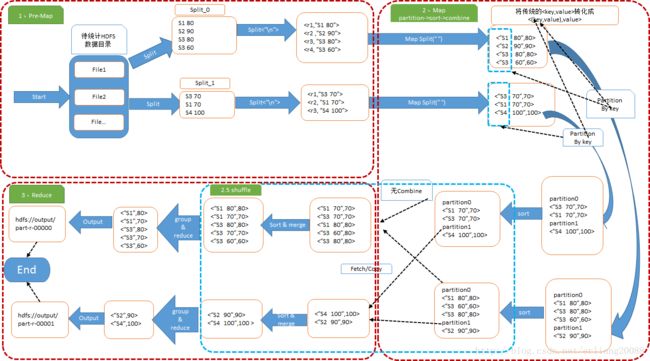
06-天亮大数据系列教程之hadoop二次排序详解
二次排序定义
mapreduce计算过程和输出,都是按key自动排序
如果想要value也要排序输出,即key第一排序,value第二排序的方式。
称为二次排序。二次排序的实现
核心思想
- 将map端输出的(key,value)中的key和value组合成一个新的key,即称newKey,value值保持不变。
- map输出结构为(newKey ,value)=( (key,value),value)
- 按newKey中的key分区,其value排序
实现步骤
- 自定义newKey对应的实体类,重在继承WritableComparable(新引用数据类型)
- 自定义partioner,保证分区的一致性(例题中还是按工号做分区)。重在继承partitioner
- 自定义分组,实现组比较器,保证相同的key(即工号)依然在一个组内。重在继承 WritableComparator/RawComparator
- 完整代码
package com.tianliangedu.core.secondsort;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
// 启动mr的driver类
public class SecondSortV3 {
/**
* 自定义的newKey
*/
public static class KeyPairWritable implements
WritableComparable {
// 组合key,key1是分区key,key2是二次排序key
private String key1;
private int key2;
public KeyPairWritable() {
}
public KeyPairWritable(String key1, int key2) {
this.set(key1, key2);
}
// 一次性将两个key设置成完
public void set(String key1, int key2) {
this.key1 = key1;
this.key2 = key2;
}
// 当map端写出的时候的序列化方法,即map如何将对象写出去,保证与读取的顺序一致
@Override
public void write(DataOutput arg0) throws IOException {
arg0.writeUTF(key1);
arg0.writeInt(key2);
}
// 在reducer读取数据时候的反序列化方法,即reduce如何将对象读取出来,保证与写入的顺序一致
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput arg0) throws IOException {
this.key1 = arg0.readUTF();
this.key2 = arg0.readInt();
}
// 自定义比较器方法,先比较key1,确定分区号。在分区号相同的情况下,去比较key2
// 就不需要单独写一个Comparator了
public int compareTo(KeyPairWritable o) {
int compare = this.key1.compareTo(o.key1);
if (compare != 0) {
return compare;
} else {
// 降序排列,故将o放到前边即可
return Integer.valueOf(o.key2).compareTo(
Integer.valueOf(this.getkey2()));
}
}
public int getkey2() {
return key2;
}
public void setkey2(int key2) {
this.key2 = key2;
}
public String getkey1() {
return key1;
}
public void setkey1(String key1) {
this.key1 = key1;
}
}
// map类,实现map函数
public static class LineProcessMapper extends
Mapper {
// 暂存每个传过来的词的值,省掉重复申请空间
private KeyPairWritable outputKey = new KeyPairWritable();
private IntWritable outputValue = new IntWritable();
// 核心map方法的具体实现,逐个对去处理
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 通过context对象,将map的输出逐个输出
String tempLine = value.toString();
if (tempLine != null && tempLine.trim().length() > 0) {
String[] columnArray = tempLine.split("\\s");
outputKey.set(columnArray[0], Integer.parseInt(columnArray[1]));
outputValue.set(Integer.parseInt(columnArray[1]));
context.write(outputKey, outputValue);
}
}
}
/**
* 自定义分区类,包证同key的记录,如S1,S2等,能映射到相同的reduce端去处理
*/
public static class SecondPartitioner extends
Partitioner {
// 采集默认的HashPartiton实现即可
@Override
public int getPartition(KeyPairWritable key, IntWritable value,
int numPartitions) {
/*
* 默认的实现 (key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numPartitions
* 让key中first字段作为分区依据
*/
return (key.getkey1().hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE)
% numPartitions;
}
}
/**
* 在shuffle阶段的sort全局排序完成后,如何对数据记录进行分组
*/
public static class SecondSortGroupComparator extends WritableComparator {
