Android高手秘笈之View的绘制你应该知道的一切
目录
1. 简述android的UI系统的层级关系?
2. View绘制的整体流程?
3. MeasureSpec是什么?
4. 简述measure的测量流程?
5. 简述view的布局流程?
6. 简述onDraw绘制的基本流程?
7. View绘制简易流程?
8. 怎么在view绘制之前获取控件的宽和高?
1. 简述android的UI系统的层级关系?
PhoneWindow是Android系统中最基本的系统窗口,每个Activity都会创建一个,PhoneWindow是Activity和View系统交互的接口,DecorView本质上是一个FrameLayout,是所有Activity中所有View的祖先
2. View绘制的整体流程?
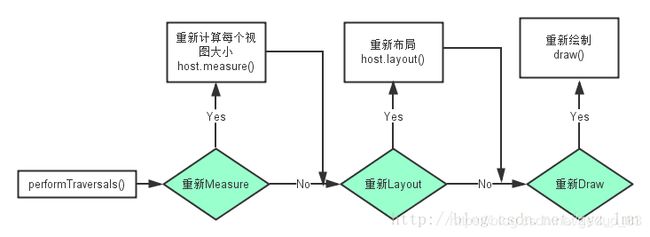
当一个应用启动时,会启动一个主Activity,Android系统会根据Activity的布局来对它进行绘制,绘制会从视图VewRoot的performTraversals()方法开始,从上到下遍历整个视图树,每个View控件负责绘制自己,而ViewGroup还需要通知自己的子View进行绘制操作。整个绘制过程分为三个步骤,分别是测量(Measure),布局(Layout)和绘制(Draw)。
private void performTraversals() {
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mHeight, lp.height);
}
//执行测量流程
performMeasure(childWidchMeasureSpec,childHeightMeasureSpec);//执行布局流程
performLayout(lp,desiredWindowWidth,desiredWindowHeight);//执行绘制流程
performDraw();3. MeasureSpec是什么?
MeasureSpec表示的是一个32位的整型值,它的高2位表示测量模式SpecMode,低30位表示某种测量模式下的规格大小SpecSize。MeasureSpec是View类的一个静态内部类,用来说明应该如何测量这个View
测量模式有三种:
- UNSPECIFIED:不指定测量模式,父视图没有限制子视图的大小,子视图可以是想要的任何尺寸,通常用于系统内部
- EXACTLY:精确测量值,当view的宽或者高指定为具体的数值或者match_parent时生效,表示父视图已经决定了子视图的精确大小
- AT_MOST:最大模式值,当view的宽或者高执行为wrap_content时,此时子View的大小为不超过父视图的尺寸的任意大小的值
- DecorView:MeasureSpec由窗口的尺寸和自身的LayoutParams共同决定
- 普通View:MeasureSpec由父view的MeasureSpec和自身的LayoutParams共同决定
4.简述measure的测量流程?
- 4.1 ViewRoot的performMeasure方法开始
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
try {
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}- 4.2 ViewGroup.measureChildren方法调用测量各个子View
protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int size = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) {
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}- 4.3 ViewGroup.measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec)方法调用
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}- 4.4 View的measure()方法调用
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
...
// measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
...
}- 4.5 View.onMeasure()方法调用
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}5. 简述view的布局流程?
- 5.1 ViewRoot.performLayout方法执行
private void performLayout(WindowManager.LayoutParams lp, int desiredWindowWidth,int desiredWindowHeight) {
host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight()))
}- 5.2 View.layout方法确定子View的位置
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if ((mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT) != 0) {
onMeasure(mOldWidthMeasureSpec, mOldHeightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
int oldL = mLeft;
int oldT = mTop;
int oldB = mBottom;
int oldR = mRight;
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners != null) {
ArrayList listenersCopy =
(ArrayList)li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners.clone();
int numListeners = listenersCopy.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; ++i) {
listenersCopy.get(i).onLayoutChange(this, l, t, r, b, oldL, oldT, oldR, oldB);
}
}
}
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_IS_LAID_OUT;
} - 5.3 ViewGroup.onLayout确定子view的位置,需要复写该方法
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {}6. 简述onDraw绘制的基本流程?
