CUDA(18)之TLP,ILP策略
摘要
本文主要讲述CUDA的TLP, ILP策略。
1. 什么是TLP?
TLP是基于线程的并行策略。换句话说,并行的最小粒度是以线程为单位。
2. 什么是ILP?
ILP是基于指令的并行策略。换句话说,并行的最小粒度是以指令为单位。其中,线程与指令的关系是:一个线程由一条或者多条指令所构成。
3. 优化策略:结合TLP&ILP
在寄存器数目硬件的能力允许范围内,尽可能地增加一个线程内可并发指令的条数。
4. 若干实验
OS Version:Windows7 sp1
CUDA Version:CUDA 8.0
GPU:NVIDIA GTX 780Ti
CPU:Intel Core I7
Memory Size (host):32G
实验一:TLP
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define NUM_ITERATIONS ( 1024 * 1024)
#define OP_COUNT 1*2*NUM_ITERATIONS
#define WARP_SIZE 32
#define BLOCK_SIZE 1024
__device__ float d_a[32];
__global__ void kernel(float a, float b, float c){
#pragma unroll 16
for(int i=0; i < NUM_ITERATIONS; i++) {
a = a * b + c;
}
d_a[threadIdx.x] = a;
}
int main(){
cout << "Number_of_Warps"<<" "<< "Number_of_Threads" <<" "<<"Throughput" << endl;
for(int nThreads=WARP_SIZE; nThreads <= BLOCK_SIZE; nThreads += WARP_SIZE) {
//start timing
float time_elapsed=0;
cudaEvent_t start,end;
cudaEventCreate(&start);
cudaEventCreate(&end);
cudaEventRecord(start,0);
// run kernel
kernel<<<1, nThreads>>>(1., 2., 3.);
if(cudaGetLastError() != cudaSuccess) {
cerr << "Launch error " << endl;
return(1);
}
cudaThreadSynchronize();
// Finish timing
cudaEventRecord(end,0);
cudaEventSynchronize(start);
cudaEventSynchronize(end);
cudaEventElapsedTime(&time_elapsed,start,end);
// print sub results
cout <
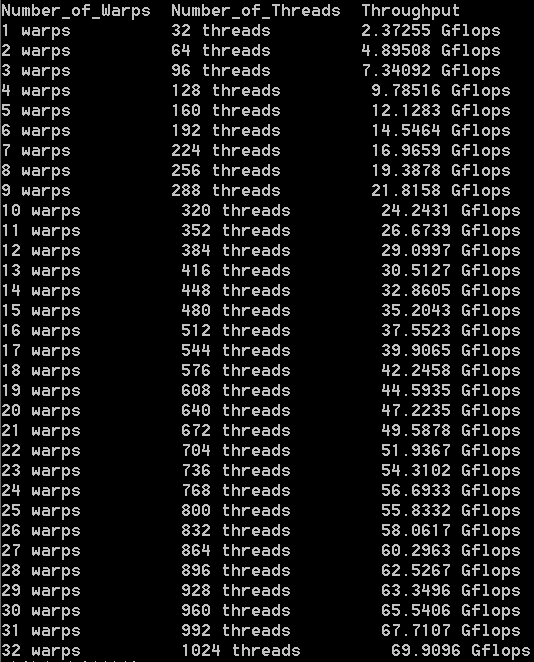
实验一测试结果
实验二:ILP-4 instructions per thread
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define NUM_ITERATIONS ( 1024 * 1024)
#define OP_COUNT 4*2*NUM_ITERATIONS
#define WARP_SIZE 32
#define BLOCK_SIZE 1024
__device__ float d_a[32], d_d[32];
__device__ float d_e[32], d_f[32];
__global__ void kernel(float a, float b, float c){
register float d=a, e=a, f=a;
#pragma unroll 16
for(int i=0; i < NUM_ITERATIONS; i++) {
a = a * b + c;
d = d * b + c;
e = e * b + c;
f = f * b + c;
}
d_a[threadIdx.x] = a;
d_d[threadIdx.x] = d;
d_e[threadIdx.x] = e;
d_f[threadIdx.x] = f;
}
int main(){
cout << "Number_of_Warps"<<" "<< "Number_of_Threads" <<" "<<"Throughput" << endl;
for(int nThreads=WARP_SIZE; nThreads <= BLOCK_SIZE; nThreads += WARP_SIZE) {
//start timing
float time_elapsed=0;
cudaEvent_t start,end;
cudaEventCreate(&start);
cudaEventCreate(&end);
cudaEventRecord(start,0);
// run kernel
kernel<<<1, nThreads>>>(1., 2., 3.);
if(cudaGetLastError() != cudaSuccess) {
cerr << "Launch error " << endl;
return(1);
}
cudaThreadSynchronize();
// Finish timing
cudaEventRecord(end,0);
cudaEventSynchronize(start);
cudaEventSynchronize(end);
