- gitlab修改DNS解析配置文件
中东大鹅
gitlablinuxgit
在Linux(CentOS7.9)云服务器上解压gitlab时提示需要Python的环境[root@rainyun-v1vct1josrc]#rpm-ivhgitlab-ce-10.8.4-ce.0.el7.x86_64.rpmwarning:gitlab-ce-10.8.4-ce.0.el7.x86_64.rpm:HeaderV4RSA/SHA1Signature,keyIDf27eab47:N
- Prometheus(六)黑盒监控
疯狂的大饼
性能linux运维centos
黑盒监控(blackbox_exporter)之前介绍的对exporter的使用可以称为“白盒监控”,既需要把对应的exporter程序安装到被监控的目标主机上,从而实现对主机资源及其状态的数据采集工作。黑盒监控,blackbox_exporter无须安装在被监控的目标环境中,用户只需要将其安装在于promethenus和被监控目标互通的环境中,通过HTTP、HTTPS、DNS、TCP、ICMP等
- RocketMQ 高可用集群架构与一致性机制解析
乘风破浪~~
rocketmq架构
分布式场景中一致性问题:1.服务器不稳定:随时泵机的可能2.网络问题:导致请求丢失3.网速问题:难以保证请求顺序性,最终结果数据一致性需要操作顺序性保证4.快速响应:不能因为一致性,导致响应以集群中最慢的为准。常见的算法弱一致性算法:DNS系统,Gossip协议(RedisCluster)强一致性算法:Basic-Paxos、Multi-Paxos包括Raft系列(Nacos的JRaft,Kafk
- 大白话讲【2】DHCP服务器配置
学习向前冲
服务器运维网络华为
DHCP动态主机配置协议是应用层协议;作用是分配IP地址,子网掩码,网关地址和DNS(可设置IP地址租期等)DHCP服务器可以是路由器,三交换机,Windowsserver2016(后续编写),linux服务器(后续编写)1.三层交换机上搭DHCP服务器1.1在三层交换机开启DHCP功能sy[Huawei]dhcpenable1.2创建地址池[Huawei]ippolicy-based-route
- 揭秘网络通信:数据传输的完整流程解析
网络通信是一个复杂但高度结构化的过程,涉及多个层次和协议的协作。以下是其核心原理和步骤的详细解析:1.网络通信的分层模型网络通信基于分层架构(如OSI七层模型或TCP/IP四层模型),每一层专注于特定功能,确保数据可靠传输:OSI模型TCP/IP模型功能应用层应用层提供用户接口(如HTTP、FTP、DNS)。表示层—数据格式转换(如加密、压缩)。会话层—建立、管理会话(如RPC、SQL)。传输层传
- DNS 服务器简单介绍
Risehuxyc
#Windows运维服务器前端linux
DNS服务器分类:根域名服务器顶级域名服务器权威域名服务器本地域名服务器国内公共域名腾讯:DNSPod-免费智能DNS解析服务商-电信_网通_教育网,智能DNS-烟台帝思普网络科技有限公司119.29.29.29和182.254.118.118阿里:阿里公共DNS223.5.5.5和223.6.6.6whatisdnsdnsmeaning百度:百度iDNS-帮助中心-公共DNS180.76.76.
