C++对象Json序列化最佳实践(基于Rapidjson库):C++内存对象和Json字符串互相转换
介绍:Rapidjson
Rapidjson库是C++对象序列化到Json字符串的非常好的工具,以效率著称,腾讯的人写的。
官方网站:点击打开链接
本文全部资源百度云
这个库的缺点(个人拙见):
1 暴露的细节相对较多:容器,迭代器,类型,成员函数,序列化,反序列化,都有非常细致的操作。这个给使用者带来记忆负担较重。至少需要同时暴露Value类型和Document类型才能完整的实现Object内部包含Object类型。但这个包装起来很麻烦。
2 使用移动语义和自动内存回收:这个是内存占用小的保障,但是光是移动语义就给使用者造成很多不便。移动语义当然提高了效率,但是和使用者的程序代码风格不能很好的融合。移动语义使得Document的管理的内存数据在Document释放的时候就被析构,Object内包含Object的时候不好像C++基础类型语义那样去赋值操作(赋值就是副本,不担心原对象释放)。为了既能够使用移动语义和Document自动管理内存,又能够使用子对象的数据赋值,本文实现的CJsonObject对象返回和设置子对象均使用std::shared_ptr
3 序列化的思路好,但是没有和反序列化很好的结合:
官网上的序列化实现的思路是仿照STL的思路,使用类似输出操作符重载的方式给类增加序列化的函数(而不是输出操作符重载),从而使得复杂的类型(包括类类型成员的)可以借助成员类型的序列化来实现自己的序列化。
这种方式好处是明显的,程序结构清晰,Rapidjson对现有代码的冲击最小,想序列化哪一个就实现个序列化的成员函数就行了。但是却没有发现反序列化的例子。反序列化就是将json字符串通过Parse来创建一个C++内存对象,从而使用这个内存对象。
其实和序列化的场景一样,大多数人使用json都是想让原有类型支持序列化和反序列化,而不是抛弃原有类型(原有类型存在于大量的已有代码中,这样冲击太大)
还有一种思路是:将Rapidjson视为反序列化的工具,需要反序列化的时候临时创建Document对象来实现。但是数据在Document中,要想让现有C++类拿到这些数据,还是要一个一个的GetInt,GetBool,GetDouble等取出来再赋值给现有C++对象。这个是无法忍受的,只能再实现一套帮助类来做转换。这样增加了一批帮助类其实也是负担,而且程序代码分散而不集中。
本文的思路:
1 借鉴Rapidjson序列化的思路,让需要序列化的类自己实现统一的(通过实现基类CJsonBase来做到)序列化和反序列化成员函数。这样对现有代码的冲击最小,需要新写的代码量最小,最大程度的保护的原有的C++业务类
2 为序列化和反序列化实现一个执行类:CJsonObject,该类型提供序列化和反序列化时的所有操作实现。包括:CreateFromJson,ToJson,Get/SetInt GetSetBool 等。
3 优点:对现有代码的冲击最小(只需要包含添加CJsonObject类即可);只针对对现有代码的序列化和反序列化场景(比如C++对象存储到Redis;公开接口API形式跟外部通信,等等)
