如何正确使用 HTTP proxy
目录
- 两种 HTTP 代理
- Proxy 如何获取目标服务器地址
- 两种 request-URL 格式
- 如何代理 HTTPS
- 编程实现
两种 HTTP 代理
第一种是 RFC 7230 - HTTP/1.1: Message Syntax and Routing(即修订后的 RFC 2616,HTTP/1.1 协议的第一部分)描述的普通代理。其代理过程为:
- client 请求 proxy
- proxy 解析请求获取 origin server 地址
- proxy 向 origin server 转发请求
- proxy 接收 origin server 的响应
- proxy 向 client 转发响应
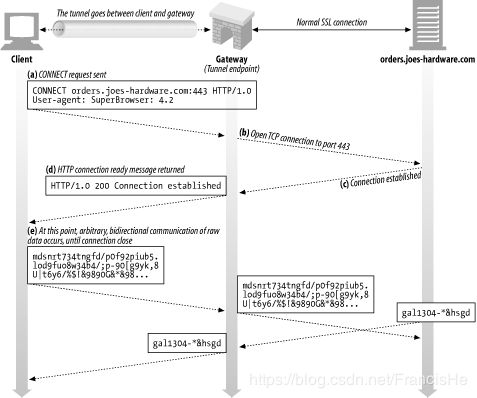
第二种是 Tunneling TCP based protocols through Web proxy servers(通过 Web 代理服务器用隧道方式传输基于 TCP 的协议)描述的隧道代理。其代理过程为:
- client 向 proxy 发送 CONNET 请求(包含了 origin server 的地址)
- proxy 与 origin server 建立 TCP 连接
- proxy 向 client 发送响应
- client 向 proxy 发送请求,proxy 原封不动向 origin server 转发请求,请求数据不做任何封装,为原生 TCP packet.
- 响应过程同请求过程
Proxy 如何获取目标服务器地址
对于第一种代理方式,有两种获取 origin server 地址的方式:
- 解析 request line 里的 request-URL
- Host header
其中,解析 request-URL 的方法为标准方法,Host 头部的方法有些 proxy 无法处理。
两种 request-URL 格式
对于直接请求,推荐使用 partial request-URL, 例如 /foo, 因为有些 web server 无法处理 full request-URL(工作中就遇到有些 CDN 传 full request-UR 返回 404);
对于通过 proxy 的请求,推荐使用 full request-URL, 例如 http://host/foo, 因为有些 proxy 不会从 Host 头取目的服务器地址。
如何代理 HTTPS
由于第一种代理方式需要 proxy 解析请求,因此无法适用于 HTTPS 的代理,因为请求经过加密。所以,代理 HTTPS 只能使用第二种,即隧道代理。
隧道代理包括两个阶段,一是连接(隧道)建立阶段,而是数据通信(请求响应)阶段。由于数据通信是基于 TCP packet 的,因此可以代理 HTTPS 请求和响应。
编程实现
_M.REDIRECT_STATUS = {
[301] = "Moved Permanently",
[302] = "Found",
[303] = "See Other",
[307] = "Temporary Redirect",
[308] = "Permanent Redirect",
}
function _M.request_raw(url, method, data, headers, timeout, proxy, ssl_verify, redirect)
local httpc = http.new()
if timeout then
httpc:set_timeout(timeout * 1000)
else
httpc:set_timeout(60 * 1000)
end
if not redirect then
redirect = 5
end
if redirect < 0 then
return nil, "exceeded maximum redirect times"
end
local parsed_uri, err = httpc:parse_uri(url, false)
if not parsed_uri then
return nil, "failed to parse url " .. url .. ": " .. err
end
local scheme, host, port, path, query = unpack(parsed_uri)
-- We always add "Host" field to the headers.
