MySQL-SpringBoot集成JPA实现数据读写分离
在上篇博客《MySQL-主从复制之同步主从数据》中,我们实现了读库和写库的数据同步。今天,我们继续学习SpringBoot集成JPA如何实现数据读写分离。废话不多话直接上代码。
一、配置数据源
# 数据源
spring.datasource.druid.write.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3380/test
spring.datasource.druid.write.username=root
spring.datasource.druid.write.password=Anbang713
spring.datasource.druid.write.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.druid.read.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3381/test
spring.datasource.druid.read.username=root
spring.datasource.druid.read.password=Anbang713
spring.datasource.druid.read.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
# JPA
spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
spring.jpa.database=mysql
spring.jpa.generate-ddl=false
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=none
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming-strategy=org.hibernate.cfg.DefaultComponentSafeNamingStrategy
spring.jpa.show-sql=false二、数据源配置类
/**
* 数据源配置
*
* @author Administrator
*
*/
@Configuration
public class DataSourceConfig {
public final static String WRITE_DATASOURCE_KEY = "writeDruidDataSource";
public final static String READ_DATASOURCE_KEY = "readDruidDataSource";
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.druid.read")
@Bean(name = READ_DATASOURCE_KEY)
public DataSource readDruidDataSource() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.druid.write")
@Bean(name = WRITE_DATASOURCE_KEY)
@Primary
public DataSource writeDruidDataSource() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
/**
* 注入AbstractRoutingDataSource
*
* @param readDruidDataSource
* @param writeDruidDataSource
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Bean
public AbstractRoutingDataSource routingDataSource(
@Qualifier(READ_DATASOURCE_KEY) DataSource readDruidDataSource,
@Qualifier(WRITE_DATASOURCE_KEY) DataSource writeDruidDataSource) throws Exception {
DynamicDataSource dataSource = new DynamicDataSource();
Map targetDataSources = new HashMap();
targetDataSources.put(WRITE_DATASOURCE_KEY, writeDruidDataSource);
targetDataSources.put(READ_DATASOURCE_KEY, readDruidDataSource);
dataSource.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSources);// 配置数据源
dataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(writeDruidDataSource);// 默认为主库用于写数据
return dataSource;
}
} 三、使用ThreadLocal使数据源与线程绑定
public class DynamicDataSourceHolder {
// 使用ThreadLocal把数据源与当前线程绑定
private static final ThreadLocal dataSources = new ThreadLocal();
public static void setDataSource(String dataSourceName) {
dataSources.set(dataSourceName);
}
public static String getDataSource() {
return (String) dataSources.get();
}
public static void clearDataSource() {
dataSources.remove();
}
} 四、动态数据源配置
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
// 可以做一个简单的负载均衡策略
String lookupKey = DynamicDataSourceHolder.getDataSource();
System.out.println("------------lookupKey---------" + lookupKey);
return lookupKey;
}
}五、写数据源配置类
@Configuration
@EnableJpaRepositories(value = "com.study.mysql.jpa.dao",
entityManagerFactoryRef = "writeEntityManagerFactory",
transactionManagerRef = "writeTransactionManager")
public class WriteDataSourceConfig {
@Autowired
JpaProperties jpaProperties;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("writeDruidDataSource")
private DataSource writeDruidDataSource;
/**
