【springboot系列】springboot+JSR303+全局异常处理
springboot+JSR303
文章目录
- springboot+JSR303
- 前言
- 正文
- 一、引入依赖
- 二、在Controller的入参处加上@Valid关键字
- 三、给参数对象添加需要的注解:
- 四、实现自定义注解IsMoible
- 五、后端对错误进行统一处理:
- 六、展示效果:
- 七、如何使代码更加优雅
前言
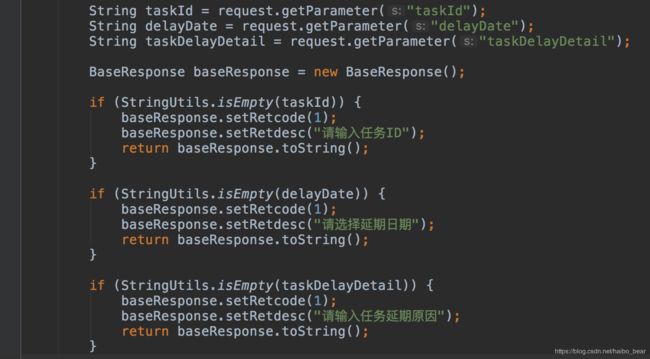
每次校验都要写一堆判空语句,判断字段长度,例如下面的代码,是否觉得很多余、很繁琐?
正文
一、引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validationartifactId>
dependency>
二、在Controller的入参处加上@Valid关键字
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/login")
public class LoginController {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LoginController.class);
@Autowired
private UserInfoSerivice userInfoSerivice;
@RequestMapping(value = "/doLogin", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public Result<LoginUser> login(@Valid @RequestBody LoginUser loginUser){
logger.info("loginUser:"+loginUser.toString());
LoginUser result = userInfoSerivice.getByUsername(loginUser.getUsername());
if (result==null){
return Result.error(CodeMsg.MOBILE_NOT_EXIST);
}
if (MD5Util.formPassToDBPass(loginUser.getPassword(),loginUser.getSalt()).equals(result.getPassword())){
return Result.success(result);
}else {
return Result.error(CodeMsg.PASSWORD_ERROR);
}
}
}
三、给参数对象添加需要的注解:
package xyz.haibofaith.miaosha.model;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Length;
import xyz.haibofaith.miaosha.validator.IsMobile;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
/**
* @author:haibo.xiong
* @date:2019/5/14
* @description:
*/
public class LoginUser {
private Integer id;
@NotNull
@IsMobile(required = true)
private String username;
@NotNull
private String password;
@NotNull
private String salt;
public String getSalt() {
return salt;
}
public void setSalt(String salt) {
this.salt = salt;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "LoginUser{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", salt='" + salt + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
四、实现自定义注解IsMoible
实现当手机号为空或者手机号位数不是11位的时候直接报错。不进行数据库校验。
1、仿造NotNull注解写
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE, ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.TYPE_USE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Constraint(
validatedBy = {IsMobileValidator.class}
)
public @interface IsMobile {
boolean required() default true;
String message() default "手机号码格式错误";
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};
}
2、实现校验类:
public class IsMobileValidator implements ConstraintValidator<IsMobile,String>{
private boolean required = false;
@Override
public void initialize(IsMobile constraintAnnotation) {
required = constraintAnnotation.required();
}
@Override
public boolean isValid(String s, ConstraintValidatorContext constraintValidatorContext) {
if (required){
//必须
return ValidatorUtil.isMobile(s);
}else {
//非必须
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(s)){
return true;
}else {
return ValidatorUtil.isMobile(s);
}
}
}
}
3、校验工具类(校验逻辑分离:方便管理)
public class ValidatorUtil {
public static Boolean isMobile(String value){
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(value)){
return false;
}
if (value.length()!=11){
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
五、后端对错误进行统一处理:
前面四步处理完后,后端系统已经可以区分前端传来的参数是否合规。但是,一旦校验不通过,会给前端一个非常不友好的提示,如下。
{"timestamp":"2019-05-16T08:08:31.062+0000","status":400,"error":"Bad Request",
"errors":[{"codes":["IsMobile.loginUser.username","IsMobile.username",
"IsMobile.java.lang.String","IsMobile"],
"arguments":[{"codes":["loginUser.username","username"],
"arguments":null,"defaultMessage":"username","code":"username"},true],
"defaultMessage":"手机号码格式错误","objectName":"loginUser","field":"username",
"rejectedValue":"185110686061","bindingFailure":false,"code":"IsMobile"}],
"message":"Validation failed for object='loginUser'. Error count: 1",
"path":"/login/doLogin"}
前端同学可能就会说,怎么返回错误提示不按照标准格式来呢?
