Shell 脚本集合
文章目录
- 本篇
- NO.1 echo 和read
- NO.2 检查一下文件是否存在
- NO.3 将文件拷贝到指定目录下
- No.4 批量检查ip地址是否被占用
- No.5 检查端口情况
- No.6 检查CPU情况
- No.7 检查内存情况
- No.9 trap捕获信号
- No.10 数组和函数
- No.11 函数的返回值
- No.12 awk输出所有字符串
- No.13 练习函数传递数组
- No.14 使用getopts接收输入参数
- No.15 将脚本添加到全局命令
- No.16 查看网络情况和系统信息
- No.17 查看系统网络
- No.18 自动提交push代码到远程
本篇
- 练习Shell编程,以每个脚本为单位
- 不定期更新
- 目前脚本数量为16个
- 更新时间2019-01-31
- 项目已放到github,希望可以被start
NO.1 echo 和read
这次主要玩一下echo 和read
echo 输出内容
read 输入内容
$ 的使用
#!/bin/bash
#2018-09-04 baron
#github: https://github.com/MyBaron/Shell_practice
# 练习一:
# echo 输出内容
# read 读取输入
# $ 的使用
#--------------------------------------------
# $ 是代表变量替换
# 输出PATH变量
echo $PATH
echo '\n Hello World! baron \a \n'
# 定义一个变量
name='helloName'
# '' 和"" 的区别就是 "" 会识别$符号
echo "输出name变量的值:${name}"
echo '单引号是不会识别$的:${name}'
# read 输入 输入的值赋值到fistname这个变量中 -p 是提示
read -p "please enter your firstname " firstname
read -p "and then please enter your lastname " lastname
echo "just a minute..........."
# 引用变量 输出自己输入的内容
echo "your name is" ${firstname}${lastname}
# $() 是使用命令,这里是使用了data命令输出日志
echo "Hellp ${firstname}${lastname} today is $(date +%Y%m%d) "
exit 0
NO.2 检查一下文件是否存在
功能:检查一下文件是否存在
练习内容:
- echo 内容输出
- read 内容输入
- test 检查条件
- 命令使用
#!/bin/bash
#2018-09-14 baron
#github: https://github.com/MyBaron/Shell_practice
# 文件测试
# test 命令 -e 是如果文件存在则为真
# && ,com1 && com2,只有当com1 为true时,才会执行com2
# || ,与&& 相反 只有com1 为false时,才会执行com2
echo "the bash is check one file is exist or not \n"
read -p "请输入你想检查的文件 " file
test -e ${file} && echo "${file}文件存在" || echo "${file}文件不存在"
# 数值比较
# -lt 是小于的意思
num1=100
num2=200
echo "\nnum1=100,num2=200"
test ${num1} -lt ${num2} && echo "num1小于num2" || echo "num1大于num2"
# 字符串
str1="str"
str2="str"
echo "\nstr1=str,str2=str"
test ${str1}=${str2} && echo "相等" || echo "不相等"
exit 0
NO.3 将文件拷贝到指定目录下
将文件拷贝到指定目录下
练习内容
- 输入参数
- 逻辑判断 If-elif-else
#!/bin/bash
#2018-09-015 baron
#github: https://github.com/MyBaron/Shell_practice
#将文件拷贝到指定目录下
#输入参数
# 执行该脚本命令 sh xx.sh hello.sh /baron/path
# hello 为输入的参数
# ${n} 为第n个传入参数 从1开始 0是文件名称
# $# 为传入参数的个数
file=${1}
path=${2}
echo "输入的file为${file}"
echo "输入的path为${path}"
echo "输入的参数个数为$#"