本文示例代码:借鉴了官网的serialize.cpp实现
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "JsonObject.h"
#include "Person.h"
#include
#include
using namespace std;
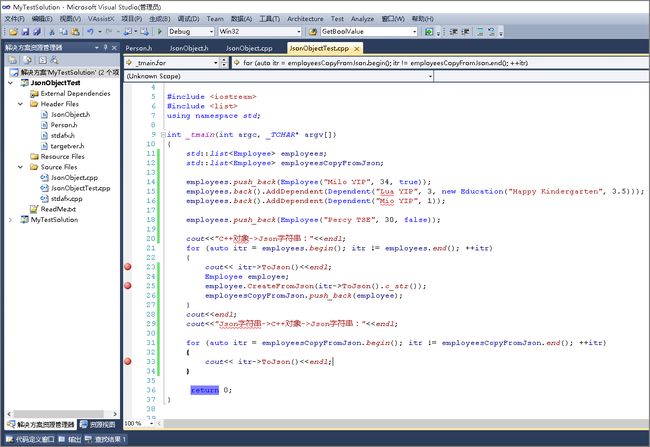
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
std::list employees;
std::list employeesCopyFromJson;
employees.push_back(Employee("Milo YIP", 34, true));
employees.back().AddDependent(Dependent("Lua YIP", 3, new Education("Happy Kindergarten", 3.5)));
employees.back().AddDependent(Dependent("Mio YIP", 1));
employees.push_back(Employee("Percy TSE", 30, false));
cout<<"C++对象->Json字符串:"<ToJson()<ToJson().c_str());
employeesCopyFromJson.push_back(employee);
}
cout<C++对象->Json字符串:"<ToJson()<
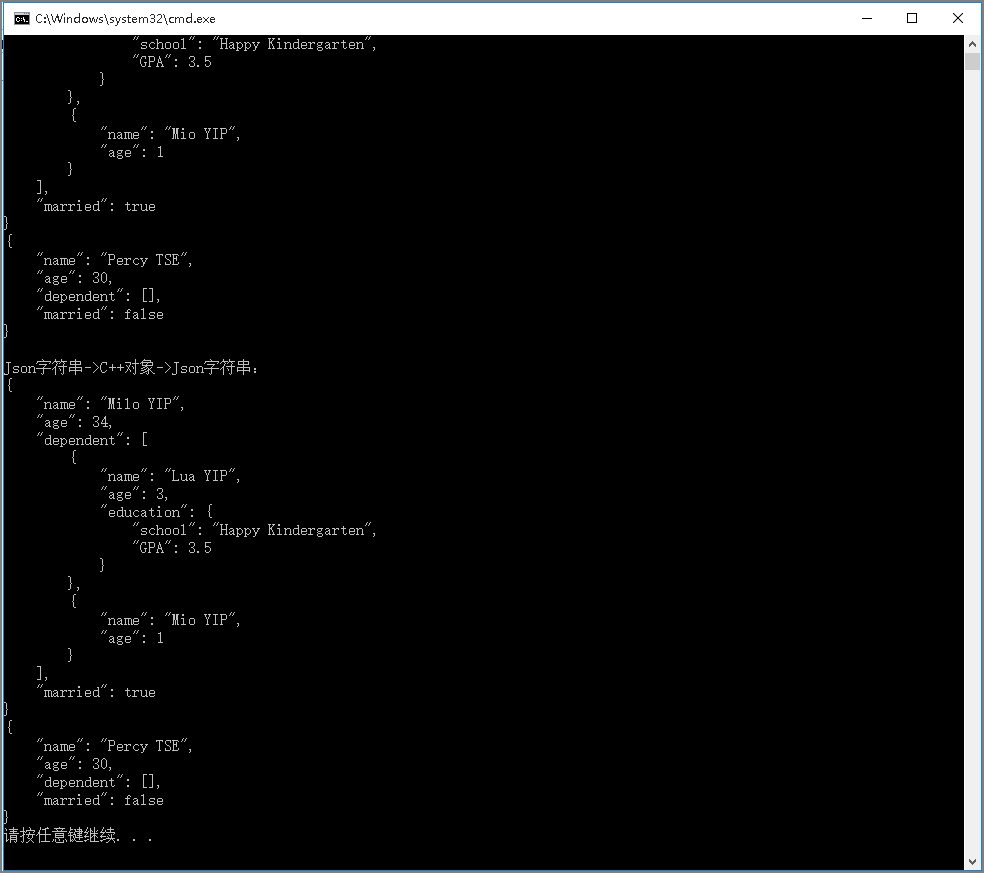
程序输出:
C++对象->Json字符串:
{
"name": "Milo YIP",
"age": 34,
"dependent": [
{
"name": "Lua YIP",
"age": 3,
"education": {
"school": "Happy Kindergarten",
"GPA": 3.5
}
},
{
"name": "Mio YIP",
"age": 1
}
],
"married": true
}
{
"name": "Percy TSE",
"age": 30,
"dependent": [],
"married": false
}
Json字符串->C++对象->Json字符串:
{
"name": "Milo YIP",
"age": 34,
"dependent": [
{
"name": "Lua YIP",
"age": 3,
"education": {
"school": "Happy Kindergarten",
"GPA": 3.5
}
},
{
"name": "Mio YIP",
"age": 1
}
],
"married": true
}
{
"name": "Percy TSE",
"age": 30,
"dependent": [],
"married": false
}
请按任意键继续. . .
