默认的数组容量为 16,负载因子为 0.75。Map 在使用过程中不断的往里面存放数据,当数量达到了 16 * 0.75 = 12 就需要将当前 16 的容量进行扩容,而扩容这个过程涉及到 rehash、复制数据等操作,所以非常消耗性能。因此通常建议能提前预估 HashMap 的大小最好,尽量的减少扩容带来的性能损耗。
JDK7中HashMap源码中的构造器
/** 默认的初始化容量、默认的加载因子
* Constructs an empty HashMap with the default initial capacity
* (16) and the default load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashMap() { //16 0.75
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
/**
* Constructs an empty HashMap with the specified initial
* capacity and the default load factor (0.75).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative.
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
/** 做了两件事:1、为threshold、loadFactor赋值 2、调用init()
* Constructs an empty HashMap with the specified initial
* capacity and load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) //限制最大容量
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) //检查 loadFactor
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
//真正在做的,只是记录下loadFactor、initialCpacity的值
this.loadFactor = loadFactor; //记录下loadFactor
threshold = initialCapacity; //初始的 阈值threshold=initialCapacity=16
init();
}
/**
* Constructs a new HashMap with the same mappings as the
* specified Map. The HashMap is created with
* default load factor (0.75) and an initial capacity sufficient to
* hold the mappings in the specified Map.
*
* @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public HashMap(Map m) {
this(Math.max((int) (m.size() / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) + 1,
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY), DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
inflateTable(threshold);
putAllForCreate(m);
}
JDK7中HashMap源码中的put方法
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with key, or
* null if there was no mapping for key.
* (A null return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated null with key.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold); //初始化表 (初始化、扩容 合并为了一个方法)
}
if (key == null) //对key为null做特殊处理
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key); //计算hash值
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); //根据hash值计算出index下标
for (Entry e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { //遍历下标为i处的链表
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { //如果key值相同,覆盖旧值,返回新值
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value; //新值 覆盖 旧值
e.recordAccess(this); //do nothing
return oldValue; //返回旧值
}
}
modCount++; //修改次数+1,类似于一个version number
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
/**
* Adds a new entry with the specified key, value and hash code to
* the specified bucket. It is the responsibility of this
* method to resize the table if appropriate.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of put method.
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) { //如果size大于threshold && table在下标为index的地方已经有entry了
resize(2 * table.length); //扩容,将数组长度变为原来两倍
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0; //重新计算 hash 值
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length); //重新计算下标
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); //创建entry
}
/**
* Rehashes the contents of this map into a new array with a
* larger capacity. This method is called automatically when the
* number of keys in this map reaches its threshold.
*
* If current capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY, this method does not
* resize the map, but sets threshold to Integer.MAX_VALUE.
* This has the effect of preventing future calls.
*
* @param newCapacity the new capacity, MUST be a power of two;
* must be greater than current capacity unless current
* capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY (in which case value
* is irrelevant).
*/
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { //状态检查
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; //实例化新的table
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity)); //赋值数组元素到新的数组
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
/**
* Transfers all entries from current table to newTable.
*/
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry e : table) {
while(null != e) {
Entry next = e.next;
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key); //对key进行hash
}
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); //用新的index来取模
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e; //把元素存入新table新的新的index处
e = next;
}
}
}
/**
* Like addEntry except that this version is used when creating entries
* as part of Map construction or "pseudo-construction" (cloning,
* deserialization). This version needn't worry about resizing the table.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of HashMap(Map),
* clone, and readObject.
*/
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry e = table[bucketIndex]; //获取table中存的entry
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); //将新的entry放到数组中,next指向旧的table[i]
size++; //修改map中元素个数
}
JDK7中HashMap源码中的put方法
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null :
* key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise
* it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
*
A return value of {@code null} does not necessarily
* indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also
* possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}.
* The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to
* distinguish these two cases.
*
* @see #put(Object, Object)
*/
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
Entry entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
/**
* Returns the entry associated with the specified key in the
* HashMap. Returns null if the HashMap contains no mapping
* for the key.