// 对象KeyPairWritable.class注册,让比较器知道该对象并能够初始化
protected SecondSortGroupComparator() {
super(KeyPairWritable.class, true);
}
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable first, WritableComparable second) {
if (first == null || second == null) {
return 0;
}
KeyPairWritable newKey1 = (KeyPairWritable) first;
KeyPairWritable newKey2 = (KeyPairWritable) second;
// 自定义按原始数据中第一个key分组
return newKey1.getkey1().compareTo(newKey2.getkey1());
}
}
// reduce类,实现reduce函数
public static class SortReducer extends
Reducer {
private Text outputKey = new Text();
// 核心reduce方法的具体实现,逐个去处理
public void reduce(KeyPairWritable keyPair,
Iterable values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 进来时已经排序完成
outputKey.set(keyPair.getkey1());
for (IntWritable val : values) {
context.write(outputKey, val);
}
}
}
// 启动mr的driver方法
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 得到集群配置参数
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
// 参数解析器
GenericOptionsParser optionParser = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args);
String[] remainingArgs = optionParser.getRemainingArgs();
if ((remainingArgs.length != 2)) {
System.err
.println("Usage: yarn jar jar_path main_class_path -D参数列表 " );
System.exit(2);
}
// 设置到本次的job实例中
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "天亮二次排序(标准版)");
// 指定本次执行的主类是WordCount
job.setJarByClass(SecondSortV3.class);
// 指定map类
job.setMapperClass(LineProcessMapper.class);
// 指定partition类
job.setPartitionerClass(SecondPartitioner.class);
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(SecondSortGroupComparator.class);
// 指定reducer类
job.setReducerClass(SortReducer.class);
// 指定job输出的key和value的类型,如果map和reduce输出类型不完全相同,需要重新设置map的output的key和value的class类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(KeyPairWritable.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 指定输入数据的路径
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(remainingArgs[0]));
// 指定输出路径,并要求该输出路径一定是不存在的
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(remainingArgs[1]));
// 指定job执行模式,等待任务执行完成后,提交任务的客户端才会退出!
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
- 脚本调用
yarn jar TlHadoopCore-jar-with-dependencies.jar \
com.tianliangedu.examples.secondsort.SecondSortV3 \
-Dmapred.output.compress=true \
-Dmapred.output.compression.codec=org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodec \
-Dmapred.reduce.tasks=1 \
/tmp/tianliangedu/input_secondsort /tmp/tianliangedu/output55
天亮教育是一家从事Java、Hadoop大数据云计算、Python的教育培训、产品开发、咨询服务、人才优选为一体的综合型互联网科技公司。
公司由一批BAT等一线互联网IT精英人士创建,
以”快乐工作,认真生活,打造高端职业技能教育的一面旗帜”为愿景,
胸怀”让天下没有难找的工作”使命,
坚持”客户第一、诚信、激情、拥抱变化”的价值观,
全心全意为学员赋能提效,践行技术改变命运的初心。
欢迎关注天亮教育公众号,大数据技术资料与课程、招生就业动态、教育资讯动态、创业历程分享一站式分享,官方微信公众号二维码:

更多学习讨论, 请加入
官方爬虫、nlp技术qq群320349384
天亮教育官方群318971238,
hadoop & spark & hive技术群297585251,
官网:myhope365.com
官方天亮论坛:http://bbs.myhope365.com/
天亮教育视频链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1jIxI4IU 密码:zqa7