ffmpeg 视频解码流程及对应API使用
1、ffmpeg解码流程
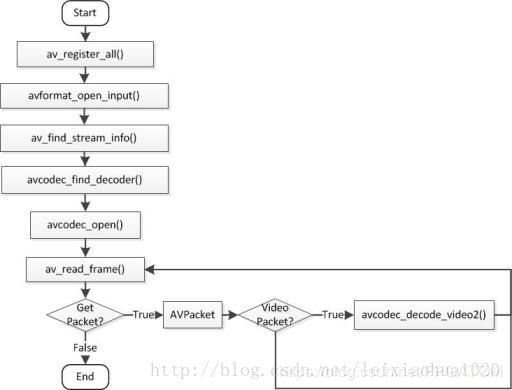
《1》、ffmpeg旧接口的解码流程
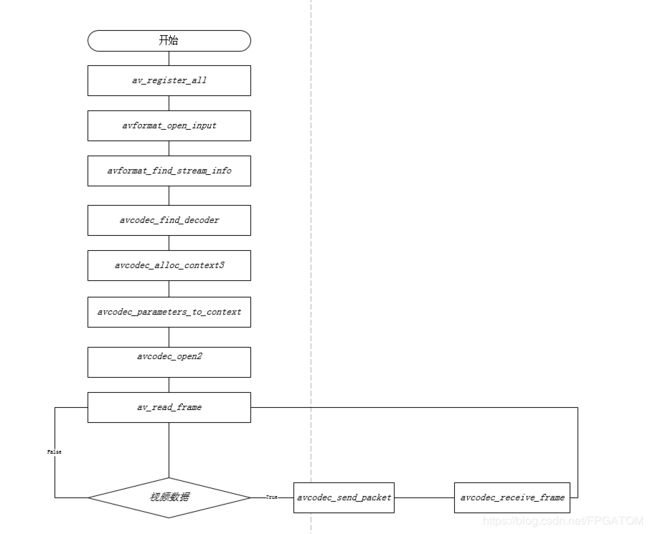
《2》、新接口解码流程
注意在新接口流程中使用avcodec_parameters_to_context函数来初始解码器参数,在未加入该步骤之前解析avi封装的mpeg4视频没问题但是解析MP4封装的mpeg4视频会报如下错误
Picture size is 0x00
加上该步骤后解决(解析wmv格式视频也必须加入这一步)
2、使用到的ffmpeg结构体及API说明
《1》、AVFormatContext结构体
该结构体描述了一个媒体文件或媒体流的构成和基本信息。它是一个贯穿始终的数据结构,很多函数调用需要使用到它。它也是FFMPEG解封装(flv,avi,mp4)功能的结构体。
其主要的几个变量(主要考虑解码情况):
struct AVInputFormat *iformat;//输入数据的封装格式。仅解封装用,由avformat_open_input()设置。
struct AVOutputFormat *oformat;//输出数据的封装格式。仅封装用,调用者在avformat_write_header()之前设置。
AVIOContext *pb;// I/O上下文。
解封装:由用户在avformat_open_input()之前设置(然后用户必须手动关闭它)或通过avformat_open_input()设置。
封装:由用户在avformat_write_header()之前设置。 调用者必须注意关闭/释放IO上下文。
unsigned int nb_streams;//AVFormatContext.streams中元素的个数。
AVStream **streams;//文件中所有流的列表。char filename[1024];//输入输出文件名。
int64_t start_time;//第一帧的位置。
int64_t duration;//流的持续时间
int64_t bit_rate;//总流比特率(bit / s),如果不可用则为0。
int64_t probesize;
//从输入读取的用于确定输入容器格式的数据的最大大小。
仅封装用,由调用者在avformat_open_input()之前设置。
AVDictionary *metadata;//元数据
AVCodec *video_codec;//视频编解码器
AVCodec *audio_codec;//音频编解码器
AVCodec *subtitle_codec;//字母编解码器
AVCodec *data_codec;//数据编解码器
int (*io_open)(struct AVFormatContext *s, AVIOContext **pb, const char *url, int flags, AVDictionary **options);
//打开IO stream的回调函数。
void (*io_close)(struct AVFormatContext *s, AVIOContext *pb);
//关闭使用AVFormatContext.io_open()打开的流的回调函数。
使用时可以通过avformat_alloc_context分配后使用,也可以直接avformat_open_input。
//1、方法一
AVFormatContext *fmt_ctx = NULL;
string filename = "test.avi" ;
fmt_ctx = avformat_alloc_context();
avformat_open_input(&fmt_ctx, ilename.c_str(), NULL, NULL);
avformat_close_input(&fmt_ctx);
//2、方法二
AVFormatContext *fmt_ctx = NULL;
string filename = "test.avi" ;
int ret = avformat_open_input(&fmt_ctx, filename.c_str(), NULL, NULL);
avformat_close_input(&fmt_ctx);
推荐使用方法2,因为若传进avformat_open_input的fmt_ctx为NULL,该函数内部会调用avformat_alloc_context函数。相应的avformat_close_input内部会调用avformat_free_context。
《2》、AVCodec
ffmpeg中的解码器及编码器都用AVCodec结构体保存一些编解码的配置信息。
对解码来说可以按照下面方式使用。
```
//解码H264流
AVCodec* Vcodec = NULL;
Vcodec = avcodec_find_decoder(AV_CODEC_ID_H264);
//或者直接通过解码器名字找到解码器
Vcodec = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name("h264_mediacodec");
```
《3》、AVCodecContext
该结构体用于存储编解码器上下文的数据结构,包含了众多编解码需要的参数信息。这些信息参数需要进行初始化,使用avcodec_parameters_to_context进行初始化。不初始化解析一些格式的封装视频会导致编解码失败。该结构体内很多参数是编码时使用的,解码用不上。
几个主要的成员:
enum AVMediaType codec_type:编解码器的类型(视频,音频...)