- 【软件系统架构】系列七:系统性能——网络性能深入解析
目录一、什么是网络性能?网络性能的核心指标二、网络性能影响因素1.物理层因素2.链路质量3.网络设备性能4.协议栈影响5.应用层特性三、网络性能测试指标详解网络性能测试方法四、网络性能测试方法1.链路测试2.路径分析3.协议级分析4.大规模监控五、网络性能优化策略1.带宽优化2.延迟与抖动优化3.丢包率控制4.TCP调优5.DNS优化六、网络性能瓶颈诊断流程(实战推荐)七、不同网络环境的性能关注重
- Jenkins pipeline 部署docker通用模板
longze_7
jenkinsdockerJenkinsfilejenkinspipeline
Jenkinsfile:Docker的NETWORK_NAME不要使用bridge默认网络,要使用自定义的网络如test默认bridge网络:容器间不能用名字互相访问,只能用IP。自定义网络:容器间可以用名字互相访问,Docker自动做了DNS解析。pipeline{agentanyenvironment{//定义镜像名称和标签作为环境变量IMAGE_NAME='my-application'IM
- Docker报错:No address associated with hostname
longze_7
docker
进入Docker容器终端执行命令检查,在容器内能不能访问到外部容器的接口dockerexec-it/bin/bash不同的docker容器内部互相访问方式,http://容器名:开放的端口号,但是注意互相通信的容器要加入自定义网络而不是默认网络bridge:默认bridge网络:容器间不能用名字互相访问,只能用IP。自定义网络:容器间可以用名字互相访问,Docker自动做了DNS解析。http:/
- C语言手写一个简易 DNS 客户端
(Charon)
服务器linux网络
本文聚焦讲解如何通过C语言构造并发送一个最小化的DNS请求,特别以dns_client_commit()函数为主线,带你一步步理解DNS请求的构造过程。为什么要学习DNS报文构造?我们平时在浏览器里输入一个网址(比如www.baidu.com),浏览器其实背后会通过操作系统的DNS模块发送一个查询请求,将域名解析为IP地址。而如果我们手动用C语言自己构造DNS请求,我们可以更深刻地理解底层网络通信
- C语言手写简易 DNS 客户端(接收部分)
(Charon)
c语言开发语言
本文通过纯C语言手动构造DNS请求报文,使用UDP协议发送到公共DNS服务器,并接收响应,完整演示DNS请求流程。主流程:dns_client_commit()这是整个流程的核心函数,下面我们按顺序拆解每一步的逻辑,尤其突出发送sendto与接收recvfrom的设计思路和实现。第一步:创建UDP套接字intsockfd=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_DGRAM,0);if(sockfd
- 【C语言网络编程】HTTP 客户端请求(域名解析过程)
在做C语言网络编程或模拟HTTP客户端时,第一步就离不开“把域名解析为IP地址”这一步。很多人可能直接复制粘贴一段gethostbyname的代码,但未必真正理解它的原理。本篇博客将围绕一个经典函数:char*host_to_ip(constchar*hostname)深入剖析DNS解析过程、IP地址转换机制,并进一步带你了解HTTP请求是如何基于TCP通信进行的。一、核心函数:host_to_i
- 家庭网络中的服务器怎么对外提供服务?
行而不知
服务器运维内网穿透DDNS
家庭网络中的服务器怎么对外提供服务?方案1DDNS(家庭网络需要有公网ip)方案2内网穿透(需要有一台公网ip的服务器)方案1DDNS(家庭网络需要有公网ip) 怎么判断是否有公网ip?大致的流程就是光猫改桥接,由光猫拨号改为路由器拨号,在路由器管理页面查看拨号获取的ip,用这个ip去ip查询网站验证,具体的操作可自行搜索,这里不进行赘述了。 我们都知道,ip有两种,ipv4和ipv6 网络
- 访问远程共享文件时“连到系统上的设备没有发挥作用”错误解决方法
s_nshine
文件服务器
问题症状:在访问远程共享目录(比如Moabn)有时可能会遇到这个错误,提示“连到系统上的设备没有发挥作用”的错误。解决方法:1、按下Win+R组合键(Win是Alt旁边那个键),在“运行”里输入services.msc,点击确定。2、在打开的系统服务窗口中,检查下面三个系统服务项是否启动。如果没有启动,双击在属性里启动,另外“启动类型”也建议设置为自动。DHCPClientDNSClientRou
- 5G RAN接入场景的IMS语音业务开通全流程
码农老gou
5G5G网络
1.UE注册请求声明语音能力UE→AMF:发送RegistrationRequestNAS消息,关键参数:-UE'susagesetting="VoiceCentric"//终端以语音业务为核心-RequestedNSSAI:包含IMS切片标识(S-NSSAI)技术意义:通知网络优先保障语音业务资源(如QoS、移动性管理)。触发AMF按语音终端策略处理注册流程。规范依据:TS24.501§5.5.
