人脸关键点检测算法--MTCNN
本文是对MTCNN进行人脸关键点检测和对齐的原理的描述,具体代码请见:https://github.com/Emma0118/preprocessing-images-for-Face-Recognition
一、概述
MTCNN(Multi-task Cascaded Convolutional Networks)是 一种多任务级联卷积神经网络,用以同时处理人脸检测和人脸关键点定位问题。作者认为人脸检测和人脸关键点检测两个任务之间往往存在着潜在的联系,然而大多数方法都未将两个任务有效的结合起来,MTCNN充分利用两任务之间潜在的联系,将人脸检测和人脸关键点检测同时进行,可以实现人脸检测和5个特征点的标定。
目前人脸检测大体分为两个阶段:找出所有可能是人脸的候选区域,从候选区域中选择出最可能是人脸的区域。
MTCNN为了解决人脸识别的两阶段问题,提出三个级联的多任务卷积神经网络(Proposal Network (P-Net)、Refine Network (R-Net)、Output Network (O-Net),每个多任务卷积神经网络均有三个学习任务,分别是人脸分类、边框回归和关键点定位。每一级的输出作为下一级的输入。
二、算法主体流程
1.Image Pyramid(图像金字塔):
MTCNN使用了“Image Pyramid(图像金字塔)”方法,解决不同尺度的人脸的检测。通过把原图按照一定的比例(如0.5),多次等比缩放得到多尺度的图片。
- 由于MTCNN下一阶段使用的P-Net是基于12x12的图片训练出来的,所以MTCNN在本阶段将缩放图片,直至最小边小于或者等于12,由此生成具有不同尺度的图片金字塔。
- 具体实现:先把原图等比缩放`12/minsize`,再按缩放因子`factor`(例如0.5)用上一次的缩放结果不断缩放,直至最短边小于或等于12。(code from detector.py)
# scales for scaling the image
scales = []
# scales the image so that
# minimum size that we can detect equals to
# minimum face size that we want to detect
m = min_detection_size/min_face_size
min_length *= m
factor_count = 0
while min_length > min_detection_size:
scales.append(m*factor**factor_count)
min_length *= factor
factor_count += 1- factor(缩放因子):官方使用了0.709,基于面积每次等比缩放1/2,因此没边缩放sqrt(1/2), 约等于 0.709
- 图片归一化处理,使图片像素分布于[-1, 1]区间内:(x – 127.5)/128
2.Proposal Network (P-Net):
该网络结构主要获得了人脸区域的候选窗口和边界框的回归向量。并用该边界框做回归,对候选窗口进行校准,然后通过非极大值抑制(NMS)来合并高度重叠的候选框。
- 该网络是 Fully Convolutional Network,可以接受任意尺寸的输入。
- 3次卷积、1次池化、经过全卷积层,输出1*1*2的三维矩阵,每个点对应原始输入的每个12x12区域。
- 将不同尺寸的金字塔图像输入到p-net中,最终得到包含box位置信息及其置信度和box的回归系数信息
金字塔图像输入
with torch.no_grad(): output = net(img) probs = output[1].cpu().data.numpy()[0, 1, :, :] offsets = output[0].cpu().data.numpy() # probs: probability of a face at each sliding window # offsets: transformations to true bounding boxes
- 生成box,设置阈值为0.6,得到一系列点,影射回原img,以此点为左上角,向右向下各扩展12pixel,得到12*12的矩形框
- 接下来对一帧图像上检测到的所有12*12矩形框进行nms运算
- 最后得到的所有box会放置在一个number*9的数组里,number表示box的数量,9代表box的坐标信息、score、坐标回归信息[x1、y1、x2、y2、score、reg_x1、reg_y1、reg_x2、reg_y2]
boxes及NMS操作
boxes = _generate_bboxes(probs, offsets, scale, threshold) if len(boxes) == 0: return None keep = nms(boxes[:, 0:5], overlap_threshold=0.5)
- 对box进行坐标修正,修正过程可表示为
new_x1 = x1 + reg_x1 * width_of_box
new_y1 = y1 + reg_y1 * height_of_box
new_x2 = x2 + reg_x2 * width_of_box
new_y2 = y2 + reg_y2 * height_of_box
其中,由于原始窗口和真实窗口的尺寸差异不大,上面等式中reg_x1, reg_x2, reg_y1, reg_y2可以通过线性映射,先做平移,再做变换,学习到。
窗口对精细调整