struct AVCodec *codec:采用的解码器AVCodec(H.264,MPEG2...)
int bit_rate:平均比特率
uint8_t *extradata; int extradata_size:针对特定编码器包含的附加信息(例如对于H.264解码器来说,存储SPS,PPS等)
AVRational time_base:根据该参数,可以把PTS转化为实际的时间(单位为秒s)
int width, height:如果是视频的话,代表宽和高
int refs:运动估计参考帧的个数(H.264的话会有多帧,MPEG2这类的一般就没有了)
int sample_rate:采样率(音频)
int channels:声道数(音频)
enum AVSampleFormat sample_fmt:采样格式
int profile:型(H.264里面就有,其他编码标准应该也有)
int level:级(和profile差不太多)
使用:
AVCodec* Vcodec = NULL;
Vcodec = avcodec_find_decoder(AV_CODEC_ID_H264);
AVCodecContext* AvContext = NULL;
AvContext = avcodec_alloc_context3(mVcodec);
avcodec_parameters_to_context(mAvContext,
fmt_ctx->streams[mVideoStreamIdx]->codecpar);
《4》、AVStream
该结构体用于描述一个流媒体,该结构体中大部分值域可以由avformat_open_input函数根据文件头的信息确定,缺少的信息需要通过调用av_find_stream_info进一步获得。
av_find_stream_info函数读取一部分音视频来获取有关视频文件的一些信息,如编码宽高、视频时长等。对于一些没有头部信息的视频文件(如mpeg编码的文件)调用该函数是必须的。调用该函数可能会带了很大的延迟。
延迟优化方法参考。
主要的成员域:
-
index/id:index对应流的索引,这个数字是自动生成的,根据index可以从AVFormatContext::streams表中索引到该流;而id则是流的标识,依赖于具体的容器格式。比如对于MPEG TS格式,id就是pid。
-
time_base:流的时间基准,是一个实数,该流中媒体数据的pts和dts都将以这个时间基准为粒度。通常,使用av_rescale/av_rescale_q可以实现不同时间基准的转换。
-
start_time:流的起始时间,以流的时间基准为单位,通常是该流中第一个帧的pts。
-
duration:流的总时间,以流的时间基准为单位。
-
need_parsing:对该流parsing过程的控制域。
-
nb_frames:流内的帧数目。
-
avg_frame_rate:帧率相关。
-
codec:指向该流对应的AVCodecContext结构,调用avformat_open_input时生成。
-
parser:指向该流对应的AVCodecParserContext结构,调用av_find_stream_info时生成。
《5》、AVIOContext
用于管理FFMPEG输入输出数据的结构体。
主要成员:
unsigned char *buffer:缓存开始位置
int buffer_size:缓存大小(默认32768)
unsigned char *buf_ptr:当前指针读取到的位置
unsigned char *buf_end:缓存结束的位置
void *opaque:URLContext结构体
在解码的情况下,buffer用于存储ffmpeg读入的数据。如打开一个视频文件时,先把数据从硬盘读入buffer,然后在送给解码器解码。
opaque按照这篇博客说是指向URLContext,找源码没有找到相关的赋值操作但是在aviobuf.c的下面这个函数找到佐证。
/*
typedef struct AVIOInternal {
URLContext *h;
} AVIOInternal;
*/
static void *ff_avio_child_next(void *obj, void *prev)
{
AVIOContext *s = obj;
AVIOInternal *internal = s->opaque;
return prev ? NULL : internal->h;
}
URLContext结构体中有一个URLProtocol。每种协议(rtp,rtmp,file,udp等)都有一个对应的URLProtocol。
《6》、AVPacket
该结构体是ffmpeg中很重要的一个结构体,它保存了解码后或编码前的数据(仍然是压缩数据)和这些数据的一些附加信息,如显示时间戳(pts)、数据时长、所在媒体的索引等。
对于视频来说,一个AVPacket通常包含一帧压缩数据,而音频则有可能包含多个压缩的Frame。
重要的成员变量:
- uint8_t *data:压缩编码的数据。
例如对于H.264来说。1个AVPacket的data通常对应一个NAL。
注意:在这里只是对应,而不是一模一样。他们之间有微小的差别:使用FFMPEG类库分离出多媒体文件中的H.264码流
因此在使用FFMPEG进行视音频处理的时候,常常可以将得到的AVPacket的data数据直接写成文件,从而得到视音频的码流文件。
- int size:data的大小
- int64_t pts:显示时间戳
- int64_t dts:解码时间戳
- int stream_index:标识该AVPacket所属的视频/音频流。
avpacket.h内有API说明,常用的几个API
av_packet_ref,av_packet_unref
av_new_packet, av_packet_alloc, av_init_packet, av_packet_unref,av_packet_free(free这个API为旧接口)
av_packet_clone:拷贝packet
《7》、AVFrame
AVFrame结构体一般用于存储原始数据(非压缩的YUV,RGB数据等),此外还包含一些相关信息,比如解码的时候存储宏块类型表,QP表,运动矢量等数据。