- 2025年UDP洪水攻击防护实战全解析:从T级流量清洗到AI智能防御
上海云盾商务经理杨杨
udp人工智能网络协议
一、2025年UDP洪水攻击的新特征AI驱动的自适应攻击攻击者利用生成式AI动态调整UDP报文特征(如载荷内容、发送频率),攻击流量与正常业务流量差异率低至0.5%,传统指纹过滤规则失效。反射放大攻击升级黑客通过劫持物联网设备(如摄像头、传感器)构建僵尸网络,利用DNS/NTP协议漏洞发起反射攻击,1Gbps请求可放大至50-500倍流量,峰值突破8Tbps。混合协议打击70%的UDP攻击伴随TC
- 【mac】取消crashx代理后上不了网
木有会
杂七杂八mac常用操作技巧macos
crashx取消后上不了网的话,可以修改一下取消crashx代理后的dnsmac电脑点wifi图标--点网络偏好设置--高级--dns点加号新增114.114.114.114保存后就可以上网了
- 网安学习NO.14
防火墙基础实验传统防火墙配置实验拓扑图PC:ip192.168.10.1255.255.255.0192.168.10.254ipdns114.114.114.114二层交换机vl10exinte0/0swmoacswacvl10exinre0/1swtrendoswmotr三层交换机vl10exintg0/0swtrendoswmotrexiproutingintvl10ipaddress192
- 计算机网络实训教程实训总结,计算机网络实训报告
定乎内外之分
计算机网络实训教程实训总结
开学第一周我们就迎来了计算机网络实训,这门课程与上学期所学的计算机网络相对应,给了我们一个更深刻理解和掌握所学知识的机会。实训的内容包括了网线的压制,虚拟机的使用,服务器的安装,dhcp,dns,iis,ftp,web等基本内容,使我们对网络的组建、运作有个初步的了解。实训第一阶段的内容包括压制网线。eia/tia-568标准规定了两种rj45接头网线的连接标准(并没有实质上的差别),即eia/t
- 计算机网络实训报告,计算机网络实训报告范文
amulee998
计算机网络实训报告
开学第一周我们就迎来了计算机网络实训,这门课程与上学期所学的计算机网络相对应,给了我们一个更深刻理解和掌握所学知识的机会。实训的内容包括了网线的压制,虚拟机的使用,服务器的安装,dhcp,dns,iis,ftp,web等基本内容,使我们对网络的组建、运作有个初步的了解。实训第一阶段的内容包括压制网线。eia/tia-568标准规定了两种rj45接头网线的连接标准(并没有实质上的差别),即eia/t
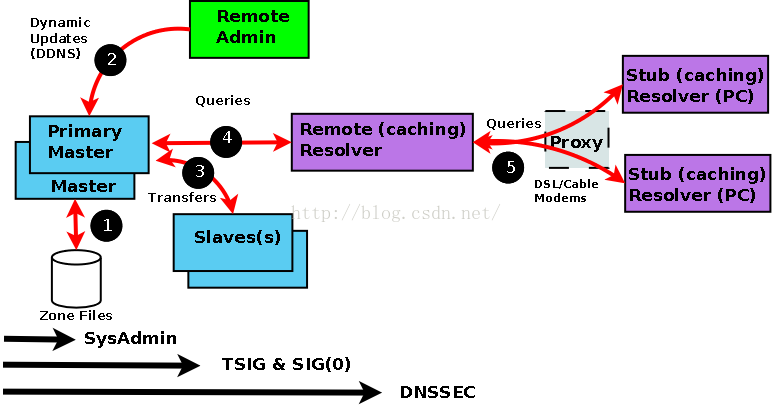
- Linux-DNS域名解析服务
系列文章目录`提示:仅用于个人学习,进行查漏补缺使用。1.Linux网络设置2.LinuxDHCP服务提示:写完文章后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档文章目录系列文章目录前言`提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考`一.概述二.DNS的定义三.域名结构四、DNS域名解析方式五.DNS域名解析的流程:六.Linux中的DNS配置:_DNS缓存:_七.DNS查找顺序八.DNS服
- 常见DDOS攻击方式与防护详解
“萌面大虾”
网络安全ddos网络网络安全
常见DDOS攻击方式与防护详解1四层DDOS1.1基于UDP协议的DDOS攻击与防护1.1.1UDPFlood攻击原理:攻击者发送大量UDP协议报文,UDP协议报文是面向无连接的,受害者只能被动接受所有报文,导致业务资源被占用。防护方法1、常见端口限速:如常见DNS、NTP、SNMP等协议均有固定端口,可以对其端口进行阈值限速处理,防止流量过大。2、特征提取过滤:UDP协议报文多为工具输出,具有一
- Kubernetes Pod DNS 配置
