Mybatis(五)——parameterType、调用存储过程
一、parameterType
映射文件中select标签中,parameterType可以填两种类型
- 简单类型(8中基本类型+String)
- 对象类型
Mybatis提供了两种支持动态sql的语法:#{}和${},这两种语法针对不同的参数类型有不同的使用方式。
#{} 与 ${} 的区别
- #{} 是以预编译的形式,将参数设置到sql语句中,并且参数会有单引号包裹。
如select * from student where stuno = #{stuNo},假设传入的参数为1,
编译之后是select * from student where stuno = '1',不会出错
对于数值字段,加不加单引号都行,但对于文本字段,在sql语句中必须加单引号 - ${} 取出的值直接拼装在sql语句中,不会自动添加单引号,且存在sql注入问题。
如select * from student where stuno = ${stuName},假设传入的参数为wql,
编译之后是select * from student where stuno = wql,会出错
正确的使用方式应该为select * from student where stuno = '${stuName}'
1. 简单类型
针对简单类型,如果要使用#{}的形式,大括号里面的标识符可以写成任意字符串,但是为了满足见名知意,还是根据sql表字段名写比较好
<select id="queryStudentByStuNo" resultType="Student" parameterType="int">
select * from student2 where stuno = #{anyString}
select>
针对简单类型,如果要使用${}的形式,大括号里面的标识符必须是value,不能更改
<select id="queryStudentByStuNo" resultType="Student" parameterType="int">
select * from student2 where stuno = ${value}
select>
2. 对象类型
针对对象类型,无论使用#{}还是${},大括号里面的参数必须为对象的属性值,如下所示
<select id="queryStudentByStuName" resultType="Student" parameterType="Student">
select * from student2 where stuno = '${stuName}'
select>
<select id="queryStudentByStuName2" resultType="Student" parameterType="Student">
select * from student2 where stuno = #{stuName}
select>
还有一种情况,如果Student类有一个address属性,但这个address也是一个类对象,address对象有两个属性,分别为homeAddress和schoolAddress,如何根据address查询学生
以下有三种方法
一、 parameterType=“Address”
<select id="queryStudentByAddress2" resultType="Student" parameterType="Address">
select * from student2 where homeaddress like #{homeAddress} or schooladdress like '%${schoolAddress}%'
select>
二、级联属性parameterType=“Student”
<select id="queryStudentByAddress1" resultType="Student" parameterType="Student">
select * from student2 where homeaddress like #{address.homeAddress} or schooladdress like '%${address.schoolAddress}%'
select>
三、 parameterType=“HashMap”
<select id="queryStudentByAddress3" resultType="Student" parameterType="HashMap">
select * from student2 where stuage = #{stuAge} or stuname like '%${stuName}%'
select>
与之相对应的测试函数如下
public static void queryStudentByAddress3(){