AVFrame必须用av_frame_alloc分配,用av_frame_free释放。注意av_frame_alloc函数只创建实例但是该实例存储数据的buffer则需要通过另外的操作进行分配,如av_image_fill_arrays
接口。
AVFrame内部几个常用的成员:
-
uint8_t *data[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]:解码后原始数据(对视频来说是YUV,RGB,对音频来说是PCM)
-
int linesize[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]:data中“一行”数据的大小。注意:未必等于图像的宽,一般大于图像的宽。
-
int width, height:视频帧宽和高(1920x1080,1280x720…)
-
int nb_samples:音频的一个AVFrame中可能包含多个音频帧,在此标记包含了几个
-
int format:解码后原始数据类型(YUV420,YUV422,RGB24…)
-
int key_frame:是否是关键帧
-
enum AVPictureType pict_type:帧类型(I,B,P…)
-
AVRational sample_aspect_ratio:宽高比(16:9,4:3…)
-
int64_t pts:显示时间戳
-
int coded_picture_number:编码帧序号
-
int display_picture_number:显示帧序号
-
int interlaced_frame:是否是隔行扫描
-
uint8_t motion_subsample_log2:一个宏块中的运动矢量采样个数,取log的
2、解码demo
AVCodecID strm_to_av_map_coding_type[STRM_CODEC_MAX] =
{
AV_CODEC_ID_NONE, //0
AV_CODEC_ID_H264, //1
AV_CODEC_ID_H265, //2
AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG1VIDEO, //3
AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG2VIDEO, //4
AV_CODEC_ID_MJPEG, //5
AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4 //6
};
AVPixelFormat strm_to_av_map_pixel_format[STRM_PIXFMT_MAX] =
{
AV_PIX_FMT_NONE,
AV_PIX_FMT_RGB24,
AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA,
AV_PIX_FMT_RGB565,
AV_PIX_FMT_ARGB,
AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P,
AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P,
AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P,
AV_PIX_FMT_GRAY8,
AV_PIX_FMT_NV21,
AV_PIX_FMT_UYVY422,
AV_PIX_FMT_YUYV422
};
static AVFrame* mVideoFrame = NULL;
static AVFrame* mFrameYUV = NULL;
// 颜色转换上下文
static struct SwsContext* mImgConvertCtx = NULL;
///< 解码器
static AVCodec* mVcodec = NULL;
///< 解码上下文
static AVCodecContext* mAvContext = NULL;
static AVFormatContext* mFormatCtx = NULL; // 用于读取文件
static int mVideoStreamIdx = 0;
int test_decode(unsigned int mInputCodecType, unsigned int mOutputPixelFormat,
string &filename, string &error)
{
FILE* fp_YUV = fopen("decode_out.yuv", "wb+");
if (!fp_YUV)
{
perror("open out.yuv :");
return -1;
}
av_register_all();
mVideoFrame = av_frame_alloc();
mFrameYUV = av_frame_alloc();
bool mHasKeyFrame = false;
AVPacket mPktPacket;
int ret = avformat_open_input(&mFormatCtx, filename.c_str(), NULL, NULL);
if (ret < 0)
{
printf("avformat_open_input fail \n");
error = "avformat_open_input fail";
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Cannot open file: %s.\n", filename.c_str());
return false;
}
if (avformat_find_stream_info(mFormatCtx, NULL) < 0)
{
return false;
}
av_dump_format(mFormatCtx, 0, filename.c_str(), 0);
//获取视频的编码信息
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < mFormatCtx->nb_streams; ++i)
{
if (mFormatCtx->streams[i]->codec->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO)
{
mVideoStreamIdx = i;