cudaEventElapsedTime(&time_elapsed,start,end);
// print sub results
cout <
实验二测试结果
实验三:ILP-21 instructions per thread
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define NUM_ITERATIONS ( 1024 * 1024)
#define OP_COUNT 21*2*NUM_ITERATIONS
#define WARP_SIZE 32
#define BLOCK_SIZE 1024
__device__ float d_d[32];
__device__ float d_e[32];
__device__ float d_f[32];
__device__ float d_g[32];
__device__ float d_h[32];
__device__ float d_j[32];
__device__ float d_k[32];
__device__ float d_l[32];
__device__ float d_m[32];
__device__ float d_n[32];
__device__ float d_o[32];
__device__ float d_p[32];
__device__ float d_q[32];
__device__ float d_r[32];
__device__ float d_s[32];
__device__ float d_u[32];
__device__ float d_v[32];
__device__ float d_w[32];
__device__ float d_x[32];
__device__ float d_y[32];
__device__ float d_z[32];
__global__ void kernel(float a, float b, float c){
register float d, e, f, g, h, j, k, l, n, m, o, p, q, r, s, u, v, w, x, y, z;
for(int i=0; i < NUM_ITERATIONS; i++) {
d = a * b + c;
e = a * b + c;
f = a * b + c;
g = a * b + c;
h = a * b + c;
j = a * b + c;
k = a * b + c;
l = a * b + c;
m = a * b + c;
n = a * b + c;
o = a * b + c;
p = a * b + c;
q = a * b + c;
r = a * b + c;
s = a * b + c;
u = a * b + c;
v = a * b + c;
w = a * b + c;
x = a * b + c;
y = a * b + c;
z = a * b + c;
}
d_d[threadIdx.x] = d;
d_e[threadIdx.x] = e;
d_f[threadIdx.x] = f;
d_g[threadIdx.x] = g;
d_h[threadIdx.x] = h;
d_j[threadIdx.x] = j;
d_k[threadIdx.x] = k;
d_l[threadIdx.x] = l;
d_m[threadIdx.x] = m;
d_n[threadIdx.x] = n;
d_o[threadIdx.x] = o;
d_p[threadIdx.x] = p;
d_q[threadIdx.x] = q;
d_r[threadIdx.x] = r;
d_s[threadIdx.x] = s;
d_u[threadIdx.x] = u;
d_v[threadIdx.x] = v;
d_w[threadIdx.x] = w;
d_x[threadIdx.x] = x;
d_y[threadIdx.x] = y;
d_z[threadIdx.x] = z;
}
int main(){
cout << "Number_of_Warps"<<" "<< "Number_of_Threads" <<" "<<"Throughput" << endl;
for(int nThreads=WARP_SIZE; nThreads <= BLOCK_SIZE; nThreads += WARP_SIZE) {
//start timing
float time_elapsed=0;
cudaEvent_t start,end;
cudaEventCreate(&start);
cudaEventCreate(&end);
cudaEventRecord(start,0);
// run kernel
kernel<<<1, nThreads>>>(1., 2., 3.);
if(cudaGetLastError() != cudaSuccess) {
cerr << "Launch error " << endl;
return(1);
}
cudaThreadSynchronize();
// Finish timing
cudaEventRecord(end,0);
cudaEventSynchronize(start);
cudaEventSynchronize(end);
cudaEventElapsedTime(&time_elapsed,start,end);
// print sub results
cout <
实验三测试结果
实验总结
在寄存器数目能力范围内,随着一个线程内可并行指令条数的增加,throughput以S型曲线的形式在不断增加。