附件:本文修改官网序列化示例代码的Person.h文件
#include
#include
#include
#include "JsonObject.h"
class Person : public CJsonObjectBase
{
public:
Person(void){}
Person(const std::string& name, unsigned age) : name_(name), age_(age) {}
Person(const Person& rhs) : name_(rhs.name_), age_(rhs.age_) {}
virtual ~Person();
//序列化
virtual std::string ToJson(void) const
{
CJsonObject json;
json.SetStringValue("name", name_);
json.SetULongValue("age", age_);
return json.ToJson();
}
//反序列化
virtual void CreateFromJson(const char* _json)
{
CJsonObject jsonObj;
jsonObj.CreateFromJson(_json);
name_ = jsonObj.GetStringValue("name");
age_ = jsonObj.GetULongValue("age");
}
Person& operator=(const Person& rhs) {
name_ = rhs.name_;
age_ = rhs.age_;
return *this;
}
public:
std::string name_;
unsigned age_;
};
Person::~Person() {
}
class Education : public CJsonObjectBase{
public:
Education(void) {}
Education(const std::string& school, double GPA) : school_(school), GPA_(GPA) {}
Education(const Education& rhs) : school_(rhs.school_), GPA_(rhs.GPA_) {}
//序列化
virtual std::string ToJson(void) const
{
CJsonObject json;
json.SetStringValue("school", school_);
json.SetDoubleValue("GPA", GPA_);
return json.ToJson();
}
//反序列化
virtual void CreateFromJson(const char* _json)
{
CJsonObject jsonObj;
jsonObj.CreateFromJson(_json);
school_ = jsonObj.GetStringValue("school");
GPA_ = jsonObj.GetDoubleValue("GPA");
}
public:
std::string school_;
double GPA_;
};
class Dependent : public Person {
public:
Dependent(void):education_(0){};
Dependent(const std::string& name, unsigned age, Education* education = 0) : Person(name, age), education_(education) {}
Dependent(const Dependent& rhs) : Person(rhs), education_(0) { education_ = (rhs.education_ == 0) ? 0 : new Education(*rhs.education_); }
virtual ~Dependent();
Dependent& operator=(const Dependent& rhs) {
if (this == &rhs)
return *this;
delete education_;
education_ = (rhs.education_ == 0) ? 0 : new Education(*rhs.education_);
return *this;
}
//序列化
virtual std::string ToJson(void) const
{
CJsonObject json;
json.CreateFromJson(Person::ToJson().c_str());
std::shared_ptr spEducationObj = std::make_shared();
if (education_ != nullptr)
{
spEducationObj->CreateFromJson(education_->ToJson().c_str());
json.SetObjectValue("education", spEducationObj);
}
else
{
//空指针的话,Json中根本就没这个成员
}
return json.ToJson();
}
//反序列化
virtual void CreateFromJson(const char* _json)
{
Person::CreateFromJson(_json);
CJsonObject jsonObj;
jsonObj.CreateFromJson(_json);
if (education_ != nullptr)
{
delete education_;
education_ = nullptr;
}
try
{
auto spEdution = jsonObj.GetObjectValue("education");
education_ = new Education;
education_->CreateFromJson(spEdution->ToJson().c_str());
}
catch (CJsonException e)
{
delete education_;
education_ = nullptr;
}
}
public:
Education *education_;
};
Dependent::~Dependent() {
delete education_;
}
class Employee : public Person {
public:
Employee(void){};
Employee(const std::string& name, unsigned age, bool married) : Person(name, age), dependents_(), married_(married) {}
Employee(const Employee& rhs) : Person(rhs), dependents_(rhs.dependents_), married_(rhs.married_) {}
virtual ~Employee();
//序列化
virtual std::string ToJson(void) const;
//反序列化
virtual void CreateFromJson(const char* _json);
Employee& operator=(const Employee& rhs) {
static_cast(*this) = rhs;
dependents_ = rhs.dependents_;
married_ = rhs.married_;
return *this;
}
void AddDependent(const Dependent& dependent) {
dependents_.push_back(dependent);
}
public:
std::vector dependents_;
bool married_;
};
Employee::~Employee() {
}
std::string Employee::ToJson(void) const
{
std::list> listJsonObj;
for (auto itr = dependents_.begin(); itr != dependents_.end(); ++itr)
{
std::shared_ptr pJsonDependent = std::make_shared();
pJsonDependent->CreateFromJson(itr->ToJson());
listJsonObj.push_back(pJsonDependent);
//listJsonObj.push_back(CJsonObject);//这种写法:复制到容器的副本会导致原来的对象析构
}
CJsonObject json;
json.CreateFromJson(Person::ToJson());
json.SetObjectListValue("dependent", listJsonObj);
json.SetBoolValue("married", married_);
std::string str = json.ToJson();
return std::move(str);
}
void Employee::CreateFromJson(const char* _json)
{
Person::CreateFromJson(_json);
CJsonObject jsonObj;
jsonObj.CreateFromJson(_json);
married_ = jsonObj.GetBoolValue("married");
auto listDependents = jsonObj.GetObjectListValue("dependent");
for (auto itr = listDependents.begin(); itr != listDependents.end(); ++itr)
{
Dependent dependent;
dependent.CreateFromJson((*itr)->ToJson().c_str());
this->dependents_.push_back(dependent);
}
}
全部资源:
有需要的扫描我头像加我即可。(付费资源哦!)