python数据可视化
- 使用scatter()绘制一系列点
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x_values = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
y_values = [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
plt.scatter(x_values, y_values, s=100)
plt.title("Square Numbers", fontsize=24)
plt.xlabel("Value", fontsize=14)
plt.tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=14)
plt.show()
- 自动计算数据
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x_values = list(range(1, 1001))
y_values = [x**2 for x in x_values]
plt.scatter(x_values, y_values, s=40)
plt.title("Square Numbers", fontsize=24)
plt.xlabel("Value", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("Square of Value", fontsize=14)
plt.axis([0, 1100, 0, 1100000])
plt.show()
- 删除数据点的轮廓
plt.scatter(x_values, y_values, edgecolors='none', s=40)
- 自定义颜色
plt.scatter(x_values, y_values, c='red', edgecolors='none', s=40)
还可以使用RGB颜色模式自定义颜色。 例如,下面的代码创建一个由淡蓝色组成的散点图:
plt.scatter(x_values, y_values, c=(0, 0, 0.8), edgecolors='none', s=40)
- 使用颜色映射
颜色映射(colormap)时一些列颜色,用于突出数据的规律。
plt.scatter(x_values, y_values, c=y_values, cmap=plt.cm.Blues,
edgecolors='none', s=40)
- 自动保存图片
plt.savefig('squares_plot.png', bbox_inches='tight')
第一个实参表示文件名,第二个实参指定将图表多余的空白区域裁剪掉。
- 随机漫步
plot.py
from random import choice
class RandomWalk():
def __init__(self, num_points=5000):
self.num_points = num_points
self.x_values = [0]
self.y_values = [0]
def fill_walk(self):
while len(self.x_values) < self.num_points:
x_direction = choice([1, -1])
x_distance = choice([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
x_step = x_direction*x_distance
y_direction = choice([1, -1])
y_distance = choice([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
y_step = y_direction * y_distance
if x_step == 0 and y_step == 0:
continue
next_x = self.x_values[-1]+x_step
next_y = self.y_values[-1]+y_step
self.x_values.append(next_x)
self.y_values.append(next_y)
rw_visual.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from plot import RandomWalk
#创建一个RandomWalk实例,并将其包含的点都绘制出来
rw = RandomWalk()
rw.fill_walk()
plt.scatter(rw.x_values, rw.y_values, s=15)
plt.show()
- 模拟多次随机漫步
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from plot import RandomWalk
#创建一个RandomWalk实例,并将其包含的点都绘制出来
while True:
rw = RandomWalk()
rw.fill_walk()
plt.scatter(rw.x_values, rw.y_values, s=15)
plt.show()
keep_running = input("Make another walk? (y/n)")
if keep_running == 'n':
break
- 设置随机漫步图的样式
-
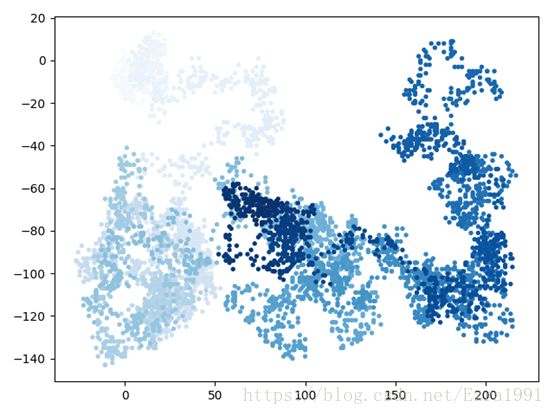
- 给点着色
plt.scatter(rw.x_values, rw.y_values, c=point_numbers,
cmap=plt.cm.Blues, edgecolor='none', s=15)
-
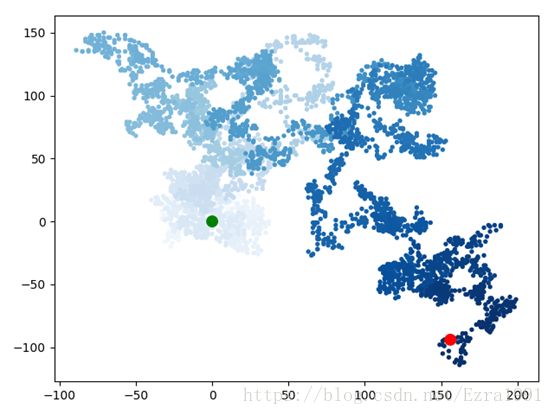
- 重新绘制起点和终点
着色:指出它们的先后顺序
还可以让起点和终点变得更大,并显示为不同的颜色。
plt.scatter(rw.x_values, rw.y_values, c=point_numbers,
cmap=plt.cm.Blues, edgecolor='none', s=15)
plt.scatter(0, 0, c='green', edgecolor='none', s=100)
plt.scatter(rw.x_values[-1], rw.y_values[-1], c='red',
edgecolor='none', s=100)
-
- 隐藏坐标轴
plt.axes().get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.axes().get_yaxis().set_visible(False)