KSP算法的实现(Top-k-shortest paths 的Matlab实现)
摘要
本文主要讲述前K条最短路径的Matlab的实现。
1. all_paths_gen.m函数
function [] = all_paths_gen(weight_matrix, k, output_file)
len = length(weight_matrix);
fileID = fopen(output_file,'wt');
fprintf(fileID,'%d nodes \n\n', len);
fclose(fileID);
node_pairs = combnk(1:len,2);
for index = 1: length(node_pairs)
src = node_pairs(index, 1);
dst = node_pairs(index, 2);
gen_k_shortest_path(weight_matrix, src, dst, k, output_file, index);
end2. dijkstra.m函数
function [shortestPath, totalCost] = dijkstra(netCostMatrix, s, d)
n = size(netCostMatrix,1);
for i = 1:n
% initialize the farthest node to be itself;
farthestPrevHop(i) = i; % used to compute the RTS/CTS range;
farthestNextHop(i) = i;
end
% all the nodes are un-visited;
visited(1:n) = false;
distance(1:n) = inf; % it stores the shortest distance between each node and the source node;
parent(1:n) = 0;
distance(s) = 0;
for i = 1:(n-1),
temp = [];
for h = 1:n,
if ~visited(h) % in the tree;
temp=[temp distance(h)];
else
temp=[temp inf];
end
end;
[t, u] = min(temp); % it starts from node with the shortest distance to the source;
visited(u) = true; % mark it as visited;
for v = 1:n, % for each neighbors of node u;
if ( ( netCostMatrix(u, v) + distance(u)) < distance(v) )
distance(v) = distance(u) + netCostMatrix(u, v); % update the shortest distance when a shorter shortestPath is found;
parent(v) = u; % update its parent;
end;
end;
end;
shortestPath = [];
if parent(d) ~= 0 % if there is a shortestPath!
t = d;
shortestPath = [d];
while t ~= s
p = parent(t);
shortestPath = [p shortestPath];
if netCostMatrix(t, farthestPrevHop(t)) < netCostMatrix(t, p)
farthestPrevHop(t) = p;
end;
if netCostMatrix(p, farthestNextHop(p)) < netCostMatrix(p, t)
farthestNextHop(p) = t;
end;
t = p;
end;
end;
totalCost = distance(d);3. gen_k_shortest_path.m函数
function [shortestPaths, totalCosts] = ...
gen_k_shortest_path(weight_matrix, src, dst, k, ...
output_file, demand_id)
fileID = fopen(output_file,'at');
%------Call kShortestPath------:
[shortestPaths, totalCosts] = kShortestPath(weight_matrix, src, dst, k);
%------Display results------:
if isempty(shortestPaths)
fprintf(fileID,'No path available between these nodes\n\n');
else
for i = 1: length(shortestPaths)
%fprintf(fileID,'Path # %d: %d %d : ',i, src, dst);
fprintf(fileID,'%d %d ', src, dst);
%disp(shortestPaths{i});
len = length(shortestPaths{i});
for j = 1: len - 1
fprintf(fileID, '%d ', shortestPaths{i}(j));
end
fprintf(fileID,'%d', shortestPaths{i}(len));
%fprintf(fileID,'x_%d_%d \n', demand_id, i);
fprintf(fileID,'\n');
%fprintf(fileID,'Cost of path %d is %5.2f\n\n',i,totalCosts(i));
end
end
fclose(fileID);
function [shortestPaths, totalCosts] = kShortestPath(netCostMatrix, source, destination, k_paths)
if source > size(netCostMatrix,1) || destination > size(netCostMatrix,1)
warning('The source or destination node are not part of netCostMatrix');
shortestPaths=[];
totalCosts=[];
else
%---------------------INITIALIZATION---------------------
k=1;
[path cost] = dijkstra(netCostMatrix, source, destination);
%P is a cell array that holds all the paths found so far:
if isempty(path)
shortestPaths=[];
totalCosts=[];
else
path_number = 1;
P{path_number,1} = path; P{path_number,2} = cost;
current_P = path_number;
%X is a cell array of a subset of P (used by Yen's algorithm below):
size_X=1;
X{size_X} = {path_number; path; cost};
%S path_number x 1
S(path_number) = path(1); %deviation vertex is the first node initially
% K = 1 is the shortest path returned by dijkstra():
shortestPaths{k} = path ;
totalCosts(k) = cost;
%--------------------------------------------------------
while (k < k_paths && size_X ~= 0 )
%remove P from X
for i=1:length(X)
if X{i}{1} == current_P
size_X = size_X - 1;
X(i) = [];%delete cell
break;
end
end
%---------------------------------------
P_ = P{current_P,1}; %P_ is current P, just to make is easier for the notations
%Find w in (P_,w) in set S, w was the dev vertex used to found P_
w = S(current_P);
for i = 1: length(P_)
if w == P_(i)
w_index_in_path = i;
end
end
for index_dev_vertex= w_index_in_path: length(P_) - 1 %index_dev_vertex is index in P_ of deviation vertex
temp_netCostMatrix = netCostMatrix;
%------
%Remove vertices in P before index_dev_vertex and there incident edges
for i = 1: index_dev_vertex-1
v = P_(i);
temp_netCostMatrix(v,:)=inf;
temp_netCostMatrix(:,v)=inf;
end
%------
%remove incident edge of v if v is in shortestPaths (K) U P_ with similar sub_path to P_....
