搜索 ( 八数码问题详解:BFS,A*,IDA* )——Eight ( POJ 1077 )
参考文章:
1. DBFS,A*,IDA*,转自链接 (侵删)
2. 一份非常详细的实验报告:http://blog.csdn.net/ray58750034/article/details/599897#comments
题目链接:
http://poj.org/problem?id=2449分析:
又称为九宫格问题,给出一个状态的九宫格,判断是否有解,如果有则输出解。八数码问题有无解的结论:
一个状态表示成一维的形式,求出除0之外所有数字的逆序数之和(每个数字前面比它大的数字的个数的和,称为这个状态的逆序)。
若两个状态的逆序数奇偶性相同,则可相互到达,否则不可相互到达。由于原始状态的逆序为0(偶数),则逆序为偶数的状态有解。
证明:当左右移动空格时,逆序数不变。当上下移动空格时,相当于将一个数字向前(或向后)移动两格,跳过 的这两个数字要么都比它大(小),逆序可能±2;要么一个较大一个较小,逆序不变。所以可得结论:只要是相互可达的两个状态,它们的逆序奇偶性相同。详细的证明请参考:
http://blog.csdn.net/tiaotiaoyly/article/details/2008233
康拓展开(将每一种排列都康拓展开,得到与其唯一对应的一个数,是对于全排列的一种很好的哈希函数):
公式: X=an×(n−1)!+an−1×(n−2)!+...+ai×(i−1)!+...+a2×1!+a1×0! 其中,ai表示的是第i-1个数(从0开始数),在这个排列中的大小位置(从0开始计算)。
代码如下:
int fac[] = { 1,1,2,6,24,120,720,5040,40320 };//打表表示前几个数的阶乘。
int Cantor( int s[])//参数为排列。
{
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<9;i++)
{
int cnt = 0;
for(int j=i+1;j<9;j++)
{
if( s[i] > s[j] ) cnt++;
}
sum+=(cnt*fac[9-i-1]);
}
return sum+1;
}通过康拓逆展开生成与其对应的全排列:
如果已知一个排列的康拓展开数,那么可以使用辗转相除的方法得到这个排列中的每一个 ai :
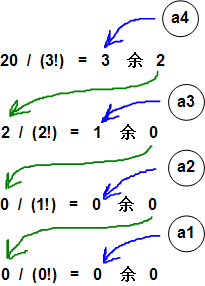
如果排列中的元素为A,B,C,D,那么a4 = 3表示剩余元素为4的时候它排在第三位(均从第0位开始计数),即D;a3 = 1表示剩余元素为3的时候它排再第一位,即B;a2 = 0表示剩余元素为2的时候它排在第0位,即A,最后一个a1就是C了。
BFS + 康拓展开 解决八数码问题:
#include else
printf("unsolvable\n");
}
return 0;
} 双向广搜 :
由于目标态和初始态都已知,可以采用从两个状态同时开始搜,当搜到同一个节点时,搜索结束,将两边的步数加起来输出。这道题里在每个节点,用一个值标记,此节点是由哪个状态访问的,故只需用一个队列交替扩展。双向广搜会少扩展许多节点,时间效率得到大幅提升。
#include A*搜索:
有两种可行的启发函数: 不在位数(difference)与曼哈顿距离(manhattan)
在每一个节点中,加一个int型变量存储此节点的估价。此时用优先队列存储节点。但是若启发函数效率不高,减少的扩展节点的时间可能还不足以抵过小顶堆调整的时间,结果就是时间效率可能比普通的bfs还差。
基于不在位函数的A*搜索:
#include 基于 manhattan距离函数的A*搜索:
#include IDA*搜索:
由于普通的深搜在此问题上,要么搜索到错误的结果,要么需要搜索所有的状态,才能确定是否是最优,故在这里使用IDA*。IDA*是一种迭代加深的深度搜索,若在此深度下没有搜到目标点,则将深度加一重新搜索。无须状态判重,无需估价排序,用不到哈希表,堆上也不必应用,空间需求变的超级少,实现也最简单。在深搜过程中,根据启发函数做剪枝,可以使效率达到很高。另外在求路径的时候,IDA*也是最方便的。
基于不在为函数的IDA*搜索:
#include 基于manhattan距离函数的搜索:
#include - 总结:
从效率上来看 IDA* > A* > DBFS > BFS+Canton >BFS ,其中,manhattan估价函数优余difference估价函数。