mybatis一级缓存的实现
我们使用mybatis与数据库进行交互,每开启一次和数据库的会话,都会创建一个SqlSession。
/**
* 获取Session
*
* @return
*/
public static SqlSession getSqlSession() {
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}在mybatis源码中DefaultSqlSessionFactory中,可以看到每次opensession都是new出来的。
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
在同一次会话中,如果我们执行相同的查询语句,mybatis并不会每次都去数据库中查询,query会先去一级缓存中根据cachekey拿到缓存,如果缓存为空,则再去数据库中查询。
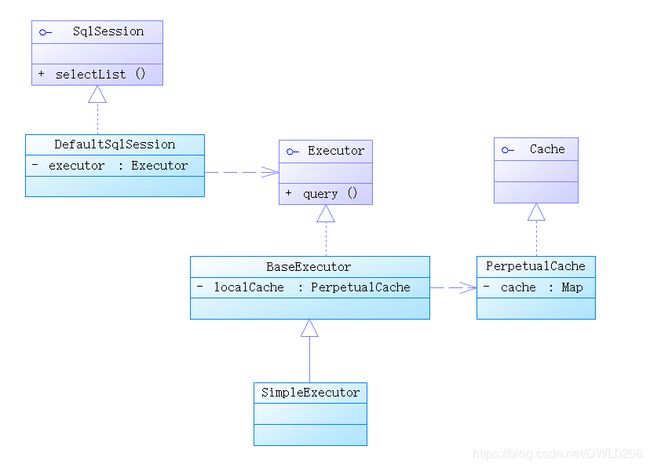
为了更好的理解一级缓存的实现,我画了UML图例,涉及到其中几个主要接口和实现类。
从上图中我们可以看到,每个sqlsession拥有一个executor,sqlsession并不会自己去执行sql,而是交给executor去执行,executor 对象中有一个类型为PerpetualCache的localCache,PerpetualCache实现了Cache接口,localCache即为sqlsession的一级缓存,这个PerpetualCache也不是什么高大上的东西,我们看看内部实现。
package org.apache.ibatis.cache.impl;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock;
import org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache;
import org.apache.ibatis.cache.CacheException;
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class PerpetualCache implements Cache {
private final String id;
private Map cache = new HashMap();
public PerpetualCache(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String getId() {
return id;
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return cache.size();
}
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
cache.put(key, value);
}
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
return cache.get(key);
}
@Override
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
return cache.remove(key);
}
@Override
public void clear() {
cache.clear();
}
@Override
public ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock() {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (getId() == null) {
throw new CacheException("Cache instances require an ID.");
}
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof Cache)) {
return false;
}
Cache otherCache = (Cache) o;
return getId().equals(otherCache.getId());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
if (getId() == null) {
throw new CacheException("Cache instances require an ID.");
}
return getId().hashCode();
}
}
PerpetualCache内部维护了一个map实现缓存,实现了cache的几个获取,移除方法。
打几个断点,执行一个查询方法,继续看看内部逻辑。
在DefaultSqlSession类中,select方法中将执行过程交给了executor。
@Override
public List selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
} 继续往下走,进入executor的query方法。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public List query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
//清空缓存
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List list;
try {
queryStack++;
//从一级缓存中获取数据
list = resultHandler == null ? (List) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
//缓存中没有数据,从数据库中获取数据
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
private List queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
//将数据库中获取的数据放入一级缓存
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
} 以上就是mybatis一级缓存实现的大致逻辑。