CTF密码学之SM4
介绍
SM4.0(原名SMS4.0)是中华人民共和国政府采用的一种分组密码标准,由国家密码管理局于2012年3月21日发布。相关标准为“GM/T 0002-2012《SM4分组密码算法》(原SMS4分组密码算法)”。在商用密码体系中,SM4主要用于数据加密,其算法公开,分组长度与密钥长度均为128bit,加密算法与密钥扩展算法都采用32轮非线性迭代结构,S盒为固定的8比特输入8比特输出。SM4.0中的指令长度被提升到大于64K(即64×1024)的水平,这是SM 3.0规格(渲染指令长度允许大于512)的128倍。
加密过程
这里我简要介绍一下SM4算法,详细的过程可以查看参考链接,首先我们要知道SM4是一个对称加密算法,也就是说加密和解密的密钥相同,首先我们要清楚下面几个概念
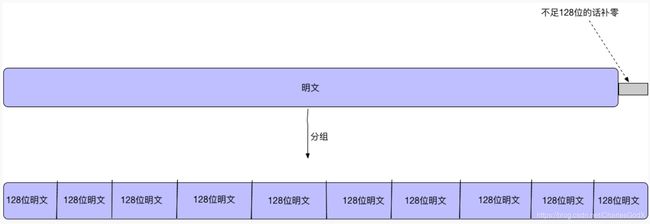
- SM4是分组密码,所以我们要将明文分组,将明文分成128位一组
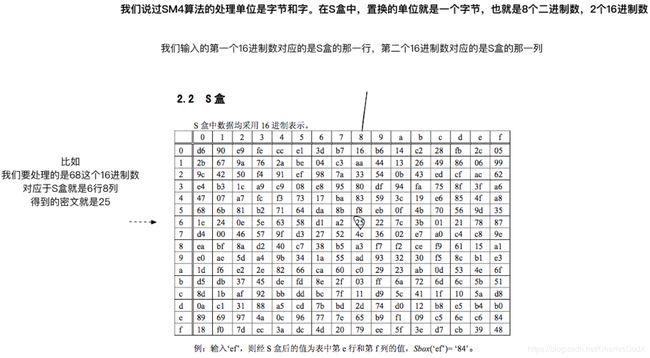
- S(Sbox)盒负责置换我们的明文
-
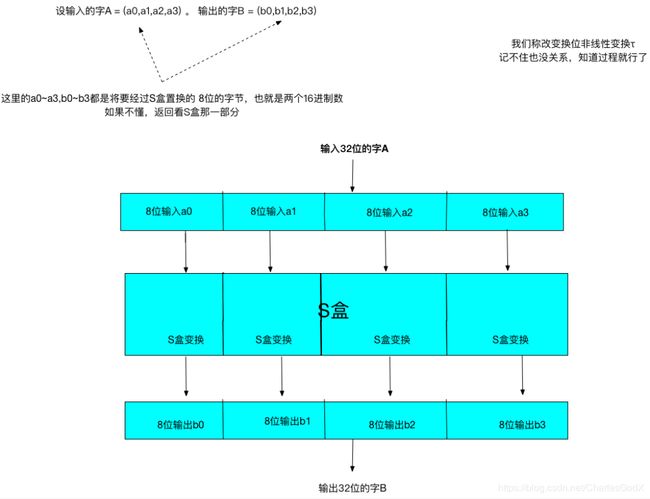
因为SM4面向的是32bit的字(word),S盒处理的是两个16进制数也就是8bit的字节,所以我们要用4个S盒来置换
-
轮函数F的概念如下图,以字为单位进行加密运算,称一次迭代运算为一轮变换
-
合成置换T就是非线性变换和线性变换的一个组合过程
了解上述一些概念之后加密解密的过程如下图

在SM4算法中,轮秘钥的产生是通过用户选择主秘钥作为基本的秘钥数据,在通过一些算法生成轮秘钥,在密钥拓展中,我们通过一些常数对用户选择的主钥进行操作,增大随机性。密钥扩展算法如下
实现
代码出自这里
sm4.c加密解密函数的实现
// sm4.c
// Test vector 1
// plain: 01 23 45 67 89 ab cd ef fe dc ba 98 76 54 32 10
// key: 01 23 45 67 89 ab cd ef fe dc ba 98 76 54 32 10
// round key and temp computing result:
// rk[ 0] = f12186f9 X[ 0] = 27fad345
// rk[ 1] = 41662b61 X[ 1] = a18b4cb2
// rk[ 2] = 5a6ab19a X[ 2] = 11c1e22a
// rk[ 3] = 7ba92077 X[ 3] = cc13e2ee
// rk[ 4] = 367360f4 X[ 4] = f87c5bd5
// rk[ 5] = 776a0c61 X[ 5] = 33220757
// rk[ 6] = b6bb89b3 X[ 6] = 77f4c297
// rk[ 7] = 24763151 X[ 7] = 7a96f2eb
// rk[ 8] = a520307c X[ 8] = 27dac07f
// rk[ 9] = b7584dbd X[ 9] = 42dd0f19
// rk[10] = c30753ed X[10] = b8a5da02
// rk[11] = 7ee55b57 X[11] = 907127fa
// rk[12] = 6988608c X[12] = 8b952b83
// rk[13] = 30d895b7 X[13] = d42b7c59
// rk[14] = 44ba14af X[14] = 2ffc5831
// rk[15] = 104495a1 X[15] = f69e6888
// rk[16] = d120b428 X[16] = af2432c4
// rk[17] = 73b55fa3 X[17] = ed1ec85e
// rk[18] = cc874966 X[18] = 55a3ba22
// rk[19] = 92244439 X[19] = 124b18aa
// rk[20] = e89e641f X[20] = 6ae7725f
// rk[21] = 98ca015a X[21] = f4cba1f9
// rk[22] = c7159060 X[22] = 1dcdfa10
// rk[23] = 99e1fd2e X[23] = 2ff60603
// rk[24] = b79bd80c X[24] = eff24fdc
// rk[25] = 1d2115b0 X[25] = 6fe46b75
// rk[26] = 0e228aeb X[26] = 893450ad
// rk[27] = f1780c81 X[27] = 7b938f4c
// rk[28] = 428d3654 X[28] = 536e4246
// rk[29] = 62293496 X[29] = 86b3e94f
// rk[30] = 01cf72e5 X[30] = d206965e
// rk[31] = 9124a012 X[31] = 681edf34
// cypher: 68 1e df 34 d2 06 96 5e 86 b3 e9 4f 53 6e 42 46
//
// test vector 2
// the same key and plain 1000000 times coumpting
// plain: 01 23 45 67 89 ab cd ef fe dc ba 98 76 54 32 10
// key: 01 23 45 67 89 ab cd ef fe dc ba 98 76 54 32 10
// cypher: 59 52 98 c7 c6 fd 27 1f 04 02 f8 04 c3 3d 3f 66
#include "sm4.h"
#include sm4.h头文件,mode选择加密模式
/**
* \file sm4.h
*/
#ifndef XYSSL_SM4_H
#define XYSSL_SM4_H
#define SM4_ENCRYPT 1
#define SM4_DECRYPT 0