riverz1227
k8sk8s
一、概述Kubernetes提供多种DNS策略(dnsPolicy),同时kubelet参数也影响最终的DNS行为。二、dnsPolicy策略说明dnsPolicy含义说明Default使用宿主机的DNS配置(kubelet的--resolv-conf)ClusterFirst优先使用集群DNS(如CoreDNS),仅在无法解析时退回宿主机DNS(默认策略)ClusterFirstWithHost
- 技术面试题,HR面试题
爱莉希雅&&&
学习开发语言面试
#1.技术面试题(1)TCP与UDP的区别是什么?答:TCP面向连接,提供可靠传输,通过序列号、确认应答、重传机制等方法,有流量控制和拥塞控制,传输效率较低,适用于对准确性要求高的场景,如文件传输、HTTP等。UDP无连接,不保证可靠传输,无需建立连接和维护状态,传输效率高,适用于实时性要求高的场景,如视频流、语音通话、DNS。(2)DHCP和DNS的作用是什么?答:DHCP,是动态主机配置协议,
- C语言实现DNS客户端 | 详解dns_create_question函数的设计与实现
(Charon)
服务器网络linux
在实现一个简易的DNS查询客户端时,构造DNS报文是最关键的一步。DNS报文大致由两个部分组成:Header(报文头)Question(问题)本文聚焦于dns_create_question函数,即如何将用户输入的域名(如"www.example.com")编码为符合DNS协议格式的查询字段,并构造相关的qtype与qclass信息。一、DNSQuestion结构体定义回顾structdns_qu
- DNS和ICMP
阿沁QWQ
服务器linux网络
域名介绍在网络通信中,需要用到ip加port,但是ip并不方便记忆,于是我们常用域名来对应一个ip例如:www.baidu.com对应156.36.56.98(随便写的)com:一级域名.表示这是一个企业域名.同级的还有"net"(网络提供商),"org"(非盈利组织)等.baidu:二级域名,公司名.www:只是一种习惯用法.域名解析域名解析分为两步1.查本地/etc/hosts互连网信息中心(
- CDN分发加速技术详解
Dream Algorithm
网络架构
CDN核心原理与架构1.基本工作原理边缘节点缓存:将内容分发到离用户最近的边缘服务器DNS智能解析:引导用户访问最优节点内容预取与缓存:热点内容提前部署到边缘2.典型CDN架构组成用户请求→智能DNS→边缘节点(EdgeServer)↑二级节点(Mid-tier)↑源站(OriginServer)关键加速技术1.静态内容加速缓存策略优化:#Nginx缓存配置示例location~*\.(jpg|j
- 深入剖析F5、DNS、LVS、Nginx、Tomcat:Java架构师的流量分发指南(一)
呢喃coding
系统架构设计javalvsnginx
深入剖析F5、DNS、LVS、Nginx、Tomcat:Java架构师的流量分发指南在Java架构设计中,流量分发是保障系统高性能、高可用的关键环节。F5、DNS、LVS、Nginx和Tomcat在流量分发处理中各自扮演着独特的角色,深入理解它们对于Java架构师来说至关重要。一、F5:企业级的应用交付利器(一)功能与特性F5是一款企业级的应用交付网络(ADN)设备,它集负载均衡、应用安全、SSL
- curl --resolve
雨声不在
curl
curl--resolve是一个用于在发起HTTP请求时,临时修改域名解析的选项。它允许你指定某个域名解析到某个特定的IP地址,而不使用系统默认的DNS解析结果。这个选项在测试、调试或者绕过某些DNS问题时非常有用。基本语法:curl--resolvehost:port:address:指定要修改解析的域名、端口和对应的IP地址。URL:请求的目标URL。作用:当你使用curl--resolve时
