Java创建WebService服务及客户端实现
简介
WebService是一种服务的提供方式,通过WebService,不同应用间相互间调用变的很方便,网络上有很多常用的WebService服务,如:http://developer.51cto.com/art/200908/147125.htm,不同的语言平台对WebService都有实现,Java的WebService实现,比较流行的有Axis2、Jaxws,本文介绍的是Axis2。
Axis2下载和部署
Axis2是Apache开发的一个开源项目,再次感叹Apache的伟大!
下载地址:
http://mirror.bit.edu.cn/apache/axis/axis2/java/core/1.6.2/axis2-1.6.2-war.zip
将其内axis2.war解压到
配置Axis2
true
true 编写服务
所谓服务就是编写一个类,写一些方法,方法返回数据,WebService客户端获取数据。
public class HelloService {
public String sayHello() {
return "hello";
}
}零配置发布服务
服务类创建好后,我们需要发布到服务器上,将HelloService.class放到
至此,我们已经成功的创建了一个WebService服务了,so easy!
再次访问http://localhost:8080/axis2/,点击Services,可以发现可用services中多了一个HelloService,其内有一个可用操作sayHello,说明发布成功。
HelloService
Service Description : No description available for this service
Service EPR : http://localhost:8080/axis2/services/HelloService
Service Status : Active
Available Operations
sayHello访问http://localhost:8080/axis2/services/HelloService,页面输出正是我们的返回值。
hello
这里有两点需要注意:
- 发布的类不能放在包里,既不能使用package关键字;
- 默认的发布目录是pojo,可以在
要注意多个目录间WebService要唯一,否则会重名,重名后,先部署的会成功,后部署的会报错。
services.xml配置文件发布服务
虽然上面的方式不需要配置文件,但是其服务类不能放在包内,显然是不符合我们日常开发的,Axis2也允许带包的类发布WebService,如果不允许,估计就没人用了。
首先写一个较复杂的服务类,多个方法,带参数,有返回值的。
package webservice.test;
/**
* 计算器运算
*
* @author gaoshuang
*/
public class CalculateService {
// 加法
public float plus(float x, float y) {
return x + y;
}
// 减法
public float minus(float x, float y) {
return x - y;
}
// 乘法
public float multiply(float x, float y) {
return x * y;
}
// 除法
public float divide(float x, float y) {
if (y != 0)
return x / y;
else
return -1;
}
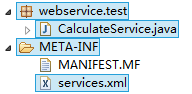
}然后编写services.xml,该文件需要放在META-INF文件夹下。
加减乘除计算服务
com.runqianapp.webservice.test.CalculateService
最后将这两个文件打成jar包,不论用工具还是手动打,打的都是最外层的文件夹。
我打的名字是server.jar,更改后缀为aar,所以最后是server.aar,Axis2建议使用aar发布WebService,将server.aar放到
CalculateService
Service Description : CalculateService
Service EPR : http://localhost:8080/axis2/services/CalculateService
Service Status : Active
Available Operations
divide
plus
minus
multiply分别访问:
http://localhost:8080/axis2/services/CalculateService/plus?x=1&y=2
http://localhost:8080/axis2/services/CalculateService/divide?x=1&y=2
http://localhost:8080/axis2/services/CalculateService/minus?x=1&y=2
http://localhost:8080/axis2/services/CalculateService/multiply?x=1&y=2
也可以发布多个WebService,可以使用serviceGroup标签。
...
...