* 我们通过LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean来获取EntityManagerFactory实例
*
* @return
*/
@Bean(name = "writeEntityManagerFactoryBean")
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean writeEntityManagerFactoryBean(
EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return builder.dataSource(writeDruidDataSource).properties(jpaProperties.getProperties())
.packages("com.study.mysql.jpa.api") // 设置实体类所在位置
.persistenceUnit("writePersistenceUnit").build();
}
/**
* EntityManagerFactory类似于Hibernate的SessionFactory,mybatis的SqlSessionFactory
* 总之在执行操作之前我们总要获取一个EntityManager,这就类似于Hibernate的Session,mybatis的sqlSession。
*
* @param builder
* @return
*/
@Bean(name = "writeEntityManagerFactory")
@Primary
public EntityManagerFactory writeEntityManagerFactory(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return this.writeEntityManagerFactoryBean(builder).getObject();
}
/**
* 配置事物管理器
*
* @return
*/
@Bean(name = "writeTransactionManager")
@Primary
public PlatformTransactionManager writeTransactionManager(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return new JpaTransactionManager(writeEntityManagerFactory(builder));
}
}六、自定义注解
@Target({
ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface TargetDateSource {
String dataSource() default "";// 数据源
}七、定义切面,实现数据源切换
@Aspect
@Component
public class DynamicDataSourceAspect {
@Around("execution(public * com.study.mysql.jpa.core..*.*(..))")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) pjp.getSignature();
Method targetMethod = methodSignature.getMethod();
if (targetMethod.isAnnotationPresent(TargetDateSource.class)) {
String targetDataSource = targetMethod.getAnnotation(TargetDateSource.class).dataSource();
System.out.println("----------数据源是:" + targetDataSource + "------");
DynamicDataSourceHolder.setDataSource(targetDataSource);
}
// 执行方法
Object result = pjp.proceed();
DynamicDataSourceHolder.clearDataSource();
return result;
}
}在完成上面的相关配置后,我们写个简单的学生增删改查接口做测试。至此,我们的项目结构是这样的:
当然在这里,我们有必要看一下业务层实现类的代码,通过注解@TargetDataSource注解实现读写分离。
@Service
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentDao studentDao;
@Override
@TargetDateSource(dataSource = DataSourceConfig.READ_DATASOURCE_KEY)
public List findAll() {
return studentDao.findAll();
}
@Override
@TargetDateSource(dataSource = DataSourceConfig.READ_DATASOURCE_KEY)
public Student findById(Integer id) {
Optional students = studentDao.findById(id);
if (students.isPresent() && students.get() != null) {
return students.get();
}
return null;
}
@Override
@Transactional
@TargetDateSource(dataSource = DataSourceConfig.WRITE_DATASOURCE_KEY)
public Integer save(Student entity) throws Exception {
if (entity.getId() != null) {
Student perz = studentDao.saveAndFlush(entity);
return perz.getId();
}
Student perz = studentDao.save(entity);
return perz.getId();
}
} 八、测试
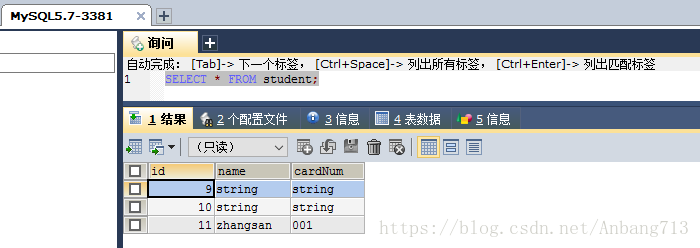
启动SpringBoot启动类,并通过http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html访问我们的学生类接口。在测试之前,我们现在看下数据库的数据。可以看到我们的主从数据库数据是一样的。(MySQL5.6-3380为主数据库,用于写数据;MySQL5.6-3381为从数据库,用于读数据)
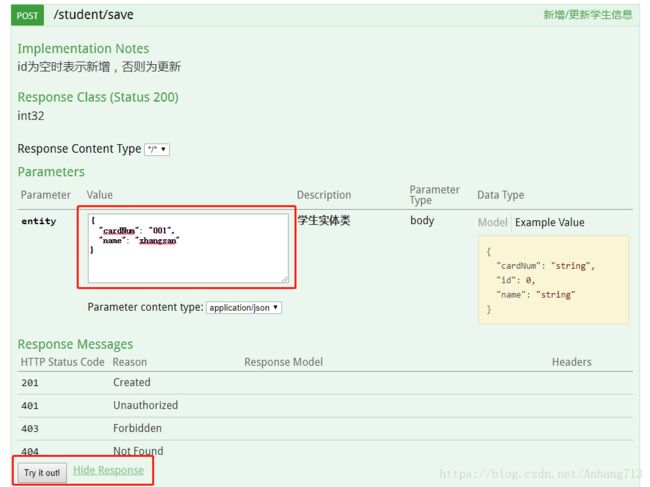
那么我们现在往数据库插入一条数据,执行save接口:
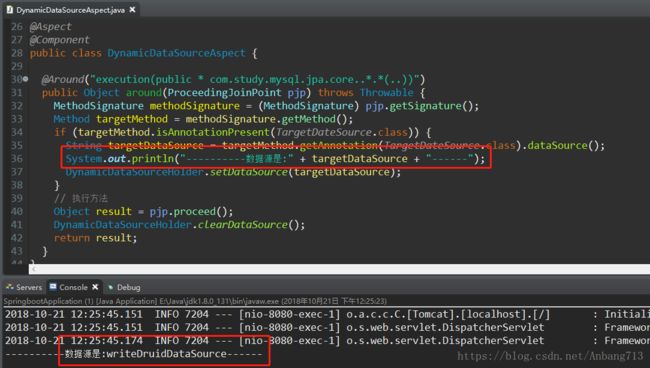
首先可以看到,在切面类中打印的日志,已经实现数据源的自动切换了。
然后我们看下数据库的数据,可以看到两边的数据是一模一样的。
最后,我们测试一下读的时候是从哪个数据源读的。
可以看到,在读请求的时候,是从从数据库读的数据。至此,我们使用SpringBoot集成JPA实现读写分离的目的已经达到。
源代码地址: https://gitee.com/chengab/MySQL
参考博客:https://www.jb51.net/article/111588.htm