# if-elif-else 逻辑"
# if判断语句在[] 里面
# 注意: [] 里面要有空格!!!!!!
# if 配合test语句使用 不需要[]
if [ "${file}" == "" ] && [ "${path}" == "" ]; then
echo "file和path都不能为空"
elif test -e ${file} ; then
echo "将${file}拷贝到${path}"
cp -r -i ${file} ${path}
else
echo "file 文件不存在"
fi
exit 0
No.4 批量检查ip地址是否被占用
功能:批量检查ip地址是否被占用
练习内容
- while循环
- for 循环
- seq 指令 用于产生从某个数到另外一个数之间的所有整数
#!/bin/bash
#@author baron
#@data 2019-1-16
#@comtent check long-range server status
network="${1}"
# while循环 循环获取用户输入Ip字段
# 用法:
# 1. 条件与If一样[] 里是判断条件
# 2. do done 里面是判断逻辑,do为开始,done为结束
while [ "${network}" == "" ]
do
read -p "please input what you want to check network ,format is x.x.x " network
done
read -p "please input what you want to start the number " start
read -p "please input what you want to end the number " end
# for循环遍历次数
# seq指令是从某个数到另外一个数之间的所有整数
# 用法
# 1. for xx in xx
# do done 里面是判断逻辑,do为开始,done为结束
#
# 2. 也可以 for ((i=1; i<=100; i ++))
#
#
for sitenu in $(seq "${start}" "${end}" )
do
ping -c 1 "${network}.${sitenu}" &> /dev/null && result=0 || result=1
if [ "${result}" == 0 ]; then
echo "Server ${network}.${sitenu} is UP."
else
echo "Server ${network}.${sitenu} is DOWN."
fi
done
echo "ok,that is checking over"
exit 0
No.5 检查端口情况
功能:检查端口情况
练习内容
- 输入流
- if 判断条件
- grep 信息筛选
#!/bin/bash
#@author baron
#@data 2018-09-06
#@content check any port is been taken
echo "Now , I will detect your Linux server's services!"
if [ "${1}" != "" ]; then
echo "The www,ftp,ssh,mail(stmp),and you want to check ${1} will be detected! \n"
else
echo "The www,ftp,ssh,mail(stmp) will be detected! \n"
fi
# 设定输出路径
testfile=checkPortResult.txt
# 将netstat结果输出到文件
# > 为输入重定向 例如 xx0 > xx1.txt 意思是将xx0的内容输入到xx1.txt中
netstat -tuln > ${testfile}
# 检测各个端口情况
# 利用grep 检索关键字
esting=$(grep ":80" ${testfile})
if [ "${testing}" != "" ]; then
echo "WWW is running in your system"
fi
testing=$(grep ":22" ${testfile})
if [ "${testing}" != "" ]; then
echo "SSH is running in your system"
fi
testing=$(grep ":21" ${testfile})
if [ "${testing}" != "" ]; then
echo "FTP is running in your system"
fi
testing=$(grep ":25" ${testfile})
if [ "${testing}" != "" ]; then
echo "Mail is running in your system"
fi
if [ "${1}" != "" ]; then
testing=$(grep ":${1}" ${testfile})
if [ "${testing}" != "" ]; then
echo "${1} port is running in your system"
fi
fi
echo "check is over , thank you"
exit 0
No.6 检查CPU情况
功能:检查CPU情况
效果图
#!/bin/bash
# baron
# 2019-01-18
# 分析cpu使用情况
# 利用vmstat 分析cpu使用情况
# 检测是否有vmstat命令
if ! which vmstat &> /dev/null ; then
echo "the sy is no vmstat commam"
exit 1
fi
# 创建临时文件
date=$(date "+%Y-%m-%d_%H:%M:%S")