客户端实现
以上介绍的都是WebService服务创建及发布,那么有了一个WebService服务后,我们如何调用呢?只在浏览器上访问是没有意义的。
下载Axis2客户端压缩包:http://mirror.esocc.com/apache/axis/axis2/java/core/1.6.2/axis2-1.6.2-bin.zip,并解压。
新建工程WebServiceClientTest,将
package webservice.client.test;
import javax.xml.namespace.QName;
import org.apache.axis2.AxisFault;
import org.apache.axis2.addressing.EndpointReference;
import org.apache.axis2.client.Options;
import org.apache.axis2.rpc.client.RPCServiceClient;
public class Client1 {
/**
* @param args
* @throws AxisFault
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws AxisFault {
// 使用RPC方式调用WebService
RPCServiceClient serviceClient = new RPCServiceClient();
Options options = serviceClient.getOptions();
// 指定调用WebService的URL
EndpointReference targetEPR = new EndpointReference(
"http://localhost:8080/axis2/services/CalculateService");
options.setTo(targetEPR);
// 调用方法的参数值
Object[] entryArgs = new Object[] {1, 2};
// 调用方法返回值的数据类型的Class对象
Class[] classes = new Class[] { float.class };
// 调用方法名及WSDL文件的命名空间
// 命名空间是http://localhost:8080/axis2/services/CalculateService?wsdl中wsdl:definitions标签targetNamespace属性
QName opName = new QName("http://test.webservice", "plus");
// 执行方法获取返回值
// 没有返回值的方法使用serviceClient.invokeRobust(opName, entryArgs)
Object result = serviceClient.invokeBlocking(opName, entryArgs, classes)[0];
System.out.println(result);
// out: 3.0
}
}
以上是实现了一个简单的WebSerivce客户端,调用CalculateService中的plus方法,由代码可见,这种调用方式比较杂乱,代码不太友好。
wsdl2java简化客户端
考虑到我们以后可能经常使用这些命令,设置环境变量,方便以后调用。在系统变量中加入AXIS2_HOME=
启动命令提示符,进入WebServiceTestClient所在目录,运行:
wsdl2java -uri http://localhost:8080/axis2/services/CalculateService?wsdl -p webservice.client.test -s参数说明:uri - wsdl文件路径,网络路径或本地路径,p - 打包,这里和上一个客户端实现类打在了一个包里,wsdl2java有很多参数,详细可以运行该命令去查看。
执行后,如果没有报错,说明运行成功,刷新项目,该包下多出了一个CalculateServiceStub类,里面的代码极其复杂,还乱呼呼的,这我们不用管,调用该类。
package webservice.client.test;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import webservice.client.test.CalculateServiceStub.Plus;
public class Client2 {
/**
* @param args
* @throws RemoteException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws RemoteException {
CalculateServiceStub stub = new CalculateServiceStub();
Plus plus = new Plus();
plus.setX(1);
plus.setY(2);
float result = stub.plus(plus).get_return();// 返回值自动转型,这也是强大之处
System.out.println(result);
}
}如此做的好处就是调用时不需要在去查看WSDL,和正常使用一个类一样,对WebService的封装都由wsdl2java自动生成,代码更优雅、简洁。
利用wsdl2java轻松使用第三方WebService服务
有了wsdl2java,已知一个WSDL文件我们就可以轻松的生成WebService客户端供我们调用,给我们服务。文章开头给出的链接包含了一些第三方服务,有一个服务是生成随机个数中文,WSDL:http://www.webxml.com.cn/WebServices/RandomFontsWebService.asmx?wsdl,同样,启动命令提示符,进入项目路径,执行:
wsdl2java -uri http://www.webxml.com.cn/WebServices/RandomFontsWebService.asmx?wsdl -p webservice.client.test -s调用该类:
package webservice.client.test;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import webservice.client.test.RandomFontsWebServiceStub.ArrayOfString;
import webservice.client.test.RandomFontsWebServiceStub.GetChineseFonts;
public class ThirdClient {
/**
* @param args
* @throws RemoteException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws RemoteException {
RandomFontsWebServiceStub stub = new RandomFontsWebServiceStub();
GetChineseFonts getChineseFonts = new GetChineseFonts();
getChineseFonts.setByFontsLength(10);// 免费使用有限制,最多8个
ArrayOfString result = stub.getChineseFonts(getChineseFonts).getGetChineseFontsResult();
for(String str : result.getString()) {
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}源码下载
文中代码尽在下面链接中,免积分下载。
http://download.csdn.net/download/ghsau/6400843
(完)
本文来自:高爽|Coder,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/ghsau/article/details/12714965