InputStream stream = Student.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("conf.xml");
SqlSessionFactory ssf=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(stream);
SqlSession session=ssf.openSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
HashMap<String ,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("stuAge", 21);
map.put("stuName", "wql");
List<Student> students = studentMapper.queryStudentByAddress3(map);
session.commit();
System.out.println(students);
session.close();
}
注意:map中的key要匹配sql语句中的标识符
如果mybatis调用存储过程,parameterType的值也为HashMap
二、mybatis调用存储过程
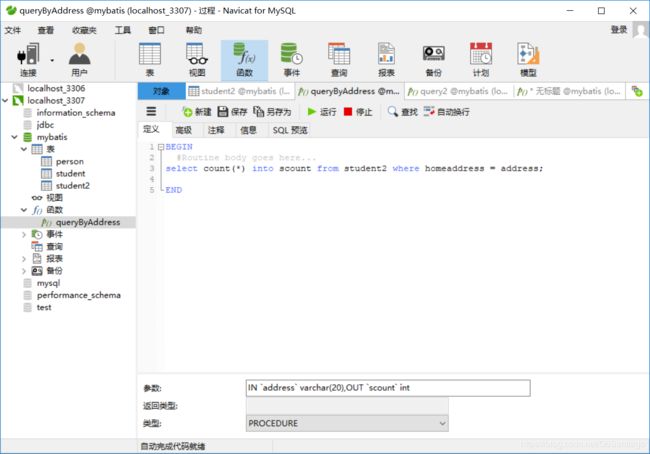
首先要建立一个存储过程,这个存储过程的描述为:根据输入的地址,判断该地址的学生人数
我使用了navicat for mysql来建立存储过程,过程如下
-
在弹出的页面输入例程的参数,IN表示输参数,OUT表示输出参数,如下所示:
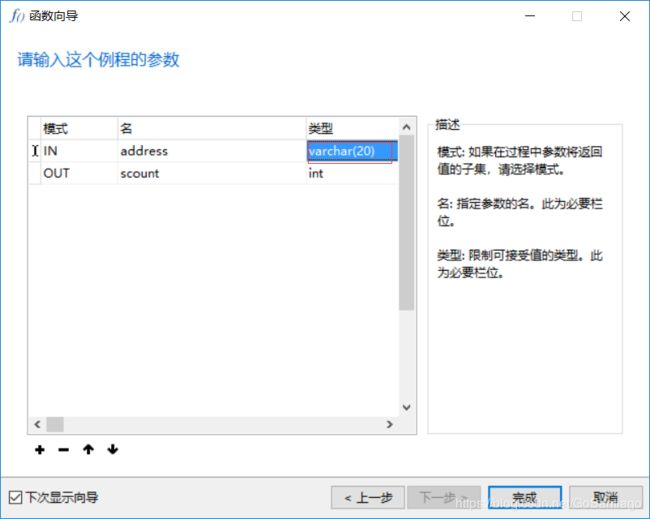
注意:如果类型为varchar的话,后面必须把长度补全,如varchar(20) -
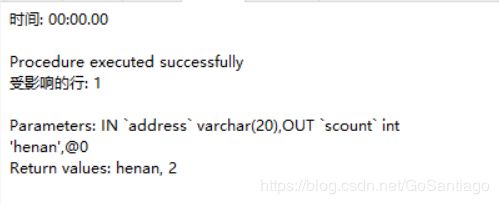
写完之后,点击保存,输入存储过程的名字,并保存测试,点击运行,输入参数
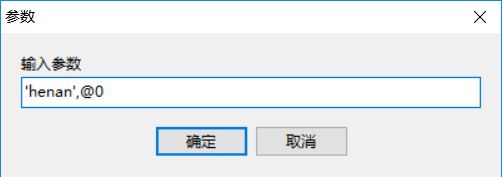
在这里,设置参数address的值为henan,按照格式添加字符@***,@字符后面的可以随便跟个字符,我也不知道啥意思
<select id="queryCountByAddress" parameterType="HashMap" statementType="CALLABLE">
{
CALL queryByAddress(
#{address,jdbcType=VARCHAR,mode=IN},
#{scount,jdbcType=INTEGER,mode=OUT}
)
}
select>
然后在接口里添加函数声明void queryCountByAddress(Map
最后测试函数,输入参数用put,输出参数用get
public static void queryCountByAddress(){
InputStream stream = Student.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("conf.xml");
SqlSessionFactory ssf=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(stream);
SqlSession session=ssf.openSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Map<String ,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("address", "henan");
studentMapper.queryCountByAddress(map);
Object count = map.get("scount");
session.commit();
System.out.println(count);
session.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
queryCountByAddress();
}
可以得到输出结果也为2
注意:如果存储过程为删除操作,在StudentMapper.xml里应该写delete标签,更新操作为update标签,如下所示
<delete id="deleteBySno" parameterType="HashMap" statementType="CALLABLE">
{
CALL deleteBySno(
#{no,jdbcType=INTEGER,mode=IN},
)
}
delete>
在测试函数中,增删改操作不要忘了提交事务。