local last_headers = {}
if headers then
for key, value in pairs(headers) do
last_headers[key] = value
end
end
if not last_headers["Host"] and not last_headers["host"] then
local host_header = host
if port then
if (scheme == "https" and port == 443) or (scheme == "http" and port == 80) then
host_header = host_header
else
host_header = host_header .. ":" .. port
end
end
last_headers["Host"] = host_header
end
local params = {
method = method,
headers = last_headers,
body = data,
path = path, -- Note: use partial request-URL for compatibility
query = query
}
if proxy then
local parsed_proxy, err = httpc:parse_uri(proxy, false)
if not parsed_proxy then
return nil, "failed to parse proxy " .. proxy .. ": " .. err
end
local _, proxy_host, proxy_port = unpack(parsed_proxy)
local ok, err = httpc:connect(proxy_host, proxy_port)
if not ok then
return nil, "failed to connect " .. proxy .. ": " .. err
end
-- HTTPS proxy
-- https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2817#section-5
-- https://github.com/pintsized/lua-resty-http/issues/63
if scheme == "https" then
local res, err = httpc:request({
version = 1.1,
method = "CONNECT",
headers = {["Host"] = last_headers["Host"]},
path = host .. ":" .. port, -- Note: must include port
})
if not res then
return nil, err
end
ngx.log(ngx.NOTICE, res.status .. " " .. res.reason)
if res.status < 200 or res.status >= 300 then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, res.status .. " " .. res.reason)
return nil, "connect proxy failed: " .. res.status .. " " .. res.reason
end
-- Note: sending a CONNECT request creates a TCP tunnel, the proxy will not
-- parse data sending by client after tunnel created. In other words, the proxy
-- will not modify request-URL in start line, so we had better use partial
-- request-URL for some web server can only recognise partial request-URL.
else
-- Note: proxy get origin server host by parsing request-URL in start line.
params.path = ngx.re.gsub(url, "\\s", "%20", "jo")
end
else
local ok, err = httpc:connect(host, port)
if not ok then
return nil, "failed to connect " .. url .. ": " .. err
end
end
if scheme == "https" then
local verify = true
if ssl_verify == false then
verify = false
end
local ok, err = httpc:ssl_handshake(nil, host, verify)
if not ok then
local ok2, err2 = httpc:close()
if not ok2 then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, err2)
end
return nil, "failed to ssl_handshake: " .. err
end
end
local res, err = httpc:request(params)
if not res then
local ok2, err2 = httpc:close()
if not ok2 then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, err2)
end
return nil, err
end
local redirect_url = res.headers["Location"] or res.headers["location"]
if _M.REDIRECT_STATUS[res.status] and redirect_url and redirect_url ~= "" then
ngx.log(ngx.NOTICE, res.status .. " " .. res.reason .. ": " .. redirect_url)
if string.char(string.byte(redirect_url, 1)) == "/" and string.char(string.byte(redirect_url, 2)) ~= "/" then
redirect_url = scheme .. "://" .. host .. ":" .. port .. redirect_url
end
if scheme == "https" then
local ok, err = httpc:close()
if not ok then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, err)
end
else
local ok, err = httpc:set_keepalive()
if not ok then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "failed to set_keepalive: " .. err)
end
end
return _M.request_raw(redirect_url, method, data, headers, timeout, proxy, ssl_verify, redirect - 1)
end
local head_method = method == "head" or method == "HEAD"
local content = ""
if res.has_body and not head_method then
local body, err = res:read_body()
if not body then
local ok2, err2 = httpc:close()
if not ok2 then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, err2)
end
return nil, err
end
content = body
end
if scheme == "https" then
local ok, err = httpc:close()
if not ok then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, err)
end
else
local ok, err = httpc:set_keepalive()
if not ok then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "failed to set_keepalive: " .. err)
end
end
return {
status = res.status,
reason = res.reason,
headers = res.headers,
content = content,
}
end
实现时需要注意几个细节:
- 对于不经过 proxy 的请求,request-URL 使用不带 host 的模式(例如
/foo); - 对于经过 proxy(普通代理方式) 的 HTTP 请求,request-URL 使用完整模式(例如
http://host/foo); - 对于经过 proxy 的 HTTPS 请求,request-URL 使用不带 host 的模式(例如
/foo).
为什么在处理 HTTP 代理和 HTTPS 代理时会有差异呢?因为对于普通代理,proxy 需要通过 request-URL 获取目的服务器的地址,proxy 转发请求时会将完整模式的 request-URL 修改为不带 host 的(http://host/foo 到 /foo);但是,对于隧道代理方式,proxy 不会解析请求内容,而是原样转发,如果请求中的 request-URL 使用完整模式,则可能遇到目的服务器不兼容的情况。
当然了,这里的本质区别不是 HTTP 还是 HTTPS, 而是普通代理还是隧道代理,毕竟隧道代理也可以代理 HTTP.