反编译async/await关键字记录
注意:本文章仅供个人学习用途,并不保证解释和想法是正确的,
新建webapi项目,在ValuesController中输入如下代码:
private static int TId()
{
return Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId;
}
// GET api/
public async Task> Get()
{
Debug.WriteLine($"thread id {TId()} before Task.Run", "Debug");
await Task.Run(() =>
{
Debug.WriteLine($"thread id {TId()} in Task.Run", "Debug");
});
Debug.WriteLine($"thread id {TId()} after Task.Run", "Debug");
return new string[] { "value1", "value2" };
} 通过.NET Reflector 7.0反编译webapi的dll
async关键字消失了,它被编译成了如下方法:
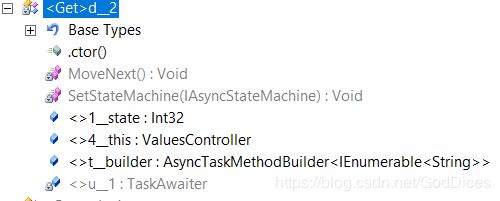
[AsyncStateMachine(typeof(d__2)), DebuggerStepThrough]
public Task> Get()
{
d__2 stateMachine = new d__2 {
<>4__this = this,
<>t__builder = AsyncTaskMethodBuilder>.Create(),
<>1__state = -1
};
//这里Start状态机
stateMachine.<>t__builder.Start<d__2>(ref stateMachine);
//new一个状态机stateMachine并且设置相关属性,__this是Controller,
//__builder是AsyncTaskMethodBuilder>
//__state = -1 ,方便起见去掉了编译器生成的前缀
//然后直接返回__builder的Task
return stateMachine.<>t__builder.Task;
} 状态机的MoveNext方法:
private void MoveNext()
{
IEnumerable enumerable;
int num = this.<>1__state;
try
{
TaskAwaiter awaiter;
if (num != 0)
{
Debug.WriteLine(string.Format("thread id {0} before Task.Run", ValuesController.TId()), "Debug");
if (ValuesController.<>c.<>9__2_0 == null)
{
Action action1 = ValuesController.<>c.<>9__2_0;
}
//await消失了,被编译成下面的语句
awaiter = Task.Run(ValuesController.<>c.<>9__2_0 = new Action(ValuesController.<>c.<>9.b__2_0)).GetAwaiter();
if (!awaiter.IsCompleted)
{
//awaiter.IsCompleted其实就是Task.IsCompleted
//awaiter没有完成完成,再调用AsyncTaskMethodBuilder.AwaitUnsafeOnCompleted
//方法设置awaiter和状态机stateMachine来达到某种目的,然后直接返回
this.<>1__state = num = 0;
this.<>u__1 = awaiter;
ValuesController.d__2 stateMachine = this;
this.<>t__builder.AwaitUnsafeOnCompletedd__2>(ref awaiter, ref stateMachine);
return;
}
}
else
{
//awaiter为什么要把值设置回去,目前还没看懂。
awaiter = this.<>u__1;
this.<>u__1 = new TaskAwaiter();
//状态恢复初始值
this.<>1__state = num = -1;
}
//Get Result获取结果
awaiter.GetResult();
Debug.WriteLine(string.Format("thread id {0} after Task.Run", ValuesController.TId()), "Debug");
string[] textArray1 = new string[] { "value1", "value2" };
enumerable = textArray1;
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
this.<>1__state = -2;
this.<>t__builder.SetException(exception);
return;
}
this.<>1__state = -2;
this.<>t__builder.SetResult(enumerable);
}
//---------------------------------
//原来await Task.Run中的的代码被编译成一个单独的方法了
//根据反编译结果,这是ValuesController.<>c.b__2_0方法
internal void b__2_0()
{
Debug.WriteLine(string.Format("thread id {0} in Task.Run", ValuesController.TId()), "Debug");
}
//---------------------------------
//System.Threading.Tasks.
