docker+rexray+minio s3fs对象存储
使用rexray挂载docker到minio
docker挂载本地比较简单,挂载到对象存储比如minio比较麻烦:
1 docker下pull好minio的image,并创建一个容器运行,访问地址为:http://172.17.0.2:9000
2 安装rexray:
sudo curl -sSL https://rexray.io/install | sh
3 编辑配置文件:/etc/rexray/config.yml,使用的是s3fs,所以文件如下:
libstorage:
service: s3fs
s3fs:
accessKey: **** #minio的key
secretKey: ****
region: us-east-1
endpoint: http://172.17.0.2:9000 #minio的访问路径
disablePathStyle: false
options:
- url=http://172.17.0.2:9000
- use_path_request_style
- nonempty
4 启动rexray服务:
service rexray start
5 创建volume(和docker容器挂载无关):
sudo rexray volume create testbucket --size=26 mount 创建的volume(和docker容器挂载无关):
sudo rexray volume mount volume testbucket[第5和第6步不用也可以直接第7步]
7 创建docker volume:
sudo docker volume create -d rexray --name testbucket
#-d 表示指定的volume驱动8 查看 volume:
sudo docker volume ls #如果没错,可看到上一步创建的testbucket
sudo docker volume inspect testbucket #看一下这个volume,Driver为rexray
9 验证::
通过docker API创建一个容器并启动,这里启用一个jupyter/notebook的容器:
container =client.create_container(str(container_),detach=True,command='jupyter notebook',host_config=client.create_host_config(binds=['testbucket:/notebooks'],port_bindings={8787: ('127.0.0.1', None)}))
client.start(container)
#通过host_config=client.create_host_config(binds=['testbucket:/notebooks'])命令将notebook的容器目录挂载到刚才创建的volume即testbucket上.
#动态创建bucket:
volume_tmp = client.create_volume(name='test_name', driver='rexray')
bucket_name=volume_tmp['Name']
container = client.create_container(str(container_),detach=True,command='jupyter notebook',host_config=client.create_host_config(binds=['%s:/notebooks'%(bucket_name)],port_bindings={8787: ('127.0.0.1', None)}))
'''
上面需要通过%s符号链接创建的bucket,如果直接写'bucket_name:/notebooks',则认为是bucket_name即是bucket的名字,容器无法挂载,而此处的bucket_name是个变量,指向name为test_name的bucket,所以通过%s可以将容器挂载到bucket_name表示的bucket即test_name上.
'''
通过返回的端口访问网页版notebook,创建一个文件1.txt
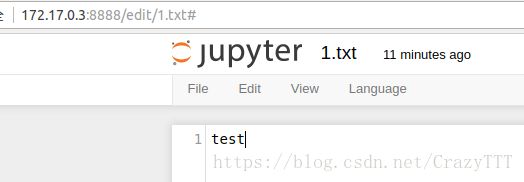
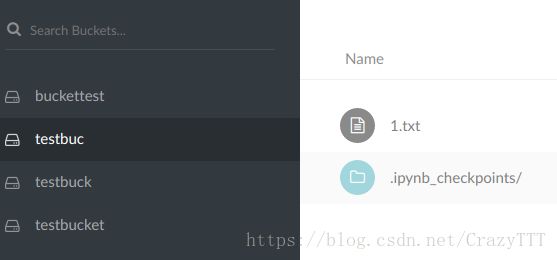
10 打开minio,即可在testbucket中看到该文件:
11 rexray创建的volume挂载在/var/lib/volumes/testbucket/下面,启动的容器挂载在目录下的./data下,容器删除后,./data随之删除,也就在本地不存在了.但是,已经同步到minio当中的文件不会变化,持久存储.