聊聊C++11标准库中堆(heap)算法的源码
STL中支持堆操作,对外暴露了std::make_heap,std::push_heap,std::pop_heap,std::sort_heap,std::is_heap,std::is_heap_until这6个函数,详细的使用方法可以参见图解STL中算法的分类、简介及其Demo。
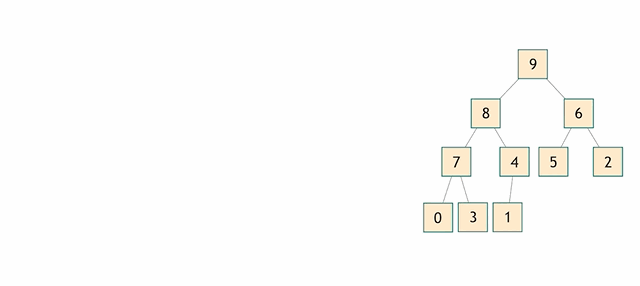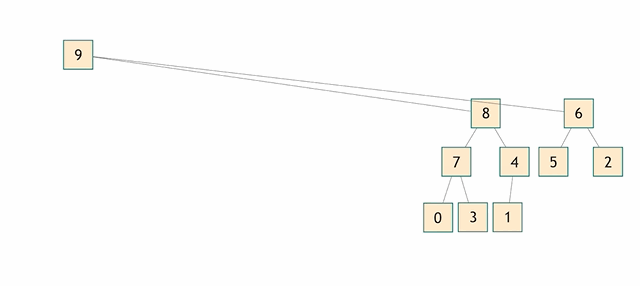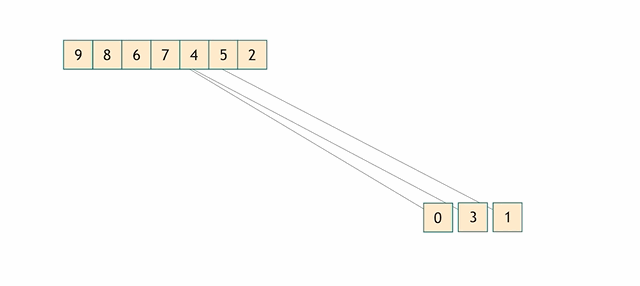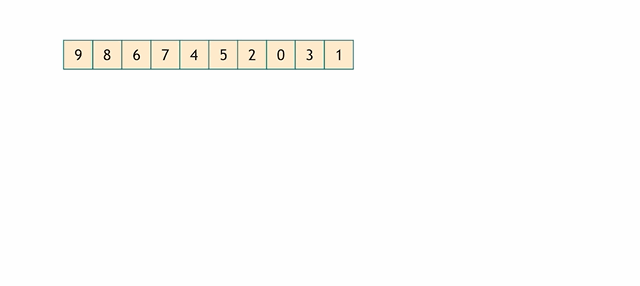
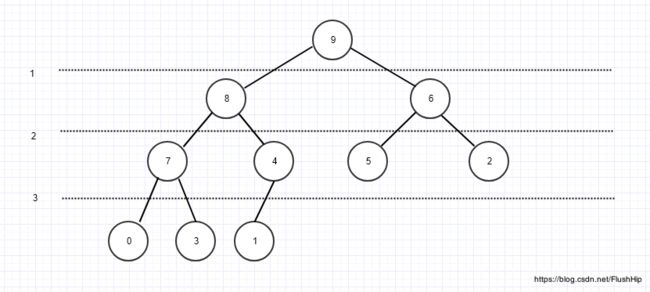
这里我简单一下讲一下我对堆这种数据结构的理解,首先,堆是完全二叉树,这意味着堆可以很方便用数组这种数据结构来表示,看下图:
其次,以大顶堆为例子,最大的元素永远在二叉树的根,根到二叉树的叶子的每条路径都是降序的,因此,调整堆的操作就是在这些路径上做插入排序。
声明一下,以下所有源码都来自MinGW中的stl_heap.h,我弄了下代码的格式化和写了点注释。
标准库中的代码写的很好,包括变量的命名,都是很形象的。比如holeIndex,“洞的下标”。
push_heap
/**
* @brief Push an element onto a heap.
* @param __first Start of heap.
* @param __last End of heap + element.
* @ingroup heap_algorithms
*
* This operation pushes the element at last-1 onto the valid heap
* over the range [__first,__last-1). After completion,
* [__first,__last) is a valid heap.