file="cpu_stat_${date}.txt"
echo "正在收集cpu情况,请等候"
vmstat 2 3 >${file}
# 睡眠三秒
sleep 3s
set US
set SY
R=0
# 循环处理数据
for NR in $(seq 3 5)
do
US1=$(vmstat |awk 'NR==3{print $13}')
SY1=$(vmstat |awk 'NR==3{print $14}')
R1=$(vmstat |awk 'NR==3{print $1}')
if [ $R1 -gt $R ]; then
R=${R1}
fi
US=`expr ${US} + ${US1} `
SY=`expr ${SY} + ${SY1} `
done
# 删除临时文件
rm -r ${file}
US=`expr ${US} / 3 `
SY=`expr ${SY} / 3 `
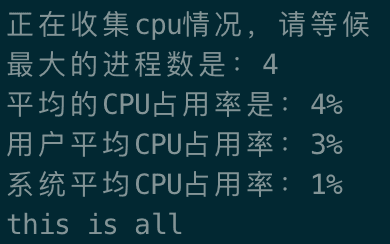
echo "最大的进程数是:${R}"
echo "平均的CPU占用率是:`expr ${US} + ${SY}`%"
echo "用户平均CPU占用率:${US}%"
echo "系统平均CPU占用率:${SY}%"
echo "this is all"
exit 0
No.7 检查内存情况
功能:检查CPU情况
使用free 命令获取内存情况
效果图
#!/bin/bash
# baron
# 2019-01-21
# 分析内存使用情况
# 利用free 分析内存使用情况
# 检测是否有free命令
if ! which free &> /dev/null ; then
echo "the sy is no free commam"
exit 1
fi
echo "正在检查内存使用情况"
TOTAL=$(free -m |awk '/Mem/{print $2}')
USE=$(free -m |awk '/Mem/{print $3}')
FREE=$(free -m |awk '/Mem/{print $4}')
CACHE=$(free -m |awk '/Mem/{print $6}')
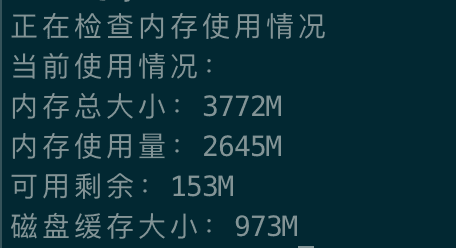
echo -e "当前使用情况: \n内存总大小:${TOTAL}M \n内存使用量:${USE}M \n可用剩余:${FREE}M\n磁盘缓存大小:${CACHE}M"
exit 0
No.9 trap捕获信号
对trap指令进行运用
#!/bin/bash
# baron
# 2019-01-23
# trap的使用 捕获信号
# trap commands signals : commands 捕获后触发的命令,signals 需要捕获的命令
echo "无法通过ctrl-c 来终止这个脚本,此脚本会运行10秒"
# SIGINT 是终止线程 SIGTERM 是尽可能终止进程
trap "echo '我已经告诉过你,你无法终止这个脚本'" SIGINT SIGTERM
count=1
while [ $count -lt 10 ]
do
echo "第${count}秒"
sleep 1
count=$[ $count + 1 ]
done
# 捕获程序退出指令
trap "echo \"脚本运行结束,运行时间${count}秒\" " EXIT
No.10 数组和函数
对数组和函数的练习
效果图
开始执行fun函数,将返回输入的数中大于10的数的数组
数组的个数为6
输入数组的值为1 2 3 33 44 55 66
大于10的数有 33 44 55 66
#!/bin/bash
# baron
# 2019-01-24
# 练习函数和数组
#
# 个人觉得数组操作是非常难用,而且功能点很少,在日常中应该避免使用数组
# 在使用数组中,经常利用到echo来构成数组
function fun(){
echo "开始执行fun函数,将返回输入的数中大于10的数的数组"
# 新建一个数组,用于返回
local newarray
local elements
local oldarray
local number=0
#获取输入的参数
elements=$[ $# -1 ]
echo "数组的个数为${elements}"
# $@相当于获取所有的参数,利用echo,相当于输入参数,()是组成数组
oldarray=(`echo "$@"`)
echo "输入数组的值为${oldarray[*]}"
for (( i=0; i<=${elements}; i++ )){
if [ $[${oldarray[$i]}] -gt 10 ]; then
newarray[${number}]=${oldarray[$i]}
# 同样可以这样写 number=`expr $number + 1`
number=$[ $number + 1 ]
fi
}
echo "大于10的数有 ${newarray[*]}"
}
testArray=(1 2 3 33 44 55 66)
# 此处echo就是相当于输入数组的值作为参数,每一个值当做一个参数
# 如果只传入数组,只能当做是一个参数
arg1=$(echo ${testArray[*]} )
fun $arg1
No.11 函数的返回值
函数的返回值
- 返回值return 非必须
- 可以将函数赋值给变量
效果
此函数是返回一个数值
用$?接收的返回值是: 200
变量:此函数是返回一个数值
命令返回值是:0
代码
#!/bin/bash
# baron
# 2019-01-25
# 联系函数的return
function fun1(){
echo "此函数是返回一个数值"
return 200
}
# 直接调用函数,使用$?获取返回值
fun1
# $? 上个命令的退出状态,或函数的返回值
echo "用\$?接收的返回值是: $?"
