题目:题解:classSolution{vector&nums;public:Solution(vector&nums):nums(nums){}intpick(inttarget){intans;for(inti=0,cnt=0;i
AtCoder Beginner Contest 363
菜比乌斯反演
AtCoder算法c++开发语言
A-PilingUp题意不同的分数段有不同的^数量,Takahashi想要使得他的^数量增加,问他所需要的最少分数增幅。思路我们只需要找到下一阶段的下限。a/100是本阶段+1变成下一阶段,再*100变成下限,再与原来的相减即可。代码inlinevoidsolve(){inta;cin>>a;cout>n>>t>>p;vectora(n+1);for(inti=1;i>a[i];nth_eleme
C++ 如何判断一个类型是STL容器的类型
好学松鼠
C++STL容器的类型
一、定义是否是容器类型#include#include#include//std::enable_if#include//std::pair#include#include#include#include#include#include#include#include//默认类型为falsetemplatestructIsContainerType{staticconstboolvalue=fal
STL集合
#Y清墨
c++开发语言
1.集合的概念集合,简称集,是数学中一个基本概念,也是集合论的主要研究对象。集合论的基本理论创立于19世纪,关于集合的最简单的说法就是在朴素集合论(最原始的集合论)中的定义,即集合是“确定的一堆东西”,集合里的“东西”则称为元素。现代的集合一般被定义为:由一个或多个确定的元素所构成的整体。生活中的关于集合的例子很多:北京海淀区中学的105班的同学,这就是一个集合。这个集合里面会有一堆同学,而且是非
面试经典 150 题 2 —(二分查找)— 74. 搜索二维矩阵
BreezeChasingDrizzle
leetcode矩阵算法leetcodec++二分查找
74.搜索二维矩阵方法classSolution{public:boolsearchMatrix(vector>&matrix,inttarget){intmatrixRows=matrix.size(),matrixCols=matrix[0].size();//先找target所在的行inttargetAtRow=-1;for(inti=0;i>&matrix,inttarget){intma
【无线通信】误差矢量幅度(EVM)
守月满空山雪照窗
无线通信无线通信
误差矢量幅度(ErrorVectorMagnitude,EVM)是一种用来评估数字通信系统中调制质量的重要指标。EVM衡量的是理想信号与实际接收信号之间的差异,通常用来评估调制质量、信号完整性和接收机性能。EVM的定义在一个数字通信系统中,理想情况下接收到的信号应该精确地落在特定的理想星座点上(比如QAM或PSK星座图)。然而,由于各种现实因素,如噪声、失真、非线性效应和相位误差,接收到的信号可能
java 基础
i0208
java开发语言
基础数据类型,方法,类,异常处理:Java零基础入门学习(小白也能看懂!)_java零基础自学-CSDN博客List在Java中,List接口是集合框架中非常重要的一个接口,它提供了存储和操作有序集合的方法。List是一个接口,因此不能直接实例化,但可以通过其实现类(如ArrayList,LinkedList,Vector等)来使用。List接口的主要实现类ArrayList:动态数组实现,适用于
2019-01-16 HTTP消息头
NoelleMu
注:本文中绝大部分内容整理自百度百科,如有错误欢迎指正。HTTP消息头定义:在HTTP的请求和响应消息中,协议头部分的组件。HTTP消息头是在客户端请求(Request)或服务器响应(Response)时传递的,位于请求或响应的第一行,HTTP消息体(请求或响应的内容)在其后传输。一个HTTP请求由请求行(requestline)、请求头(header)、空行和请求数据4个部分组成;HTTP响应也
[ docker-ce源码分析系列 ] 修改resolv.conf文件被还原的原因
nangonghen
dockerdocker
1概述:1.1环境版本信息如下:a、操作系统:centos7.6,amd64b、服务器docker版本:v18.09.22resolv.conf文件被还原的现象:容器中的/etc/resolv.conf文件,是由宿主机/var/lib/docker/containers/xxxx/resolv.conf文件挂载。在dockerrestart容器之前,手动修改了/var/lib/docker/con
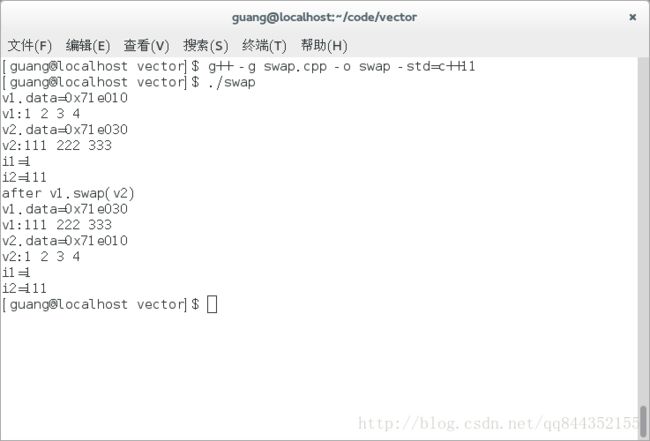
C++vector类
Ssorrymaker
C++c++
系列文章目录C++入门C++类和对象(上)C++类和对象(中)C++类和对象(下)C/C++内存管理C++string类文章目录系列文章目录一、vector是什么?二、常用接口说明1.常见的构造函数2.vectoriterator的使用3.关于vector的容量4.vector的增删改查5.迭代器失效一、vector是什么?vector是表示可变大小数组的序列容器,类似于数组,vector也采用连
【C++】手把手教你写出自己的vector类
Ornamrr
C++c++vector