*/
final Entry getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
for (Entry e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}
JDK8中HashMap的源码解读
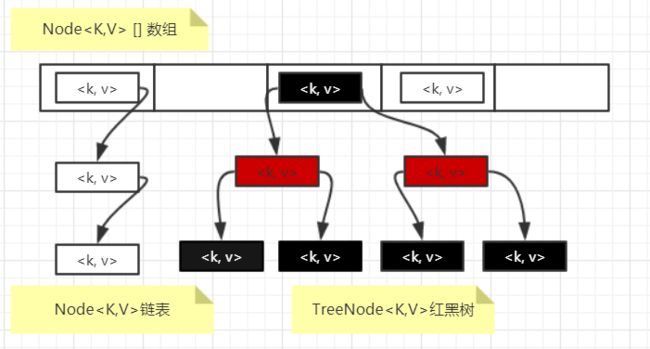
JDK8中HashMap采用Node数组来存储键值对,Node其实就是JDK7中的Entry,只不过是换了一个名字,同样每一个键值对组成了一个Node实体,然后组成链表。当 Hash 冲突严重时,链表会变的越来越长,这样在查询时的效率就会越来越低,JDK8所做的优化就是,当链表的长度达到8的时候会转变成红黑树TreeNode。
JDK8中HashMap源码中的主要字段
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
// 用于判断是否需要将链表转换为红黑树的阈值
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
// 用于判断是否需要将红黑树转换为链表的阈值
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
// 存放数据的数组
transient Node[] table;
JDK8中HashMap源码中的构造器
/**
* Constructs an empty HashMap with the default initial capacity
* (16) and the default load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}
/**
* Constructs an empty HashMap with the specified initial
* capacity and the default load factor (0.75).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative.
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
/**
* Constructs an empty HashMap with the specified initial
* capacity and load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
/**
* Constructs a new HashMap with the same mappings as the
* specified Map. The HashMap is created with
* default load factor (0.75) and an initial capacity sufficient to
* hold the mappings in the specified Map.
*
* @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public HashMap(Map m) {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
putMapEntries(m, false);
}
JDK8中HashMap源码中的put方法
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with key, or
* null if there was no mapping for key.
* (A null return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated null with key.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods. 添加元素
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node[] tab; Node p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) //若table为null
n = (tab = resize()).length; //resize
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) //计算下标i,取出i处的元素为p,如果p为null
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); //创建新的node,放到数组中
else { //若 p!=null
Node e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //若key相同
e = p; //直接覆盖
else if (p instanceof TreeNode) //如果为 树节点
e = ((TreeNode)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); //放到树中
else { //如果key不相同,也不是treeNode
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { //遍历i处的链表
if ((e = p.next) == null) { //找到尾部
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); //在末尾添加一个node
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st //如果链表长度 >= 8
treeifyBin(tab, hash); //将链表转成共黑树
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //若果key相同,直接退出循环
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
/**
* Replaces all linked nodes in bin at index for given hash unless
* table is too small, in which case resizes instead.
*/
final void treeifyBin(Node[] tab, int hash) {
int n, index; Node e;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
resize();
else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
TreeNode hd = null, tl = null;
do {
TreeNode p = replacementTreeNode(e, null);
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else {
p.prev = tl;
tl.next = p;
}
tl = p;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
if ((tab[index] = hd) != null)
hd.treeify(tab);
}
}
/**
* Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in
* accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold.
* Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the
* elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move
* with a power of two offset in the new table.
*
* @return the table
*/
final Node[] resize() {
Node[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length; // 如果 旧数组为null就讲旧的容量看做是0,否则用旧的table长度当做容量
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node[] newTab = (Node[])new Node[newCap]; //创建新的数组
table = newTab; //赋值给table
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
Node loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
JDK8中HashMap源码中的get方法
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null :
* key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise
* it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
*
A return value of {@code null} does not necessarily
* indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also
* possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}.
* The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to
* distinguish these two cases.
*
* @see #put(Object, Object)
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Node e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
/**
* Implements Map.get and related methods.