# 将函数赋值给变量
# 用变量来接收返回值
arg=$(fun1)
#这里调用变量arg,相当于执行了函数fun1
echo "变量:$arg"
#这里返回值是0,是因为这里的命令值的是echo,而不是$arg的函数命令
echo "命令返回值是:$?"
No.12 awk输出所有字符串
利用awk切割后,输出所有字符串
代码
#!/bin/bash
# baorn
# 2019-01-26
# awk 将输出所有分割的字符串
# 将echo的以空格切割然后遍历输出
# NF是awk的参数,代表切割后个数
# print $i 是输出切割后的第几列 $0是整行
val=`echo "第一 第二 第三 第四"|awk '{for(i=1;i<=NF;i++){print $i}}'`
echo $val
No.13 练习函数传递数组
练习函数传递数组
#!/bin/bash
# baron
# 2019-01-26
# 练习函数传递数组
function fun(){
local sum=0
local newarray
#接收参数
newarray=(`echo "$@"`)
#遍历数组中的每一个数
for num in ${newarray[*]}
do
sum=$[ $sum + $num ]
done
echo $sum
}
array=(1 2 3 4 5 6 )
echo "输入的数组是 ${array[*]}"
arg1=`echo ${array[*]}`
result=`fun $arg1`
echo "数组累加的结果是:$result"
No.14 使用getopts接收输入参数
使用getopts接收输入参数
getopts的命令格式:
getopts optstring name [arg…] 例如:getopts “a:fs” OPTION
getopts 作用就是接收用户在运行脚本的时候输入的参数,例如sh xx.sh -i
getopts 通常用while来循环处理,用Case去得到不同的命令处理方式
效果
baron@baron: sh expGetopts.sh -vk -i "this is value"
你输入的参数是v
你输入的参数没有找到匹配
你输入的参数是i,值是this is value
代码
#!/bin/bash
# baron
# 2019-01-28
# getopts接收输入参数
# getopts的命令格式:
# getopts optstring name [arg...] 例如:getopts "a:fs" OPTION
# getopts 作用就是接收用户在运行脚本的时候输入的参数,例如sh xx.sh -i
# getopts 通常用while来循环处理,用Case去得到不同的命令处理方式
# 在这里,接收处理的参数是i v h 三个参数
# 设置的格式是':i:vh'
# 第一个: 代表去掉系统的告警信息
# i: 是指接收i的指令,这个指令还有value,可以用$OPTARG来接收这个value
# v和h:就是单单是指令
while getopts ':i:vh' name
do
case $name in
i)
echo "你输入的参数是i,值是$OPTARG";;
v)
echo "你输入的参数是v";;
h)
echo "你输入的参数是h";;
*)
echo "你输入的参数没有找到匹配";;
esac
done
No.15 将脚本添加到全局命令
将脚本添加到全局命令
效果:
[root@sy4 shell]# sh addBin.sh -i
当前路径为/opt/ruqiAgent/shell
temp的内容 addBin.sh
脚本所在的路径 /opt/ruqiAgent/shell/addBin.sh
安装命令成功
现在可以在终端使用scriptTest命令
代码
#!/bin/bash
# baron
# 2019-01-29
# 将这个脚本添加到环境的目录中,可以使用终端执行命令
function add(){
# 获取当前路径
wd=`pwd`
echo "当前路径为$wd"
## 将脚本名称写到临时文件temp
## basename 是去掉路径,只剩下文本名称
basename "$(test -L "$0" && readlink "$0" || echo "$0")" > temp
echo "temp的内容 $(cat temp )"
## 拼接脚本所在的路径
scriptName=$(echo -e -n $wd/ && cat temp)
echo "脚本所在的路径 $scriptName"
# 将脚本添加到全局命令中
su -c "cp $scriptName /usr/bin/scriptTest" root && echo "安装命令成功" || echo "安装命令失败"