// Task.GetAwaiter方法,this指Task
public TaskAwaiter GetAwaiter()
{
return new TaskAwaiter(this);
}
先记录下上面代码中几个类型:
- TaskAwaiter (struct, System.Runtime.CompilerServices)
- AsyncTaskMethodBuilder
(struct, System.Runtime.CompilerServices)
//System.Runtime.CompilerServices.AsyncTaskMethodBuilder
//初始化状态机时调用的静态Create方法
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
public static AsyncTaskMethodBuilder Create()
{
return new AsyncTaskMethodBuilder();
}
//Get方法调用Start方法
[SecuritySafeCritical, DebuggerStepThrough, __DynamicallyInvokable]
public void Start(ref TStateMachine stateMachine) where TStateMachine: IAsyncStateMachine
{
if (((TStateMachine) stateMachine) == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("stateMachine");
}
//先不管这些代码的意义
ExecutionContextSwitcher ecsw = new ExecutionContextSwitcher();
RuntimeHelpers.PrepareConstrainedRegions();
try
{
ExecutionContext.EstablishCopyOnWriteScope(ref ecsw);
//这里调用了MoveNext方法,然后MoveNext方法再Task.Run我要await的方法,实际被编译器编译成了awaiter对象(TaskAwaiter)
stateMachine.MoveNext();
}
finally
{
ecsw.Undo();
}
} 在MoveNext方法中还有一个重要的地方,就是调用了AsyncTaskMethodBuilder
//AsyncTaskMethodBuilder.AwaitUnsafeOnCompleted
[SecuritySafeCritical, __DynamicallyInvokable]
public void AwaitUnsafeOnCompleted(ref TAwaiter awaiter, ref TStateMachine stateMachine) where TAwaiter: ICriticalNotifyCompletion where TStateMachine: IAsyncStateMachine
{
try
{
AsyncMethodBuilderCore.MoveNextRunner runnerToInitialize = null;
Action completionAction = this.m_coreState.GetCompletionAction(AsyncCausalityTracer.LoggingOn ? this.Task : null, ref runnerToInitialize);
if (this.m_coreState.m_stateMachine == null)
{
//没看懂这个builder的Task属性是怎么来的,之前Get方法返回出去的Task也是这个Task
Task builtTask = this.Task;
//this.m_coreState是AsyncMethodBuilderCore
this.m_coreState.PostBoxInitialization((TStateMachine) stateMachine, runnerToInitialize, builtTask);
}
awaiter.UnsafeOnCompleted(completionAction);
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
AsyncMethodBuilderCore.ThrowAsync(exception, null);
}
}
//-----------------------------
//之前代码提到的where TAwaiter: ICriticalNotifyCompletion,接口没有方法定义,但是awaiter是TaskAwaiter对象
//所以直接看TaskAwaiter.UnsafeOnCompleted方法
[SecurityCritical, __DynamicallyInvokable]
public void UnsafeOnCompleted(Action continuation)
{
//this.m_task就是Task.GetAwaiter中的Task
//public TaskAwaiter GetAwaiter()
//{
// return new TaskAwaiter(this);
//}
OnCompletedInternal(this.m_task, continuation, true, false);
}
[MethodImpl(MethodImplOptions.NoInlining), SecurityCritical]
internal static void OnCompletedInternal(Task task, Action continuation, bool continueOnCapturedContext, bool flowExecutionContext)
{
if (continuation == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("continuation");
}
StackCrawlMark lookForMyCaller = StackCrawlMark.LookForMyCaller;
if (TplEtwProvider.Log.IsEnabled() || Task.s_asyncDebuggingEnabled)
{
continuation = OutputWaitEtwEvents(task, continuation);
}
//根据字面意思,应该是为了await设置了Continuation(continue的名词形式,继续)
task.SetContinuationForAwait(continuation, continueOnCapturedContext, flowExecutionContext, ref lookForMyCaller);