SP_sameSubPath=[];
index =1;
SP_sameSubPath{index}=P_;
for i = 1: length(shortestPaths)
if length(shortestPaths{i}) >= index_dev_vertex
if P_(1:index_dev_vertex) == shortestPaths{i}(1:index_dev_vertex)
index = index+1;
SP_sameSubPath{index}=shortestPaths{i};
end
end
end
v_ = P_(index_dev_vertex);
for j = 1: length(SP_sameSubPath)
next = SP_sameSubPath{j}(index_dev_vertex+1);
temp_netCostMatrix(v_,next)=inf;
end
%------
%get the cost of the sub path before deviation vertex v
sub_P = P_(1:index_dev_vertex);
cost_sub_P=0;
for i = 1: length(sub_P)-1
cost_sub_P = cost_sub_P + netCostMatrix(sub_P(i),sub_P(i+1));
end
%call dijkstra between deviation vertex to destination node
[dev_p c] = dijkstra(temp_netCostMatrix, P_(index_dev_vertex), destination);
if ~isempty(dev_p)
path_number = path_number + 1;
P{path_number,1} = [sub_P(1:end-1) dev_p] ; %concatenate sub path- to -vertex -to- destination
P{path_number,2} = cost_sub_P + c ;
S(path_number) = P_(index_dev_vertex);
size_X = size_X + 1;
X{size_X} = {path_number; P{path_number,1} ;P{path_number,2} };
else
%warning('k=%d, isempty(p)==true!\n',k);
end
end
%---------------------------------------
%Step necessary otherwise if k is bigger than number of possible paths
%the last results will get repeated !
if size_X > 0
shortestXCost= X{1}{3}; %cost of path
shortestX= X{1}{1}; %ref number of path
for i = 2 : size_X
if X{i}{3} < shortestXCost
shortestX= X{i}{1};
shortestXCost= X{i}{3};
end
end
current_P = shortestX;
%******
k = k+1;
shortestPaths{k} = P{current_P,1};
totalCosts(k) = P{current_P,2};
%******
else
%k = k+1;
end
end
end
end
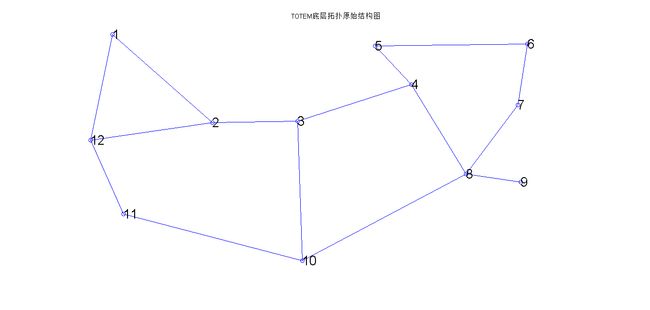
5. 测试数据
拓扑图如下图所示
其邻接矩阵(即实验测试数据如下)
>> dist=[
Inf 1 Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf 1
1 Inf 1 Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf 1
Inf 1 Inf 1 Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf 1 Inf Inf
Inf Inf 1 Inf 1 Inf Inf 1 Inf Inf Inf Inf
Inf Inf Inf 1 Inf 1 Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf
Inf Inf Inf Inf 1 Inf 1 Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf
Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf 1 Inf 1 Inf Inf Inf Inf
Inf Inf Inf 1 Inf Inf 1 Inf 1 1 Inf Inf
Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf 1 Inf Inf Inf Inf
Inf Inf 1 Inf Inf Inf Inf 1 Inf Inf 1 Inf
Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf 1 Inf 1
1 1 Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf 1 Inf];>> [path, cost]=kShortestPath(dist,1,7,5) % 测试节点1到节点7的前五条(Top5)最短路径6. 测试结果
>> path{1}
ans =
1 2 3 4 8 7
>> path{2}
ans =
1 12 11 10 8 7
>> path{3}
ans =
1 2 3 10 8 7
>> path{4}
ans =
1 2 12 11 10 8 7
>> path{5}
ans =
1 2 3 4 5 6 7