*/
template <typename _RandomAccessIterator>
inline void
push_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last)
/*
template
inline void
push_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last, _Compare __comp)
*/
{
typedef typename iterator_traits<_RandomAccessIterator>::value_type _ValueType;
typedef typename iterator_traits<_RandomAccessIterator>::difference_type _DistanceType;
_ValueType __value = std::move(*(__last - 1));
std::__push_heap(__first, _DistanceType((__last - __first) - 1),
_DistanceType(0), std::move(__value),
__gnu_cxx::__ops::__iter_less_val());
// __gnu_cxx::__ops::__iter_comp_val(__comp));
}
这里把最后一个元素,也就是新加入堆的元素(最后一个叶子结点)打了个洞,利用std::move,这样,最后一个位置是没有值的,这相当于是一个空洞;
template <typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Distance, typename _Tp, typename _Compare>
void
__push_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first,
_Distance __holeIndex, _Distance __topIndex, _Tp __value,
_Compare __comp)
{
_Distance __parent = (__holeIndex - 1) / 2;
while (__holeIndex > __topIndex && __comp(__first + __parent, __value))
{
*(__first + __holeIndex) = std::move(*(__first + __parent));
__holeIndex = __parent;
__parent = (__holeIndex - 1) / 2;
}
*(__first + __holeIndex) = std::move(__value);
}
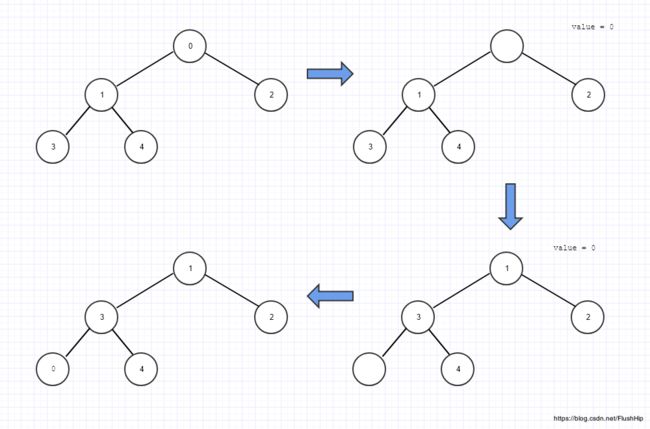
由于出现了空洞,因此需要元素来填上空洞,而且,新加入进来的元素只会影响一条路径(叶子结点到根节点的路径),因此只要在这条路径上做插入排序就好了,把父亲结点移动到孩子结点直到这条路径上满足堆的性质,这样可以填洞,但是又会把父亲结点弄成洞,所以最后用新加入的元素填住最后的洞,其实就是个向上的插入排序。这样,就把新加入的元素融入了堆。
pop_heap
/**
* @brief Pop an element off a heap.
* @param __first Start of heap.
* @param __last End of heap.
* @pre [__first, __last) is a valid, non-empty range.
* @ingroup heap_algorithms
*
* This operation pops the top of the heap. The elements __first
* and __last-1 are swapped and [__first,__last-1) is made into a
* heap.
*/
template <typename _RandomAccessIterator>
inline void
pop_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last)
/*
template
inline void
pop_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last, _Compare __comp)
*/
{
typedef typename iterator_traits<_RandomAccessIterator>::value_type _ValueType;
if (__last - __first > 1)
{
--__last;
std::__pop_heap(__first, __last, __last,
__gnu_cxx::__ops::__iter_less_iter());
// __gnu_cxx::__ops::__iter_comp_iter(__comp));
}
}
以大顶堆为例,把最大的元素弹出堆,其实就是把根节点也就是数组的第一个元素弄走就行了。
template <typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Compare>
inline void
__pop_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last,
_RandomAccessIterator __result, _Compare __comp)
{
typedef typename iterator_traits<_RandomAccessIterator>::value_type _ValueType;
typedef typename iterator_traits<_RandomAccessIterator>::difference_type _DistanceType;
_ValueType __value = std::move(*__result);
*__result = std::move(*__first);
std::__adjust_heap(__first, _DistanceType(0),
_DistanceType(__last - __first),
std::move(__value), __comp);
}
也就是把第一个元素和最后一个元素互换一下,然后把第一个元素的位置打一个洞,之后就调用__adjust_heap来填洞,其实就是个向下的插入排序。
下图是__adjust_heap向上提升结点的操作,最后再次调用__push_heap来做插入排序调整堆。
template <typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Distance, typename _Tp, typename _Compare>
void __adjust_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _Distance __holeIndex,
_Distance __len, _Tp __value, _Compare __comp)
{
const _Distance __topIndex = __holeIndex;
_Distance __secondChild = __holeIndex;
// 1
while (__secondChild < (__len - 1) / 2)
{
__secondChild = 2 * (__secondChild + 1);
if (__comp(__first + __secondChild, __first + (__secondChild - 1)))
__secondChild--;
*(__first + __holeIndex) = std::move(*(__first + __secondChild));
__holeIndex = __secondChild;
}
// 2
if ((__len & 1) == 0 && __secondChild == (__len - 2) / 2)
{
__secondChild = 2 * (__secondChild + 1);
*(__first + __holeIndex) = std::move(*(__first + (__secondChild - 1)));
__holeIndex = __secondChild - 1;
}
// 3
std::__push_heap(__first, __holeIndex, __topIndex, std::move(__value), __gnu_cxx::__ops::__iter_comp_val(__comp));
}
make_heap
/**
* @brief Construct a heap over a range.
