c语言回顾—数组与指针
**http://home.netcom.com/~tjensen/ptr/ch9x.htm**
#include 注意:1.char multi[5][10];
Let’s take the underlined part to be the “name” of an array. Then prepending the char and appending the [10] we have an array of 10 characters. But, the name multi[5] is itself an array indicating that there are 5 elements each being an array of 10 characters. Hence we have an array of 5 arrays of 10 characters each..
2.In fact, in general all dimensions of higher order than one are needed when dealing with multi-dimensional arrays. That is if we are talking about 3 dimensional arrays, the 2nd and 3rd dimension must be specified in the parameter definition.
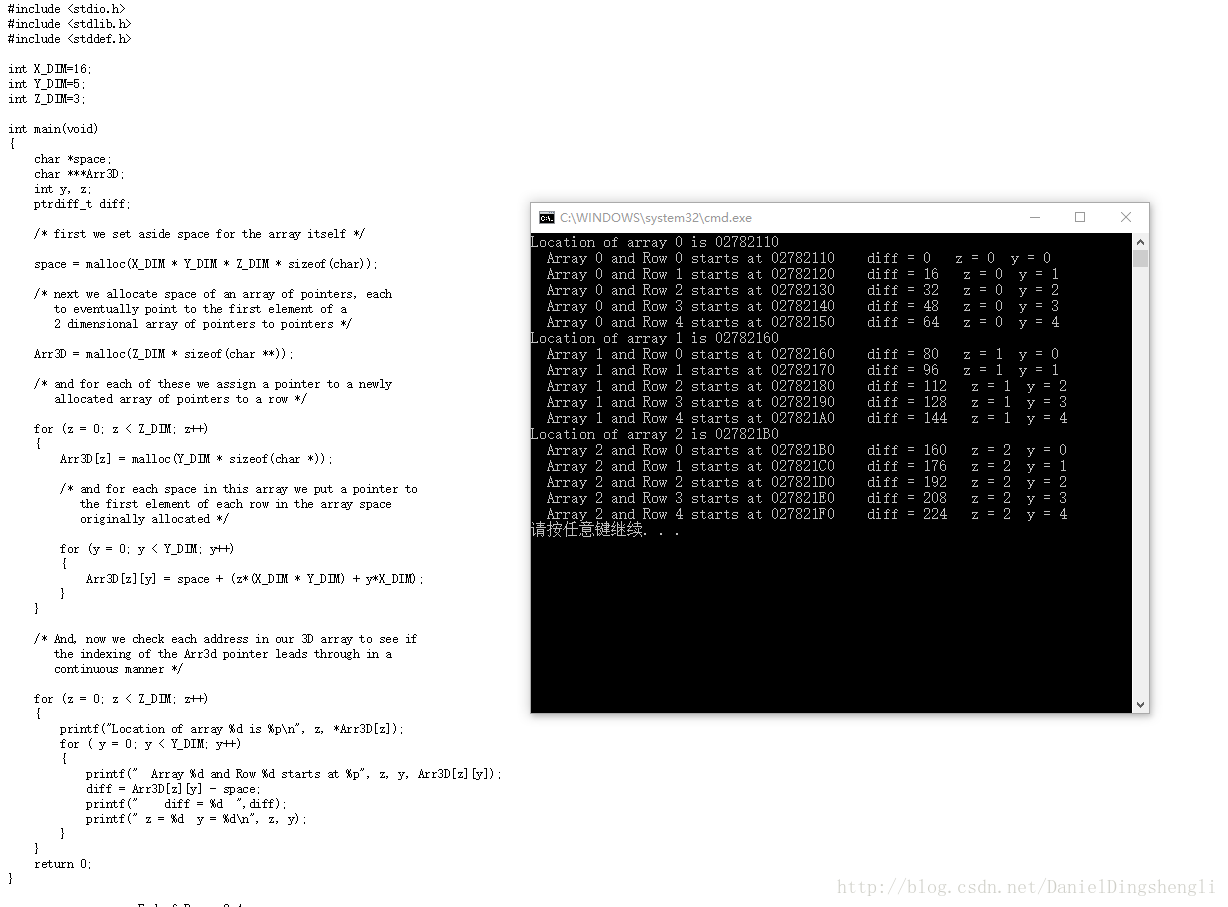
经典代码
指针和内存的动态分配
int** array_pointer;
array_pointer = (int **)malloc(r * sizeof(int*));
for (i=0; iint *)malloc(c * sizeof(int));
}
……
for(i = 0; i < r; i++) {
free(array_pointer[i]);
array_pointer[i] = NULL;
}
if (array_pointer != NULL) {
free(array_pointer);
}
return 0;
} //come from my code 方法2
核心代码
#include 三维数组的动态分配
#include 指向函数的指针
#include