- 6.1 ViewRoot.performDraw方法开始
private void performDraw(){
...
draw(fullRedrawNeeded);
...
}- 6.2 ViewRoot.draw方法调用
private void draw(boolean fullRedrawNeeded) {
...
if (!drawSoftware(surface, mAttachInfo, xOffset, yOffset, scalingRequired, dirty)) {
return;
}
...
}- 6.3 ViewRoot.draw方法调用
private boolean drawSoftware(Surface surface, AttachInfo attachInfo, int xoff, int yoff,
boolean scalingRequired, Rect dirty) {
return true;
}- 6.4 View.draw方法调用
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
final int privateFlags = mPrivateFlags;
final boolean dirtyOpaque = (privateFlags & PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) == PFLAG_DIRTY_OPAQUE &&
(mAttachInfo == null || !mAttachInfo.mIgnoreDirtyState);
mPrivateFlags = (privateFlags & ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) | PFLAG_DRAWN;
/*
* Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed
* in the appropriate order:
*
* 1. Draw the background
* 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading
* 3. Draw view's content
* 4. Draw children
* 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers
* 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance)
*/
// Step 1, draw the background, if needed
// Step 6, draw decorations (foreground, scrollbars)
onDrawForeground(canvas);
}7. View绘制简易流程?
- 7.1 确定View的大小
7.1.1 ViewGroup.measureChildWithMargins计算已经使用的宽和高、以及子View的宽和高
7.1.2 ViewGroup.getChildMeasureSpec根据父View的MeasureSpec和子View来计算子View的measureSpec
7.1.3 View通过父View的其他参数进一步的调整和计算子View的MeasureSpec【View调整MeasureSpec】
7.1.4 子View.onMeasure通过自身的其他参数进一步调整MeasureSpec的大小来设置View的宽和高 【计算View的宽和高】
- 7.2 确定View的位置(left、top、right、bottom)
7.2.1 ViewGroup首先调用了layout()确定了自己本身在其父View中的位置
7.2.2 ViewGroup然后调用onLayout()确定每个子View的位置【用户自己自定义实现】
7.2.3 每个子View又会调用View的layout()方法来确定自己的位置
在自定义View的时候如果是继承自ViewGroup则必须复写onLayout方法来确定子View的大小,如果是继承自View则可以不用处理因为已经被他的父View把位置就确定了
- 7.3 绘制View
7.3.1 View的draw方法调用绘制view的背景
7.3.2 锁定画布堆栈并创建一个layer层用于绘制View在滚动时的边框渐变效果
7.3.3 onDraw开始绘制view【抽象方法】
7.3.4 开始绘制View的子View
7.3.5 绘制View滚动时的边框渐变效果
7.3.6 绘制View的滚动条
8.怎么在view绘制之前获取控件的宽和高?
- 8.1 在该控件将要被绘制的时候开始回调,此时可以测量拿到的控件的宽和高
ViewTreeObserver vto = imageView.getViewTreeObserver();
vto.addOnPreDrawListener(newViewTreeObserver.OnPreDrawListener(){
publicboolean onPreDraw(){
imageView.getViewTreeObserver().removeOnPreDrawListener(this)
intheight = imageView.getMeasuredHeight();
intwidth = imageView.getMeasuredWidth();
textView.append("\n"+height+","+width);
returntrue;
}
});- 8.2 当全部布局发生改变或者某个子空间可视性发生改变的时候都会回调该方法
ViewTreeObserver vto2 = imageView.getViewTreeObserver();
vto2.addOnGlobalLayoutListener(newOnGlobalLayoutListener(){
@Override
publicvoidonGlobalLayout(){
imageView.getViewTreeObserver().removeGlobalOnLayoutListener(this);
textView.append("\n\n"+imageView.getHeight()+","+imageView.getWidth());
}
});