def calibrate_box(bboxes, offsets): """Transform bounding boxes to be more like true bounding boxes. 'offsets' is one of the outputs of the nets. Arguments: bboxes: a float numpy array of shape [n, 5]. offsets: a float numpy array of shape [n, 4]. Returns: a float numpy array of shape [n, 5]. """ x1, y1, x2, y2 = [bboxes[:, i] for i in range(4)] w = x2 - x1 + 1.0 h = y2 - y1 + 1.0 w = np.expand_dims(w, 1) h = np.expand_dims(h, 1) # this is what happening here: # tx1, ty1, tx2, ty2 = [offsets[:, i] for i in range(4)] # x1_true = x1 + tx1*w # y1_true = y1 + ty1*h # x2_true = x2 + tx2*w # y2_true = y2 + ty2*h # below is just more compact form of this # are offsets always such that # x1 < x2 and y1 < y2 ? translation = np.hstack([w, h, w, h])*offsets bboxes[:, 0:4] = bboxes[:, 0:4] + translation return bboxes
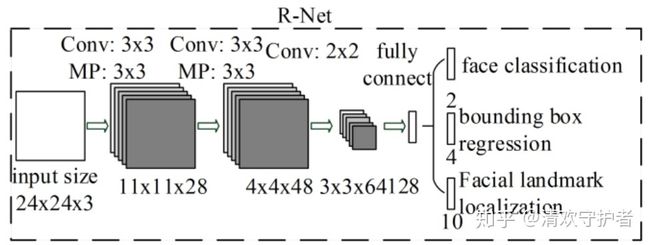
3.R-Net(refine network)
主要通过边界框回归和NMS来去掉false-positive区域。将P-Net最后输出的所有box,resize到24*24后输入R-Net。经过R-Net后,输出与P-Net类似,prob1:box坐标信息与置信度与conv5-2的回归系数信息。根据所得的置信度信息与该层阈值对比,小于阈值的直接drop掉,大于阈值的留下,经过nms、再利用回归系数信息进行精修、rec2square、pad。
stage2
# STAGE 2 img_boxes = get_image_boxes(bounding_boxes, image, size=24) img_boxes = torch.FloatTensor(img_boxes) output = rnet(img_boxes) offsets = output[0].data.numpy() # shape [n_boxes, 4] probs = output[1].data.numpy() # shape [n_boxes, 2] keep = np.where(probs[:, 1] > thresholds[1])[0] bounding_boxes = bounding_boxes[keep] bounding_boxes[:, 4] = probs[keep, 1].reshape((-1,)) offsets = offsets[keep] keep = nms(bounding_boxes, nms_thresholds[1]) bounding_boxes = bounding_boxes[keep] bounding_boxes = calibrate_box(bounding_boxes, offsets[keep]) bounding_boxes = convert_to_square(bounding_boxes) bounding_boxes[:, 0:4] = np.round(bounding_boxes[:, 0:4])
相比P-Net, 这个网络多个一个全连接层,会有更好的抑制false-positive的作用。
4.O-Net(output network
该层比R-Net层又多了一层卷基层,所以处理的结果会更加精细。作用和R-Net层作用一样。但是该层对人脸区域进行了更多的监督,同时还会输出5个地标(landmark)。
- 将R-Net最后输出的所有box,resize到48*48后输入O-Net。经过O-Net后,输出prob1:box坐标信息与置信度、conv6-2的回归系数信息、以及conv6-3的关键点坐标信息。
- conv6-3是number*10的二维数组,number代表box的数量,10则包含了5个关键点信息的x、y坐标信息:[Rx1,Rx2, Rx3, Rx4, Rx5, Ry1, Ry2, Ry3, Ry4, Ry5],此时的坐标为目标框内部的比例,最后影射回原img得到真实的坐标。
- 根据prob1置信度信息与该层阈值对比,小于阈值的直接drop掉,大于阈值的留下,再利用回归系数信息进行精修,最后再进行一次nms。
- 最后,输出一副包含人脸框与人脸关键点的检测图像。
三、算法总结与评价
1.MTCNN继承了人脸关键点检测两阶段的特征,准确度高;;
2.但是由于算法使用图片金字塔,需要多次迭代,耗时较多并且受图片大小影响较大
3.多任务级联的各级网络都需要对输入进行resize,同样增加了运行耗时。
References
1.Joint Face Detection and Alignment using Multi-task Cascaded Convolutional Networks(https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1604/1604.02878.pdf)
2.拒绝调包!且看MTCNN人脸检测推断过程详解!http://www.sfinst.com/?p=1683
3.深度学习人脸关键点检测方法----综述 https://blog.csdn.net/u011995719/article/details/78890333
4.Mutiple Human Face Detection And Reconition Using MTCNN And FaceNet https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0ShchBW4Ve8