* @param __first Start of heap.
* @param __last End of heap.
* @ingroup heap_algorithms
*
* This operation makes the elements in [__first,__last) into a heap.
*/
template <typename _RandomAccessIterator>
inline void
make_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last)
/*
template
inline void
make_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last, _Compare __comp)
*/
{
std::__make_heap(__first, __last, __gnu_cxx::__ops::__iter_less_iter());
// std::__make_heap(__first, __last, __gnu_cxx::__ops::__iter_comp_iter(__comp));
}
叶子结点本来就是一个合格的堆,那么,就要从最后一个非叶子结点向根节点逐渐调整堆,这样可以使得每一个子堆都是合格的堆,那么整体上也就是一个合格的堆了。
template <typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Compare>
void
__make_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last, _Compare __comp)
{
typedef typename iterator_traits<_RandomAccessIterator>::value_type _ValueType;
typedef typename iterator_traits<_RandomAccessIterator>::difference_type _DistanceType;
if (__last - __first < 2)
return;
const _DistanceType __len = __last - __first;
_DistanceType __parent = (__len - 2) / 2;
while (true)
{
_ValueType __value = std::move(*(__first + __parent));
std::__adjust_heap(__first, __parent, __len, std::move(__value), __comp);
if (__parent == 0)
return;
__parent--;
}
}
sort_heap
/**
* @brief Sort a heap.
* @param __first Start of heap.
* @param __last End of heap.
* @ingroup heap_algorithms
*
* This operation sorts the valid heap in the range [__first,__last).
*/
template <typename _RandomAccessIterator>
inline void
sort_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last)
/*
template
inline void
sort_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last, _Compare __comp)
*/
{
std::__sort_heap(__first, __last,
__gnu_cxx::__ops::__iter_less_iter());
// __gnu_cxx::__ops::__iter_comp_iter(__comp));
}
根据堆的性质,堆顶一定是最大或者最小的元素,那么,我们逐渐把堆顶元素和尾部元素互换,然后马上调整堆。这样子,有序的元素会从数组尾部一直扩展到头部,至此,整个数组都是有序的了。
template <typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Compare>
void __sort_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last,
_Compare __comp)
{
while (__last - __first > 1)
{
--__last;
std::__pop_heap(__first, __last, __last, __comp);
}
}
is_heap_until
从根结点找一个最大的合格的堆,如果整个数组是个合格的堆,那么返回数组大小。
/**
* @brief Search the end of a heap.
* @param __first Start of range.
* @param __last End of range.
* @return An iterator pointing to the first element not in the heap.
* @ingroup heap_algorithms
*
* This operation returns the last iterator i in [__first, __last) for which
* the range [__first, i) is a heap.
*/
template <typename _RandomAccessIterator>
inline _RandomAccessIterator
is_heap_until(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last)
/*
template
inline _RandomAccessIterator
is_heap_until(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last, _Compare __comp)
*/
{
return __first + std::__is_heap_until(__first, std::distance(__first, __last),
__gnu_cxx::__ops::__iter_less_iter());
// __gnu_cxx::__ops::__iter_comp_iter(__comp));
}
根据堆的性质 – "父亲结点一定大于或者小于两个孩子结点"来依次判断就好了。
template <typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Distance, typename _Compare>
_Distance
__is_heap_until(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _Distance __n, _Compare __comp)
{
_Distance __parent = 0;
for (_Distance __child = 1; __child < __n; ++__child)
{
if (__comp(__first + __parent, __first + __child))
return __child;
if ((__child & 1) == 0)
++__parent;
}
return __n;
}
is_heap
之前就说了,如果整个数组是个合格的堆,那么__is_heap_until返回数组大小,所以is_heap就是这儿干的。
/**
* @brief Determines whether a range is a heap.
* @param __first Start of range.
* @param __last End of range.
* @return True if range is a heap, false otherwise.
* @ingroup heap_algorithms
*/
template <typename _RandomAccessIterator>
inline bool
is_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last)
{
return std::is_heap_until(__first, __last) == __last;
// return std::is_heap_until(__first, __last, __comp) == __last;
}