- 关于有时候使用VPN后,关闭系统代理后短时间无法正常使用网络的原因及解决办法
为什么?以下是可能的原因代理设置残留关闭代理后,部分应用或系统服务仍尝试通过原代理服务器连接,导致短暂无法访问网络。DNS缓存未刷新VPN可能修改了DNS服务器,关闭代理后旧DNS缓存未及时清除,需等待缓存过期(通常几分钟到几小时)。路由表未即时恢复VPN会添加特殊路由规则,关闭后系统需要时间恢复默认路由,期间流量可能错误转发。DHCP租约续期延迟校园网/DHCP服务器可能需要时间重新分配IP或更
- java责任链模式
3213213333332132
java责任链模式村民告县长
责任链模式,通常就是一个请求从最低级开始往上层层的请求,当在某一层满足条件时,请求将被处理,当请求到最高层仍未满足时,则请求不会被处理。
就是一个请求在这个链条的责任范围内,会被相应的处理,如果超出链条的责任范围外,请求不会被相应的处理。
下面代码模拟这样的效果:
创建一个政府抽象类,方便所有的具体政府部门继承它。
package 责任链模式;
/**
*
- linux、mysql、nginx、tomcat 性能参数优化
ronin47
一、linux 系统内核参数
/etc/sysctl.conf文件常用参数 net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 32768 #允许送到队列的数据包的最大数目
net.core.rmem_max = 8388608 #SOCKET读缓存区大小
net.core.wmem_max = 8388608 #SOCKET写缓存区大
- php命令行界面
dcj3sjt126com
PHPcli
常用选项
php -v
php -i PHP安装的有关信息
php -h 访问帮助文件
php -m 列出编译到当前PHP安装的所有模块
执行一段代码
php -r 'echo "hello, world!";'
php -r 'echo "Hello, World!\n";'
php -r '$ts = filemtime("
- Filter&Session
171815164
session
Filter
HttpServletRequest requ = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpSession session = requ.getSession();
if (session.getAttribute("admin") == null) {
PrintWriter out = res.ge
- 连接池与Spring,Hibernate结合
g21121
Hibernate
前几篇关于Java连接池的介绍都是基于Java应用的,而我们常用的场景是与Spring和ORM框架结合,下面就利用实例学习一下这方面的配置。
1.下载相关内容: &nb
- [简单]mybatis判断数字类型
53873039oycg
mybatis
昨天同事反馈mybatis保存不了int类型的属性,一直报错,错误信息如下:
Caused by: java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "null"
at sun.mis
- 项目启动时或者启动后ava.lang.OutOfMemoryError: PermGen space
程序员是怎么炼成的
eclipsejvmtomcatcatalina.sheclipse.ini
在启动比较大的项目时,因为存在大量的jsp页面,所以在编译的时候会生成很多的.class文件,.class文件是都会被加载到jvm的方法区中,如果要加载的class文件很多,就会出现方法区溢出异常 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: PermGen space.