/**
* \brief SM4 context structure
*/
typedef struct
{
int mode; /*!< encrypt/decrypt */
unsigned long sk[32]; /*!< SM4 subkeys */
}
sm4_context;
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/**
* \brief SM4 key schedule (128-bit, encryption)
*
* \param ctx SM4 context to be initialized
* \param key 16-byte secret key
*/
void sm4_setkey_enc(sm4_context *ctx, unsigned char key[16]);
/**
* \brief SM4 key schedule (128-bit, decryption)
*
* \param ctx SM4 context to be initialized
* \param key 16-byte secret key
*/
void sm4_setkey_dec(sm4_context *ctx, unsigned char key[16]);
/**
* \brief SM4-ECB block encryption/decryption
* \param ctx SM4 context
* \param mode SM4_ENCRYPT or SM4_DECRYPT
* \param length length of the input data
* \param input input block
* \param output output block
*/
void sm4_crypt_ecb(sm4_context *ctx,
int mode,
int length,
unsigned char *input,
unsigned char *output);
/**
* \brief SM4-CBC buffer encryption/decryption
* \param ctx SM4 context
* \param mode SM4_ENCRYPT or SM4_DECRYPT
* \param length length of the input data
* \param iv initialization vector (updated after use)
* \param input buffer holding the input data
* \param output buffer holding the output data
*/
void sm4_crypt_cbc(sm4_context *ctx,
int mode,
int length,
unsigned char iv[16],
unsigned char *input,
unsigned char *output);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /* sm4.h */
测试代码
// test.c
#include 运行结果如下
C:\Users\thunder>"D:\AlgorithmTest.exe"
68 1e df 34 d2 06 96 5e 86 b3 e9 4f 53 6e 42 46
01 23 45 67 89 ab cd ef fe dc ba 98 76 54 32 10
59 52 98 c7 c6 fd 27 1f 04 02 f8 04 c3 3d 3f 66
解密
pysm4是国密SM4算法的Python实现,这里下载
>>> from pysm4 import encrypt, decrypt
# 明文
>>> clear_num = 0x0123456789abcdeffedcba9876543210
# 密钥
>>> mk = 0x0123456789abcdeffedcba9876543210
# 加密
>>> cipher_num = encrypt(clear_num, mk)
>>> hex(cipher_num)[2:].replace('L', '')
'681edf34d206965e86b3e94f536e4246'
# 解密
>>> clear_num == decrypt(cipher_num, mk)
True
>>>
辨别
CTF逆向可以通过判断S盒的值来猜测SM4算法,通过S盒生成4个8位的字符,我们将上面实现代码放入IDA中查看,我们可以通过输入明文密钥的格式来猜测SM4算法
__int64 main()
{
int v0; // edx
__int64 v1; // ST0C_8
unsigned int i; // [esp+D0h] [ebp-E0h]
sm4_context ctx; // [esp+DCh] [ebp-D4h]
char output[16]; // [esp+168h] [ebp-48h]
char input[16]; // [esp+180h] [ebp-30h]
char key[16]; // [esp+198h] [ebp-18h]
key[0] = 1;
key[1] = 0x23;
key[2] = 0x45;
key[3] = 0x67;
key[4] = 0x89u;
key[5] = 0xABu;
key[6] = 0xCDu;
key[7] = 0xEFu;
key[8] = 0xFEu;
key[9] = 0xDCu;
key[10] = 0xBAu;
key[11] = 0x98u;
key[12] = 0x76;
key[13] = 0x54;
key[14] = 0x32;
key[15] = 0x10;
input[0] = 1;
input[1] = 0x23;
input[2] = 0x45;
input[3] = 0x67;
input[4] = 0x89u;