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @return the node, or null if none
*/
final Node getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node[] tab; Node first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
ConcurrentHashMap源码解读
ConcurrentHashMap是一个线程安全的HashMap实现,ConcurrentHashMap在JDK7和JDK8中的实现差别比较大,JDK7中ConcurrentHashMap是使用Segment数组来存放数据,一个Segment就相当于一个HashMap的数据结构,每个Segment使用一个锁。JDK8之后Segment虽保留,但仅是为了兼容旧版本,已经不再使用,JDK8中ConcurrentHashMap使用和HashMap一样的数据结构Node数组来存储数据,每个数组位置使用一个锁。
JDK7中的ConcurrentHashMap源码解读
JDK7中ConcurrentHashMap的底层Segment组,而Segment其实就是特殊的HashMap,Segment的数据结构跟HashMap一样,同时它继承了ReentrantLock,通过ReentrantLock提供的锁实现了线程的安全。ConcurrentHashMap使用分段锁技术,将数据分成一段一段的存储,每个Segment就是一段,然后给每一段数据配一把锁,当一个线程占用锁访问其中一个段数据的时候,其他段的数据也能被其他线程访问,能够实现并发访问,Segment数组的长度就是ConcurrentHashMap的线程并行级别,Segment数组默认的长度为16,也就是说最多同时可以有16个线程去访问ConcurrentHashMap。segment 数组不能扩容,而是对 segment 数组某个位置的segmen内部的数组HashEntry[] 进行扩容,扩容后容量为原来的 2 倍,该方法没有考虑并发,因为执行该方法之前已经获取了锁。
JDK7中的ConcurrentHashMap源码中的主要字段
// 数组默认大小
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
// 默认的负载因子
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
// 默认线程并发度
static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;
static final int MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY = 2;
static final int MAX_SEGMENTS = 1 << 16;
// 数组最大大小
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
static final int RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK = 2;
JDK7中的ConcurrentHashMap源码中的构造器
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with a default initial capacity (16),
* load factor (0.75) and concurrencyLevel (16).
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL);
}
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with the specified initial capacity,
* and with default load factor (0.75) and concurrencyLevel (16).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation
* performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of
* elements is negative.
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL);
}
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with the specified initial capacity
* and load factor and with the default concurrencyLevel (16).
*
* @param initialCapacity The implementation performs internal
* sizing to accommodate this many elements.
* @param loadFactor the load factor threshold, used to control resizing.
* Resizing may be performed when the average number of elements per
* bin exceeds this threshold.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of
* elements is negative or the load factor is nonpositive
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
this(initialCapacity, loadFactor, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL);
}
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with the specified initial
* capacity, load factor and concurrency level.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation
* performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements.
* @param loadFactor the load factor threshold, used to control resizing.
* Resizing may be performed when the average number of elements per
* bin exceeds this threshold.
* @param concurrencyLevel the estimated number of concurrently
* updating threads. The implementation performs internal sizing
* to try to accommodate this many threads.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is
* negative or the load factor or concurrencyLevel are
* nonpositive.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {
if (!(loadFactor > 0) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0) //参数检查
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (concurrencyLevel > MAX_SEGMENTS) //ConcurrentcyLevel实际上就是最大并发数
concurrencyLevel = MAX_SEGMENTS;
// Find power-of-two sizes best matching arguments
int sshift = 0;
int ssize = 1;
while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) {
++sshift;
ssize <<= 1;
}
this.segmentShift = 32 - sshift;
this.segmentMask = ssize - 1;
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
int c = initialCapacity / ssize;
if (c * ssize < initialCapacity)
++c;
int cap = MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY;
while (cap < c)
cap <<= 1;
// create segments and segments[0]
Segment s0 =
new Segment(loadFactor, (int)(cap * loadFactor),
(HashEntry[])new HashEntry[cap]); //创建一个segment
Segment[] ss = (Segment[])new Segment[ssize]; //创建一个segment数组
UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(ss, SBASE, s0); // ordered write of segments[0] //将s0设置为ss的第一个元素
this.segments = ss; //将ss作为segments
}
JDK7中的ConcurrentHashMap源码中put方法
/**
* Maps the specified key to the specified value in this table.
* Neither the key nor the value can be null.