解决办法是点击eclipse里的tomcat,在
- 我的crm小结
aijuans
crm
各种原因吧,crm今天才完了。主要是接触了几个新技术:
Struts2、poi、ibatis这几个都是以前的项目中用过的。
Jsf、tapestry是这次新接触的,都是界面层的框架,用起来也不难。思路和struts不太一样,传说比较简单方便。不过个人感觉还是struts用着顺手啊,当然springmvc也很顺手,不知道是因为习惯还是什么。jsf和tapestry应用的时候需要知道他们的标签、主
- spring里配置使用hibernate的二级缓存几步
antonyup_2006
javaspringHibernatexmlcache
.在spring的配置文件中 applicationContent.xml,hibernate部分加入
xml 代码
<prop key="hibernate.cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider</prop>
<prop key="hi
- JAVA基础面试题
百合不是茶
抽象实现接口String类接口继承抽象类继承实体类自定义异常
/* * 栈(stack):主要保存基本类型(或者叫内置类型)(char、byte、short、 *int、long、 float、double、boolean)和对象的引用,数据可以共享,速度仅次于 * 寄存器(register),快于堆。堆(heap):用于存储对象。 */ &
- 让sqlmap文件 "继承" 起来
bijian1013
javaibatissqlmap
多个项目中使用ibatis , 和数据库表对应的 sqlmap文件(增删改查等基本语句),dao, pojo 都是由工具自动生成的, 现在将这些自动生成的文件放在一个单独的工程中,其它项目工程中通过jar包来引用 ,并通过"继承"为基础的sqlmap文件,dao,pojo 添加新的方法来满足项
- 精通Oracle10编程SQL(13)开发触发器
bijian1013
oracle数据库plsql
/*
*开发触发器
*/
--得到日期是周几
select to_char(sysdate+4,'DY','nls_date_language=AMERICAN') from dual;
select to_char(sysdate,'DY','nls_date_language=AMERICAN') from dual;
--建立BEFORE语句触发器
CREATE O
- 【EhCache三】EhCache查询
bit1129
ehcache
本文介绍EhCache查询缓存中数据,EhCache提供了类似Hibernate的查询API,可以按照给定的条件进行查询。
要对EhCache进行查询,需要在ehcache.xml中设定要查询的属性
数据准备
@Before
public void setUp() {
//加载EhCache配置文件
Inpu
- CXF框架入门实例
白糖_
springWeb框架webserviceservlet
CXF是apache旗下的开源框架,由Celtix + XFire这两门经典的框架合成,是一套非常流行的web service框架。
它提供了JAX-WS的全面支持,并且可以根据实际项目的需要,采用代码优先(Code First)或者 WSDL 优先(WSDL First)来轻松地实现 Web Services 的发布和使用,同时它能与spring进行完美结合。
在apache cxf官网提供
- angular.equals
boyitech
AngularJSAngularJS APIAnguarJS 中文APIangular.equals
angular.equals
描述:
比较两个值或者两个对象是不是 相等。还支持值的类型,正则表达式和数组的比较。 两个值或对象被认为是 相等的前提条件是以下的情况至少能满足一项:
两个值或者对象能通过=== (恒等) 的比较
两个值或者对象是同样类型,并且他们的属性都能通过angular
- java-腾讯暑期实习生-输入一个数组A[1,2,...n],求输入B,使得数组B中的第i个数字B[i]=A[0]*A[1]*...*A[i-1]*A[i+1]
bylijinnan
java
这道题的具体思路请参看 何海涛的微博:http://weibo.com/zhedahht
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CreateBFromATencent {
/**
* 题目:输入一个数组A[1,2,...n],求输入B,使得数组B中的第i个数字B[i]=A
- FastDFS 的安装和配置 修订版
Chen.H
linuxfastDFS分布式文件系统
FastDFS Home:http://code.google.com/p/fastdfs/
1. 安装
http://code.google.com/p/fastdfs/wiki/Setup http://hi.baidu.com/leolance/blog/item/3c273327978ae55f93580703.html
安装libevent (对libevent的版本要求为1.4.
- [强人工智能]拓扑扫描与自适应构造器
comsci
人工智能
当我们面对一个有限拓扑网络的时候,在对已知的拓扑结构进行分析之后,发现在连通点之后,还存在若干个子网络,且这些网络的结构是未知的,数据库中并未存在这些网络的拓扑结构数据....这个时候,我们该怎么办呢?