input[5] = 0xABu;
input[6] = 0xCDu;
input[7] = 0xEFu;
input[8] = 0xFEu;
input[9] = 0xDCu;
input[10] = 0xBAu;
input[11] = 0x98u;
input[12] = 0x76;
input[13] = 0x54;
input[14] = 0x32;
input[15] = 0x10;
j__sm4_setkey_enc(&ctx, key);
j__sm4_crypt_ecb(&ctx, 1, 16, input, output);
for ( i = 0; i < 0x10; ++i )
_printf("%02x ", (unsigned __int8)output[i]);
_printf("\n");
j__sm4_setkey_dec(&ctx, key);
j__sm4_crypt_ecb(&ctx, 0, 16, output, output);
for ( i = 0; i < 0x10; ++i )
_printf("%02x ", (unsigned __int8)output[i]);
_printf("\n");
i = 0;
j__sm4_setkey_enc(&ctx, key);
while ( i < 0xF4240 )
{
j__sm4_crypt_ecb(&ctx, 1, 16, input, input);
++i;
}
for ( i = 0; i < 0x10; ++i )
_printf("%02x ", (unsigned __int8)input[i]);
_printf("\n");
HIDWORD(v1) = v0;
LODWORD(v1) = 0;
return v1;
}
算法中的T变换观察返回值也有很明显的特征
unsigned int __cdecl sm4F(unsigned int x0, unsigned int x1, unsigned int x2, unsigned int x3, unsigned int rk)
{
return x0 ^ (unsigned __int64)sm4Lt(rk ^ x3 ^ x2 ^ x1); //返回多组异或
}
/************************************************************************************************/
__int64 __cdecl sm4Lt(unsigned int ka)
{
unsigned __int8 b; // STD8_1
unsigned __int8 b_1; // STD9_1
unsigned __int8 b_2; // STDA_1
unsigned __int8 v4; // al
unsigned int bb; // STFC_4
__int64 v6; // ST00_8
b = sm4Sbox(SHIBYTE(ka));
b_1 = sm4Sbox(SBYTE2(ka));
b_2 = sm4Sbox(SBYTE1(ka));
v4 = sm4Sbox(ka);
bb = v4 | (b_2 << 8) | (b_1 << 16) | (b << 24); // 分4组每组8位计算
HIDWORD(v6) = (bb >> 8) | (bb << 24);
LODWORD(v6) = HIDWORD(v6) ^ ((bb >> 14) | (bb << 18)) ^ ((bb >> 22) | (bb << 10)) ^ bb ^ ((bb >> 30) | 4 * bb);
return v6;
}
例题
2019ciscn-bbvvmm
下面的代码和上面的对比可以很容易的猜到SM4
unsigned __int64 __fastcall sub_400EE2(__int64 a1, __int64 a2, __int64 a3, __int64 a4, __int64 a5)
{
return a1 ^ sub_400D87(a5 ^ a4 ^ a3 ^ a2);
}
/************************************************************************************************/
__int64 __cdecl sm4Lt(unsigned int ka)
{
unsigned __int8 b; // STD8_1
unsigned __int8 b_1; // STD9_1
unsigned __int8 b_2; // STDA_1
unsigned __int8 v4; // al
unsigned int bb; // STFC_4
__int64 v6; // ST00_8
b = sm4Sbox(SHIBYTE(ka));
b_1 = sm4Sbox(SBYTE2(ka));
b_2 = sm4Sbox(SBYTE1(ka));
v4 = sm4Sbox(ka);
bb = v4 | (b_2 << 8) | (b_1 << 16) | (b << 24);
HIDWORD(v6) = (bb >> 8) | (bb << 24);
LODWORD(v6) = HIDWORD(v6) ^ ((bb >> 14) | (bb << 18)) ^ ((bb >> 22) | (bb << 10)) ^ bb ^ ((bb >> 30) | 4 * bb);
return v6;
}
参考链接:
https://neuqzxy.github.io/2017/06/15/欣仔带你零基础入门SM4加密算法/
https://baike.baidu.com/item/SM4.0/3901780?fr=aladdin
https://max.book118.com/html/2018/1023/8017013004001130.shtm
https://blog.csdn.net/cg129054036/article/details/83012721