*
* The value can be retrieved by calling the get method
* with a key that is equal to the original key.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with key, or
* null if there was no mapping for key
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key or value is null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public V put(K key, V value) {
Segment s;
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = hash(key); // 计算Hash值
int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask; //计算下标j
if ((s = (Segment)UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck
(segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegment
s = ensureSegment(j); //若j处有segment就返回,若没有就创建并返回
return s.put(key, hash, value, false); //将值put到segment中去
}
// Segment 中put数据的方法
final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
HashEntry node = tryLock() ? null :
scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value); //如果tryLock成功,就返回null,否则。。。
V oldValue;
try {
HashEntry[] tab = table;
int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash; //根据table数组的长度 和 hash值计算index小标
HashEntry first = entryAt(tab, index); //找到table数组在 index处链表的头部
for (HashEntry e = first;;) { //从first开始遍历链表
if (e != null) { //若e!=null
K k;
if ((k = e.key) == key ||
(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) { //如果key相同
oldValue = e.value; //获取旧值
if (!onlyIfAbsent) { //若absent=false
e.value = value; //覆盖旧值
++modCount; //
}
break; //若已经找到,就退出链表遍历
}
e = e.next; //若key不相同,继续遍历
}
else { //直到e为null
if (node != null) //将元素放到链表头部
node.setNext(first);
else
node = new HashEntry(hash, key, value, first); //创建新的Entry
int c = count + 1; //count 用来记录元素个数
if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) //如果hashmap元素个数超过threshold,并且table长度小于最大容量
rehash(node); //rehash跟resize的功能差不多,将table的长度变为原来的两倍,重新打包entries,并将给定的node添加到新的table
else //如果还有容量
setEntryAt(tab, index, node); //就在index处添加链表节点
++modCount; //修改操作数
count = c; //将count+1
oldValue = null; //
break;
}
}
} finally {
unlock(); //执行完操作后,释放锁
}
return oldValue; //返回oldValue
}
/** 将table的长度变为原来的两倍,重新打包entries,并将给定的node添加到新的table
* Doubles size of table and repacks entries, also adding the
* given node to new table
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void rehash(HashEntry node) {
/*
* Reclassify nodes in each list to new table. Because we
* are using power-of-two expansion, the elements from
* each bin must either stay at same index, or move with a
* power of two offset. We eliminate unnecessary node
* creation by catching cases where old nodes can be
* reused because their next fields won't change.
* Statistically, at the default threshold, only about
* one-sixth of them need cloning when a table
* doubles. The nodes they replace will be garbage
* collectable as soon as they are no longer referenced by
* any reader thread that may be in the midst of
* concurrently traversing table. Entry accesses use plain
* array indexing because they are followed by volatile
* table write.
*/
HashEntry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity << 1;
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
HashEntry[] newTable =
(HashEntry[]) new HashEntry[newCapacity];
int sizeMask = newCapacity - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < oldCapacity ; i++) {
HashEntry e = oldTable[i];
if (e != null) {
HashEntry next = e.next;
int idx = e.hash & sizeMask;
if (next == null) // Single node on list
newTable[idx] = e;
else { // Reuse consecutive sequence at same slot
HashEntry lastRun = e;
int lastIdx = idx;
for (HashEntry last = next;
last != null;
last = last.next) {
int k = last.hash & sizeMask;
if (k != lastIdx) {
lastIdx = k;
lastRun = last;
}
}
newTable[lastIdx] = lastRun;
// Clone remaining nodes
for (HashEntry p = e; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
V v = p.value;
int h = p.hash;
int k = h & sizeMask;
HashEntry n = newTable[k];
newTable[k] = new HashEntry(h, p.key, v, n);
}
}
}
}
int nodeIndex = node.hash & sizeMask; // add the new node
node.setNext(newTable[nodeIndex]);
newTable[nodeIndex] = node;
table = newTable;
}
JDK7中的ConcurrentHashMap源码中get方法
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code key.equals(k)},
* then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise it returns
* {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Segment s; // manually integrate access methods to reduce overhead
HashEntry[] tab;
int h = hash(key);
long u = (((h >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask) << SSHIFT) + SBASE;
if ((s = (Segment)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(segments, u)) != null &&
(tab = s.table) != null) {
for (HashEntry e = (HashEntry) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile
(tab, ((long)(((tab.length - 1) & h)) << TSHIFT) + TBASE);
e != null; e = e.next) {
K k;
if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == h && key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
}
return null;
}
JDK8中的ConcurrentHashMap源码解读
JDK8中的ConcurrentHashMap取消了基于 Segment 的分段锁思想,改用 CAS + synchronized 控制并发操作,锁的粒度变得更小,并发度更高。并且追随JDK8的HashMap底层实现,使用数组+链表+红黑树进行数据存储。
JDK8中的ConcurrentHashMap源码中的主要字段
private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16;
private static final float LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
private static final int MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE = 16;
static final int MOVED = -1; // hash for forwarding nodes //转发节点的hash值
static final int TREEBIN = -2; // hash for roots of trees //树的根节点的hash值
static final int RESERVED = -3; // hash for transient reservations //临时节点的 hash值
static final int HASH_BITS = 0x7fffffff; // usable bits of normal node hash //正常节点的hash值
JDK8中的ConcurrentHashMap源码中构造器
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with the default initial table size (16).