rm -f temp
echo "现在可以在终端使用scriptTest命令"
}
function succ(){
echo "使用命令成功"
}
while getopts ':i' name
do
case $name in
i)
add ;;
*)
succ ;;
esac
done
exit 0
No.16 查看网络情况和系统信息
查看网络情况和系统信息
联系内容:
- 变色字体
- tput sgr0还原终端配置
- ping 查看网络情况
- uname 查看系统信息
效果
网络状态:可连接
该系统类型是:GNU/Linux
系统的发行版本:3.10.0-862.el7.x86_64
系统的名称:Linux
系统的类型:x86_64
代码
#!/bash/bin
# baron
# 2019-01-31
# 测试网络和系统信息
# tput 可以更改几项终端功能,如移动或更改光标、更改文本属性,以及清除终端屏幕的特定区域
# sgr0 表示清除所有更改的配置
reset=`tput sgr0`
# 查看是否可以联网
# \E[32m 是修改字体颜色,32m 是绿色
ping -c 1 www.baidu.com &> /dev/null && echo -e '\E[32m'"网络状态:${reset}可连接 " || echo -e '\E[32m'"网络状态:${reset}未连接"
# 查看系统类型
# mac系统并没有-o选项
os=`uname -o`
echo -e '\E[32m'"该系统类型是:${reset}$os"
# 系统的发行版本
REV=`uname -r`
# 系统的名称
OS=`uname -s`
# 系统类型
MACH=`uname -m`
echo -e '\E[32m'"系统的发行版本:${reset}$REV"
echo -e '\E[32m'"系统的名称:${reset}$OS"
echo -e '\E[32m'"系统的类型:${reset}$MACH"
No.17 查看系统网络
查看网络情况和系统信息
效果图
本地ip地址: 10.10.1.234 172.17.0.1
外网ip地址: 183.238.79.207
DNS地址: 114.114.114.114 8.8.8.8
代码
#!/bin/bash
# baron
# 2019-02-12
# 查看系统网络
reset=`tput sgr0`
# 获取本地Ip
internalip=`hostname -I`
echo -e '\E[32m' "本地ip地址:"${reset} ${internalip}
# 获取外网Ip
externalip=`curl -s ipecho.net/plain`
echo -e '\E[32m' "外网ip地址:" ${reset} $externalip
# 定义DNS服务器的IP地址
# sed '1 d' 代表删除第一行
nameservers=$(cat /etc/resolv.conf | sed '1 d' | awk '{print $2}' )
# 也可以用awd 的NR 来实现sed的效果
nameservers1=$(cat /etc/resolv.conf | awk 'NR>1{print $2}' )
echo -e '\E[32m' "DNS地址:" ${reset} ${nameservers}
No.18 自动提交push代码到远程
自动提交push代码到远程
思路:
- 将本脚本的添加到忽略提交名单中
- 利用git命令进行提交
- commit 信息是当前日期
#!/bash/bin
# baron
# 2019-02-13
# 自动提交到远程代码库
# 检查当前路径是否有.git文件夹
function judge(){
if [ -x ".git" ];then
# 获取当前文件的名称
if [ -f ".git/.gitignore" ];then
echo "添加忽略提交该脚本到远程代码库"
echo "当前脚本名称${0}"
echo ${0} >> .git/.gitignore
push
else
echo "创建 .gitignore文件"
echo "当前脚本名称${0}"
touch .git/.gitignore
echo ${0} >> .git/.gitignore
push
fi
else
echo ".git文件夹不存在,请将该脚本放到与.git文件夹同一级中"
exit -1
fi
}
function push(){
git add .
git commit -m "$(date +%Y-%m-%d)"
git push origin
}
judge
echo "提交完毕"
exit 0