此处则针对此种情况,对校验不通过的异常处理捕获并展示:
1、全局异常管理:
@ControllerAdvice
@ResponseBody
public class GlobleExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
public Result<String> exceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest request,Exception e){
if (e instanceof MethodArgumentNotValidException){
MethodArgumentNotValidException ex = (MethodArgumentNotValidException) e;
List<FieldError> fieldErrors = ex.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors();
//多个错误,取第一个
FieldError error = fieldErrors.get(0);
String msg = error.getDefaultMessage();
return Result.error(CodeMsg.BIND_ERROR.fillArgs(msg));
}else {
return Result.error(CodeMsg.SERVER_ERROR);
}
}
}
六、展示效果:
用户名超过11位
七、如何使代码更加优雅
请看下面的代码是否还有改进的余地:
LoginUser result = userInfoSerivice.getByUsername(loginUser.getUsername());
if (result==null){
return Result.error(CodeMsg.MOBILE_NOT_EXIST);
}
if (MD5Util.formPassToDBPass(loginUser.getPassword(),loginUser.getSalt()).equals(result.getPassword())){
return Result.success(result);
}else {
return Result.error(CodeMsg.PASSWORD_ERROR);
}
代码详解:对手机号不存在和密码错误的时候都是通过统一的返回格式塞入,然后返回到service层,然后从service层结果集----》controller层。
这么做其实已经比较优雅,但是如何更加优雅呢?用异常,有任何问题直接抛出自定义异常,然后通过五中异常处理去控制如何展示。
修改后的代码如下:
public Result<LoginUser> getByUsername(LoginUser loginUser){
LoginUser result =userInfoDao.getByUsername(loginUser.getUsername());
if (result==null){
throw new GlobleException(CodeMsg.MOBILE_NOT_EXIST);
}
if (MD5Util.formPassToDBPass(loginUser.getPassword(),loginUser.getSalt()).equals(result.getPassword())){
return Result.success(result);
}else {
throw new GlobleException(CodeMsg.PASSWORD_ERROR);
}
}
添加自定义异常:
public class GlobleException extends RuntimeException{
private CodeMsg codeMsg;
public GlobleException(CodeMsg codeMsg) {
super(codeMsg.toString());
this.codeMsg = codeMsg;
}
public CodeMsg getCodeMsg() {
return codeMsg;
}
public void setCodeMsg(CodeMsg codeMsg) {
this.codeMsg = codeMsg;
}
}
在全局异常处理中添加如下代码:
@ControllerAdvice
@ResponseBody
public class GlobleExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
public Result<String> exceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest request,Exception e){
if (e instanceof GlobleException){
GlobleException ex = (GlobleException) e;
return Result.error(ex.getCodeMsg());
}
if (e instanceof MethodArgumentNotValidException){
MethodArgumentNotValidException ex = (MethodArgumentNotValidException) e;
List<FieldError> fieldErrors = ex.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors();
//多个错误,取第一个
FieldError error = fieldErrors.get(0);
String msg = error.getDefaultMessage();
return Result.error(CodeMsg.BIND_ERROR.fillArgs(msg));
}else {
return Result.error(CodeMsg.SERVER_ERROR);
}
}
}