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap() {
}
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size
* accommodating the specified number of elements without the need
* to dynamically resize.
*
* @param initialCapacity The implementation performs internal
* sizing to accommodate this many elements.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of
* elements is negative
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
int cap = ((initialCapacity >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor(initialCapacity + (initialCapacity >>> 1) + 1));
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size based on
* the given number of elements ({@code initialCapacity}) and
* initial table density ({@code loadFactor}).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation
* performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements,
* given the specified load factor.
* @param loadFactor the load factor (table density) for
* establishing the initial table size
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of
* elements is negative or the load factor is nonpositive
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
this(initialCapacity, loadFactor, 1);
}
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size based on
* the given number of elements ({@code initialCapacity}), table
* density ({@code loadFactor}), and number of concurrently
* updating threads ({@code concurrencyLevel}).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation
* performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements,
* given the specified load factor.
* @param loadFactor the load factor (table density) for
* establishing the initial table size
* @param concurrencyLevel the estimated number of concurrently
* updating threads. The implementation may use this value as
* a sizing hint.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is
* negative or the load factor or concurrencyLevel are
* nonpositive
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {
if (!(loadFactor > 0.0f) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (initialCapacity < concurrencyLevel) // Use at least as many bins
initialCapacity = concurrencyLevel; // as estimated threads
long size = (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor);
int cap = (size >= (long)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)size);
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
JDK8中的ConcurrentHashMap源码中的put方法
/**
* Maps the specified key to the specified value in this table.
* Neither the key nor the value can be null.
*
* The value can be retrieved by calling the {@code get} method
* with a key that is equal to the original key.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with {@code key}, or
* {@code null} if there was no mapping for {@code key}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key or value is null
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); //计算hash值
int binCount = 0;
for (Node[] tab = table;;) { //自旋
Node f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) //table==null || table.length==0
tab = initTable(); //就initTable
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) { //若下标 i 处的元素为null
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, //直接用CAS操作,i处的元素
new Node(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin 想emptybin中假如元素的时候,不需要加锁
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) //若下标 i 处的元素不为null,且f.hash==MOVED MOVED为常量值-1
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f); //
else { //如果是一般的节点
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) { //当头部元素不为null,且不需要转换成树时,需要进行同步操作
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) { //若 链表头部hash值 >=0
binCount = 1;
for (Node e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) { //如果key相同
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent) //且不为absent
e.val = value; //旧值覆盖新值
break;
}
Node pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null), { //如果链表遍历完成,还没退出,说明没有相同的key存在,在尾部添加节点
pred.next = new Node(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { //如果f是Tree的节点
Node p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
/**
* Initializes table, using the size recorded in sizeCtl.
*///通过CAS抢sizeCtl,来抢占initTable的资格,其他线程自旋等待,直到table不为null
private final Node[] initTable() {
Node[] tab; int sc;
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin //线程让步,让其他线程优先执行
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node[] nt = (Node[])new Node[n]; //初始化数组
table = tab = nt; //将nt赋值给table
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}
JDK8中的ConcurrentHashMap源码中的get方法
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code key.equals(k)},
* then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise it returns
* {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Node[] tab; Node e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}