在上一篇博客中,我们学习了vector的基本使用,以及迭代器的失效问题:【C++】深入理解vector类(一)今天我们来模拟实现以下vector类。目录成员变量接口实现构造函数迭代器拷贝构造赋值reserveresizepush_backpop_back实现[]访问成员变量我们先从原码中找出其成员变量:可以看到,原码中有三个成员变量:startfinishend_of_storage数据类型是it
Java基础day08ArrayList和继承
没有信仰的小白
ArrayList类对象数组数组长度是固定,无动态扩容java.util.ArrayList集合类,更方便image无参构造函数image基本格式,Jdk7之后右侧尖括号可以留空,但是必须保留ArrayListlist=newArrayList<>();成员方法添加元素publicbooleanadd(Ee)获取元素publicEget(intindex)集合中的元素publicintsize()
CVE-2020-24186 WordPress评论插件wpDiscuz任意文件上传漏洞
sukusec
0x00漏洞介绍Wordfence的威胁情报团队在一款名叫wpDiscuz的Wordpress评论插件(wpDiscuz是WordPress功能丰富的评论系统插件,可充实网站评论部分)中发现了一个高危漏洞,此漏洞将允许未经认证的攻击者在目标站点中上传任意文件,从而实现远程代码执行。0x01漏洞环境WordPress的gVectorswpDiscuz插件7.0至7.0.4版本中存在远程代码执行漏洞,
C++ STL概念之 算法
元凌丶
算法c++开发语言
sortdefault(1)templatevoidsort(RandomAccessIteratorfirst,RandomAccessIteratorlast);custom(2)templatevoidsort(RandomAccessIteratorfirst,RandomAccessIteratorlast,Comparecomp);作用:用于对容器中的元素进行排序。它通常采用快速排序算
【OpenHarmony嵌入式硬件开发】基于OpenHarmony标准系统的C++公共基础类库案例2:SafeMap
青少年编程作品集
嵌入式硬件c++javasqlharmonyos华为华为云
1、程序简介该程序是基于OpenHarmony的C++公共基础类库的安全关联容器:SafeMap。OpenHarmony提供了一个线程安全的map实现。SafeMap在STLmap基础上封装互斥锁,以确保对map的操作安全。本案例主要完成如下工作:创建1个子线程,负责每秒调用EnsureInsert()插入元素;创建1个子线程,负责每秒调用Insert()插入元素;创建1个子线程,负责每秒调用Er
解读Servlet原理篇二---GenericServlet与HttpServlet
周凡杨
javaHttpServlet源理GenericService源码
在上一篇《解读Servlet原理篇一》中提到,要实现javax.servlet.Servlet接口(即写自己的Servlet应用),你可以写一个继承自javax.servlet.GenericServletr的generic Servlet ,也可以写一个继承自java.servlet.http.HttpServlet的HTTP Servlet(这就是为什么我们自定义的Servlet通常是exte
MySQL性能优化
bijian1013
数据库mysql
性能优化是通过某些有效的方法来提高MySQL的运行速度,减少占用的磁盘空间。性能优化包含很多方面,例如优化查询速度,优化更新速度和优化MySQL服务器等。本文介绍方法的主要有:
a.优化查询
b.优化数据库结构
ThreadPool定时重试
dai_lm
javaThreadPoolthreadtimertimertask
项目需要当某事件触发时,执行http请求任务,失败时需要有重试机制,并根据失败次数的增加,重试间隔也相应增加,任务可能并发。
由于是耗时任务,首先考虑的就是用线程来实现,并且为了节约资源,因而选择线程池。
为了解决不定间隔的重试,选择Timer和TimerTask来完成
package threadpool;
public class ThreadPoolTest {
Oracle 查看数据库的连接情况
周凡杨
sqloracle 连接
首先要说的是,不同版本数据库提供的系统表会有不同,你可以根据数据字典查看该版本数据库所提供的表。
select * from dict where table_name like '%SESSION%';
就可以查出一些表,然后根据这些表就可以获得会话信息
select sid,serial#,status,username,schemaname,osuser,terminal,ma
类的继承
朱辉辉33
java
类的继承可以提高代码的重用行,减少冗余代码;还能提高代码的扩展性。Java继承的关键字是extends
格式:public class 类名(子类)extends 类名(父类){ }
子类可以继承到父类所有的属性和普通方法,但不能继承构造方法。且子类可以直接使用父类的public和
protected属性,但要使用private属性仍需通过调用。
子类的方法可以重写,但必须和父类的返回值类
android 悬浮窗特效
肆无忌惮_
android
最近在开发项目的时候需要做一个悬浮层的动画,类似于支付宝掉钱动画。但是区别在于,需求是浮出一个窗口,之后边缩放边位移至屏幕右下角标签处。效果图如下:
一开始考虑用自定义View来做。后来发现开线程让其移动很卡,ListView+动画也没法精确定位到目标点。
后来想利用Dialog的dismiss动画来完成。
自定义一个Dialog后,在styl
hadoop伪分布式搭建
林鹤霄
hadoop
要修改4个文件 1: vim hadoop-env.sh 第九行 2: vim core-site.xml <configuration> &n
gdb调试命令
aigo
gdb
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/hanchaoman/article/details/5517362
一、GDB常用命令简介
r run 运行.程序还没有运行前使用 c cuntinue
Socket编程的HelloWorld实例
alleni123
socket
public class Client
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Client c=new Client();
c.receiveMessage();
}
public void receiveMessage(){
Socket s=null;
BufferedRea
线程同步和异步
百合不是茶
线程同步异步
多线程和同步 : 如进程、线程同步,可理解为进程或线程A和B一块配合,A执行到一定程度时要依靠B的某个结果,于是停下来,示意B运行;B依言执行,再将结果给A;A再继续操作。 所谓同步,就是在发出一个功能调用时,在没有得到结果之前,该调用就不返回,同时其它线程也不能调用这个方法
多线程和异步:多线程可以做不同的事情,涉及到线程通知
&
JSP中文乱码分析
bijian1013
javajsp中文乱码
在JSP的开发过程中,经常出现中文乱码的问题。
首先了解一下Java中文问题的由来:
Java的内核和class文件是基于unicode的,这使Java程序具有良好的跨平台性,但也带来了一些中文乱码问题的麻烦。原因主要有两方面,
js实现页面跳转重定向的几种方式
bijian1013
JavaScript重定向
js实现页面跳转重定向有如下几种方式:
一.window.location.href
<script language="javascript"type="text/javascript">
window.location.href="http://www.baidu.c
【Struts2三】Struts2 Action转发类型
bit1129
struts2
在【Struts2一】 Struts Hello World http://bit1129.iteye.com/blog/2109365中配置了一个简单的Action,配置如下
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configurat
【HBase十一】Java API操作HBase
bit1129
hbase
Admin类的主要方法注释:
1. 创建表
/**
* Creates a new table. Synchronous operation.
*
* @param desc table descriptor for table
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the table name is res
nginx gzip
ronin47
nginx gzip
Nginx GZip 压缩
Nginx GZip 模块文档详见:http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpGzipModule
常用配置片段如下:
gzip on; gzip_comp_level 2; # 压缩比例,比例越大,压缩时间越长。默认是1 gzip_types text/css text/javascript; # 哪些文件可以被压缩 gzip_disable &q
java-7.微软亚院之编程判断俩个链表是否相交 给出俩个单向链表的头指针,比如 h1 , h2 ,判断这俩个链表是否相交
bylijinnan
java
public class LinkListTest {
/**
* we deal with two main missions:
*
* A.
* 1.we create two joined-List(both have no loop)
* 2.whether list1 and list2 join
* 3.print the join
Spring源码学习-JdbcTemplate batchUpdate批量操作
bylijinnan
javaspring
Spring JdbcTemplate的batch操作最后还是利用了JDBC提供的方法,Spring只是做了一下改造和封装
JDBC的batch操作:
String sql = "INSERT INTO CUSTOMER " +
"(CUST_ID, NAME, AGE) VALUES (?, ?, ?)";
[JWFD开源工作流]大规模拓扑矩阵存储结构最新进展
comsci
工作流
生成和创建类已经完成,构造一个100万个元素的矩阵模型,存储空间只有11M大,请大家参考我在博客园上面的文档"构造下一代工作流存储结构的尝试",更加相信的设计和代码将陆续推出.........