break;
}
}
// 寻找解码器
mVcodec = avcodec_find_decoder(strm_to_av_map_coding_type[mInputCodecType]);
mAvContext = avcodec_alloc_context3(mVcodec);
if (!mVcodec || !mAvContext)
{
return false;
}
///不初始化解码器context会导致MP4封装的mpeg4码流解码失败
ret = avcodec_parameters_to_context(mAvContext,
mFormatCtx->streams[mVideoStreamIdx]->codecpar);
if (ret < 0)
{
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Error initializing the decoder context.\n");
//exit_program(1);
}
// 打开解码器
mAvContext->pix_fmt = strm_to_av_map_pixel_format[mOutputPixelFormat];
if (avcodec_open2(mAvContext, mVcodec, NULL) != 0)
{
//DecoderDeinit();
return false;
}
//循环读入H264数据
AVPacket h264Pack;
while (1)
{
av_init_packet(&h264Pack);
int ret = av_read_frame(mFormatCtx, &h264Pack);
if (ret != 0)
{
error = "Read a frame failed";
av_packet_unref(&h264Pack);
return false;
}
else if (h264Pack.stream_index != mVideoStreamIdx)
{
// not a video packet, skip it in this version
av_packet_unref(&h264Pack);
continue;
}
{
// 初始化待解码包
av_init_packet(&mPktPacket);
mPktPacket.data = (uint8_t*)h264Pack.data; // 用于解码的压缩视频帧数据
mPktPacket.size = h264Pack.size;
mPktPacket.pts = h264Pack.pts;
mPktPacket.dts = h264Pack.dts;
// 发送待解码包
if (avcodec_send_packet(mAvContext, &mPktPacket))
{
error = "send packet failed";
mHasKeyFrame = false;
av_packet_unref(&mPktPacket);
return false;
}
av_packet_unref(&mPktPacket);
// 接收解码数据
int ret = avcodec_receive_frame(mAvContext, mVideoFrame);
if (ret != 0)
{
if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN))
{
// 暂时没有输出,需要更多输入
error = "need more data";
//return false;
continue;
}
}
DecodeFrameParams params;
params.mInputCodecType = mInputCodecType;
params.mOutputPixelFormat = mOutputPixelFormat;
int frameSize = av_image_get_buffer_size(strm_to_av_map_pixel_format[params.mOutputPixelFormat],
mVideoFrame->width, mVideoFrame->height, 1);
void* buf_ptr = NULL;
buf_ptr = (void*)new(std::nothrow) char[frameSize];
if (buf_ptr == NULL)
{
printf("decode memory allocation error! [buf_size = %d]\n", frameSize);
return false;
}
av_image_fill_arrays(mFrameYUV->data, mFrameYUV->linesize, (uint8_t*)buf_ptr,
strm_to_av_map_pixel_format[params.mOutputPixelFormat], mVideoFrame->width,
mVideoFrame->height, 1);
// 写文件保存视频数据
fwrite(buf_ptr, frameSize, 1, fp_YUV);
fflush(fp_YUV);
if(buf_ptr)
{
delete [] buf_ptr;
buf_ptr = NULL;
}
}
}
fclose(fp_YUV);
avformat_close_input(&mFormatCtx);
//printf("[strmsdk] decoder[%s] open successful.\n", mVcodec->name);
}
int main()
{
//解码demo -> YUV
string error;
string filename;
cout << "Input video: " << endl;
cin >> filename;
test_decode(6, 5, filename, error);
cout << "error: " << error << endl;
}
3、参考
《1》、ffmoeg解码流程1
《2》、ffmoeg解码流程2
《3》、ffmpeg3.0 编解码API
《4》、AVFormatContext结构体
《5》、AVCodecContext结构体
《6》、AVPacket
《7》、ffmpeg几个重要结构体间关系
《8》、AVFrame