时间序列分析之ADF检验
ADF检验
在使用很多时间序列模型的时候,如 ARMA、ARIMA,都会要求时间序列是平稳的,所以一般在研究一段时间序列的时候,第一步都需要进行平稳性检验,除了用肉眼检测的方法,另外比较常用的严格的统计检验方法就是ADF检验,也叫做单位根检验。
ADF检验全称是 Augmented Dickey-Fuller test,顾名思义,ADF是 Dickey-Fuller检验的增广形式。DF检验只能应用于一阶情况,当序列存在高阶的滞后相关时,可以使用ADF检验,所以说ADF是对DF检验的扩展。
单位根(unit root)
在做ADF检验,也就是单位根检验时,需要先明白一个概念,也就是要检验的对象——单位根。
当一个自回归过程中:![]() ,如果滞后项系数b为1,就称为单位根。当单位根存在时,自变量和因变量之间的关系具有欺骗性,因为残差序列的任何误差都不会随着样本量(即时期数)增大而衰减,也就是说模型中的残差的影响是永久的。这种回归又称作伪回归。如果单位根存在,这个过程就是一个随机漫步(random walk)。
,如果滞后项系数b为1,就称为单位根。当单位根存在时,自变量和因变量之间的关系具有欺骗性,因为残差序列的任何误差都不会随着样本量(即时期数)增大而衰减,也就是说模型中的残差的影响是永久的。这种回归又称作伪回归。如果单位根存在,这个过程就是一个随机漫步(random walk)。
ADF检验的原理
ADF检验就是判断序列是否存在单位根:如果序列平稳,就不存在单位根;否则,就会存在单位根。
所以,ADF检验的 H0 假设就是存在单位根,如果得到的显著性检验统计量小于三个置信度(10%,5%,1%),则对应有(90%,95,99%)的把握来拒绝原假设。
ADF检验的python实现
ADF检验可以通过python中的 statsmodels 模块,这个模块提供了很多统计模型。
使用方法如下:
导入adfuller函数
from statsmodels.tsa.stattools import adfulleradfuller函数的参数意义分别是:
- x:一维的数据序列。
- maxlag:最大滞后数目。
- regression:回归中的包含项(c:只有常数项,默认;ct:常数项和趋势项;ctt:常数项,线性二次项;nc:没有常数项和趋势项)
- autolag:自动选择滞后数目(AIC:赤池信息准则,默认;BIC:贝叶斯信息准则;t-stat:基于maxlag,从maxlag开始并删除一个滞后直到最后一个滞后长度基于 t-statistic 显著性小于5%为止;None:使用maxlag指定的滞后)
- store:True False,默认。
- regresults:True 完整的回归结果将返回。False,默认。
返回值意义为:
- adf:Test statistic,T检验,假设检验值。
- pvalue:假设检验结果。
- usedlag:使用的滞后阶数。
- nobs:用于ADF回归和计算临界值用到的观测值数目。
- icbest:如果autolag不是None的话,返回最大的信息准则值。
- resstore:将结果合并为一个dummy。
def adfuller(x, maxlag=None, regression="c", autolag='AIC',
store=False, regresults=False):
"""
Augmented Dickey-Fuller unit root test
The Augmented Dickey-Fuller test can be used to test for a unit root in a
univariate process in the presence of serial correlation.
Parameters
----------
x : array_like, 1d
data series
maxlag : int
Maximum lag which is included in test, default 12*(nobs/100)^{1/4}
regression : {'c','ct','ctt','nc'}
Constant and trend order to include in regression
* 'c' : constant only (default)
* 'ct' : constant and trend
* 'ctt' : constant, and linear and quadratic trend
* 'nc' : no constant, no trend
autolag : {'AIC', 'BIC', 't-stat', None}
* if None, then maxlag lags are used
* if 'AIC' (default) or 'BIC', then the number of lags is chosen
to minimize the corresponding information criterion
* 't-stat' based choice of maxlag. Starts with maxlag and drops a
lag until the t-statistic on the last lag length is significant
using a 5%-sized test
store : bool
If True, then a result instance is returned additionally to
the adf statistic. Default is False
regresults : bool, optional
If True, the full regression results are returned. Default is False
Returns
-------
adf : float
Test statistic
pvalue : float
MacKinnon's approximate p-value based on MacKinnon (1994, 2010)
usedlag : int
Number of lags used
nobs : int
Number of observations used for the ADF regression and calculation of
the critical values
critical values : dict
Critical values for the test statistic at the 1 %, 5 %, and 10 %
levels. Based on MacKinnon (2010)
icbest : float
The maximized information criterion if autolag is not None.
resstore : ResultStore, optional
A dummy class with results attached as attributes
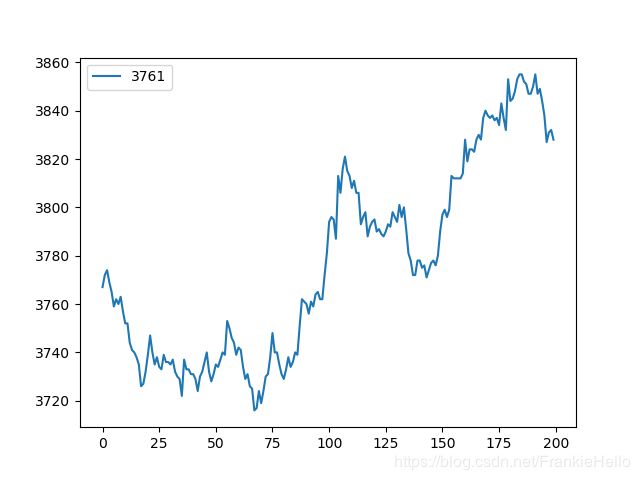
"""现在我们用一个RB1309的收盘数据来进行ADF检验,看一下结果:
result = adfuller(rb_price)
print(result)
(-0.45153867687808574, 0.9011315454402649, 1, 198, {'5%': -2.876250632135043, '1%': -3.4638151713286316, '10%': -2.574611347821651}, 1172.4579344852016)
看到 t-statistic 的值 -0.451 要大于10%,所以无法拒绝原假设,另外,p-value的值也很大。
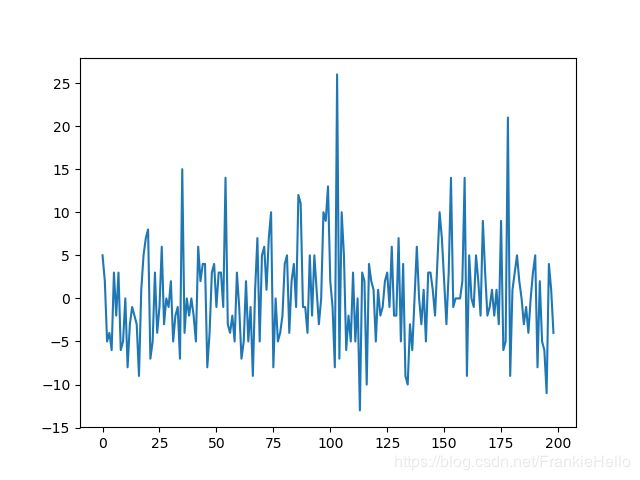
将数据进行一阶差分滞后,看一下结果如何:
rb_price = np.diff(rb_price)
result = adfuller(rb_price)
print(result)
(-15.436034211511204, 2.90628134201655e-28, 0, 198, {'5%': -2.876250632135043, '1%': -3.4638151713286316, '10%': -2.574611347821651}, 1165.1556545612445)看到 t-statistic 的值 -15 要小于5%,所以拒绝原假设,另外,p-value的值也很小。