竞争对手的能力也很强.......,我相信..你们一定能够先于我们推出大规模拓扑扫描和分析系统的....
base64编码和url编码
cuityang
base64url
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.StringWriter;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
web应用集群Session保持
dalan_123
session
关于使用 memcached 或redis 存储 session ,以及使用 terracotta 服务器共享。建议使用 redis,不仅仅因为它可以将缓存的内容持久化,还因为它支持的单个对象比较大,而且数据类型丰富,不只是缓存 session,还可以做其他用途,一举几得啊。1、使用 filter 方法存储这种方法比较推荐,因为它的服务器使用范围比较多,不仅限于tomcat ,而且实现的原理比较简
Yii 框架里数据库操作详解-[增加、查询、更新、删除的方法 'AR模式']
dcj3sjt126com
数据库
public function getMinLimit () { $sql = "..."; $result = yii::app()->db->createCo
solr StatsComponent(聚合统计)
eksliang
solr聚合查询solr stats
StatsComponent
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2169134
http://eksliang.iteye.com/ 一、概述
Solr可以利用StatsComponent 实现数据库的聚合统计查询,也就是min、max、avg、count、sum的功能
二、参数
百度一道面试题
greemranqq
位运算百度面试寻找奇数算法bitmap 算法
那天看朋友提了一个百度面试的题目:怎么找出{1,1,2,3,3,4,4,4,5,5,5,5} 找出出现次数为奇数的数字.
我这里复制的是原话,当然顺序是不一定的,很多拿到题目第一反应就是用map,当然可以解决,但是效率不高。
还有人觉得应该用算法xxx,我是没想到用啥算法好...!
还有觉得应该先排序...
还有觉
Spring之在开发中使用SpringJDBC
ihuning
spring
在实际开发中使用SpringJDBC有两种方式:
1. 在Dao中添加属性JdbcTemplate并用Spring注入;
JdbcTemplate类被设计成为线程安全的,所以可以在IOC 容器中声明它的单个实例,并将这个实例注入到所有的 DAO 实例中。JdbcTemplate也利用了Java 1.5 的特定(自动装箱,泛型,可变长度
JSON API 1.0 核心开发者自述 | 你所不知道的那些技术细节
justjavac
json
2013年5月,Yehuda Katz 完成了JSON API(英文,中文) 技术规范的初稿。事情就发生在 RailsConf 之后,在那次会议上他和 Steve Klabnik 就 JSON 雏形的技术细节相聊甚欢。在沟通单一 Rails 服务器库—— ActiveModel::Serializers 和单一 JavaScript 客户端库——&
网站项目建设流程概述
macroli
工作
一.概念
网站项目管理就是根据特定的规范、在预算范围内、按时完成的网站开发任务。
二.需求分析
项目立项
我们接到客户的业务咨询,经过双方不断的接洽和了解,并通过基本的可行性讨论够,初步达成制作协议,这时就需要将项目立项。较好的做法是成立一个专门的项目小组,小组成员包括:项目经理,网页设计,程序员,测试员,编辑/文档等必须人员。项目实行项目经理制。
客户的需求说明书
第一步是需
AngularJs 三目运算 表达式判断
qiaolevip
每天进步一点点学习永无止境众观千象AngularJS
事件回顾:由于需要修改同一个模板,里面包含2个不同的内容,第一个里面使用的时间差和第二个里面名称不一样,其他过滤器,内容都大同小异。希望杜绝If这样比较傻的来判断if-show or not,继续追究其源码。
var b = "{{",
a = "}}";
this.startSymbol = function(a) {
Spark算子:统计RDD分区中的元素及数量
superlxw1234
sparkspark算子Spark RDD分区元素
关键字:Spark算子、Spark RDD分区、Spark RDD分区元素数量
Spark RDD是被分区的,在生成RDD时候,一般可以指定分区的数量,如果不指定分区数量,当RDD从集合创建时候,则默认为该程序所分配到的资源的CPU核数,如果是从HDFS文件创建,默认为文件的Block数。
可以利用RDD的mapPartitionsWithInd
Spring 3.2.x将于2016年12月31日停止支持
wiselyman
Spring 3
Spring 团队公布在2016年12月31日停止对Spring Framework 3.2.x(包含tomcat 6.x)的支持。在此之前spring团队将持续发布3.2.x的维护版本。
请大家及时准备及时升级到Spring
fis纯前端解决方案fis-pure
zccst
JavaScript
作者:zccst
FIS通过插件扩展可以完美的支持模块化的前端开发方案,我们通过FIS的二次封装能力,封装了一个功能完备的纯前端模块化方案pure。
1,fis-pure的安装
$ fis install -g fis-pure
$ pure -v
0.1.4
2,下载demo到本地
git clone https://github.com/hefangshi/f