那么,现在我们必须设计新的模块和代码包来处理上面的问题
- oracle merge into的用法
daizj
oraclesqlmerget into
Oracle中merge into的使用
http://blog.csdn.net/yuzhic/article/details/1896878
http://blog.csdn.net/macle2010/article/details/5980965
该命令使用一条语句从一个或者多个数据源中完成对表的更新和插入数据. ORACLE 9i 中,使用此命令必须同时指定UPDATE 和INSE
- 不适合使用Hadoop的场景
datamachine
hadoop
转自:http://dev.yesky.com/296/35381296.shtml。
Hadoop通常被认定是能够帮助你解决所有问题的唯一方案。 当人们提到“大数据”或是“数据分析”等相关问题的时候,会听到脱口而出的回答:Hadoop! 实际上Hadoop被设计和建造出来,是用来解决一系列特定问题的。对某些问题来说,Hadoop至多算是一个不好的选择,对另一些问题来说,选择Ha
- YII findAll的用法
dcj3sjt126com
yii
看文档比较糊涂,其实挺简单的:
$predictions=Prediction::model()->findAll("uid=:uid",array(":uid"=>10));
第一个参数是选择条件:”uid=10″。其中:uid是一个占位符,在后面的array(“:uid”=>10)对齐进行了赋值;
更完善的查询需要
- vim 常用 NERDTree 快捷键
dcj3sjt126com
vim
下面给大家整理了一些vim NERDTree的常用快捷键了,这里几乎包括了所有的快捷键了,希望文章对各位会带来帮助。
切换工作台和目录
ctrl + w + h 光标 focus 左侧树形目录ctrl + w + l 光标 focus 右侧文件显示窗口ctrl + w + w 光标自动在左右侧窗口切换ctrl + w + r 移动当前窗口的布局位置
o 在已有窗口中打开文件、目录或书签,并跳
- Java把目录下的文件打印出来
蕃薯耀
列出目录下的文件文件夹下面的文件目录下的文件
Java把目录下的文件打印出来
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
蕃薯耀 2015年7月11日 11:02:
- linux远程桌面----VNCServer与rdesktop
hanqunfeng
Desktop
windows远程桌面到linux,需要在linux上安装vncserver,并开启vnc服务,同时需要在windows下使用vnc-viewer访问Linux。vncserver同时支持linux远程桌面到linux。
linux远程桌面到windows,需要在linux上安装rdesktop,同时开启windows的远程桌面访问。
下面分别介绍,以windo
- guava中的join和split功能
jackyrong
java
guava库中,包含了很好的join和split的功能,例子如下:
1) 将LIST转换为使用字符串连接的字符串
List<String> names = Lists.newArrayList("John", "Jane", "Adam", "Tom");
- Web开发技术十年发展历程
lampcy
androidWeb浏览器html5
回顾web开发技术这十年发展历程:
Ajax
03年的时候我上六年级,那时候网吧刚在小县城的角落萌生。传奇,大话西游第一代网游一时风靡。我抱着试一试的心态给了网吧老板两块钱想申请个号玩玩,然后接下来的一个小时我一直在,注,册,账,号。
彼时网吧用的512k的带宽,注册的时候,填了一堆信息,提交,页面跳转,嘣,”您填写的信息有误,请重填”。然后跳转回注册页面,以此循环。我现在时常想,如果当时a
- 架构师之mima-----------------mina的非NIO控制IOBuffer(说得比较好)
nannan408
buffer
1.前言。
如题。
2.代码。
IoService
IoService是一个接口,有两种实现:IoAcceptor和IoConnector;其中IoAcceptor是针对Server端的实现,IoConnector是针对Client端的实现;IoService的职责包括:
1、监听器管理
2、IoHandler
3、IoSession
- ORA-00054:resource busy and acquire with NOWAIT specified
Everyday都不同
oraclesessionLock
[Oracle]
今天对一个数据量很大的表进行操作时,出现如题所示的异常。此时表明数据库的事务处于“忙”的状态,而且被lock了,所以必须先关闭占用的session。
step1,查看被lock的session:
select t2.username, t2.sid, t2.serial#, t2.logon_time
from v$locked_obj
- javascript学习笔记
tntxia
JavaScript
javascript里面有6种基本类型的值:number、string、boolean、object、function和undefined。number:就是数字值,包括整数、小数、NaN、正负无穷。string:字符串类型、单双引号引起来的内容。boolean:true、false object:表示所有的javascript对象,不用多说function:我们熟悉的方法,也就是
- Java enum的用法详解
xieke90
enum枚举
Java中枚举实现的分析:
示例:
public static enum SEVERITY{
INFO,WARN,ERROR
}
enum很像特殊的class,实际上enum声明定义的类型就是一个类。 而这些类都是类库中Enum类的子类 (java.l