}
先记录有哪些新类型:
- AsyncMethodBuilderCore (struct, System.Runtime.CompilerServices)
- AsyncMethodBuilderCore.MoveNextRunner (sealed class)
再看AsyncMethodBuilderCore.GetCompletionAction方法
[SecuritySafeCritical]
internal Action GetCompletionAction(Task taskForTracing, ref MoveNextRunner runnerToInitialize)
{
Action defaultContextAction;
MoveNextRunner runner;
Debugger.NotifyOfCrossThreadDependency();
//捕获执行上下文
ExecutionContext context = ExecutionContext.FastCapture();
if ((context != null) && context.IsPreAllocatedDefault)
{
defaultContextAction = this.m_defaultContextAction;
if (defaultContextAction != null)
{
return defaultContextAction;
}
//这是runner
runner = new MoveNextRunner(context, this.m_stateMachine);
//默认的action就是runner.Run
defaultContextAction = new Action(runner.Run);
if (taskForTracing != null)
{
this.m_defaultContextAction = defaultContextAction = this.OutputAsyncCausalityEvents(taskForTracing, defaultContextAction);
}
else
{
this.m_defaultContextAction = defaultContextAction;
}
}
else
{
runner = new MoveNextRunner(context, this.m_stateMachine);
defaultContextAction = new Action(runner.Run);
if (taskForTracing != null)
{
defaultContextAction = this.OutputAsyncCausalityEvents(taskForTracing, defaultContextAction);
}
}
if (this.m_stateMachine == null)
{
runnerToInitialize = runner;
}
//前面这么多代码,其实最终调用的是runner.Run
return defaultContextAction;
}
//------------------------
//MoveNextRunner.Run
[SecuritySafeCritical]
internal void Run()
{
if (this.m_context != null)
{
try
{
ContextCallback callback = s_invokeMoveNext;
if (callback == null)
{
s_invokeMoveNext = callback = new ContextCallback(AsyncMethodBuilderCore.MoveNextRunner.InvokeMoveNext);
}
//让执行上下文对象去执行InvokeMoveNext方法
ExecutionContext.Run(this.m_context, callback, this.m_stateMachine, true);
return;
}
finally
{
this.m_context.Dispose();
}
}
this.m_stateMachine.MoveNext();
}
//MoveNextRunner.InvokeMoveNext
[SecurityCritical]
private static void InvokeMoveNext(object stateMachine)
{
//再调用状态机MoveNext方法
((IAsyncStateMachine) stateMachine).MoveNext();
}
所以AsyncMethodBuilderCore.GetCompletionAction方法返回的是能够执行状态机MoveNext方法的Action委托。回到之前AsyncTaskMethodBuilder
//根据字面意思,应该是为了await设置了Continuation(continue的名词形式,继续)
task.SetContinuationForAwait(continuation, continueOnCapturedContext, flowExecutionContext, ref lookForMyCaller);
[SecurityCritical]
internal void SetContinuationForAwait(Action continuationAction, bool continueOnCapturedContext, bool flowExecutionContext, ref StackCrawlMark stackMark)
{
TaskContinuation tc = null;
if (continueOnCapturedContext)
{
//之前用搜索引擎查询相关知识时,那些文章都提到了同步上下文SynchronizationContext对象,最终在这里找到了它的尊容
SynchronizationContext currentNoFlow = SynchronizationContext.CurrentNoFlow;
if ((currentNoFlow != null) && (currentNoFlow.GetType() != typeof(SynchronizationContext)))
{
tc = new SynchronizationContextAwaitTaskContinuation(currentNoFlow, continuationAction, flowExecutionContext, ref stackMark);
}
else
{
TaskScheduler internalCurrent = TaskScheduler.InternalCurrent;
if ((internalCurrent != null) && (internalCurrent != TaskScheduler.Default))
{
tc = new TaskSchedulerAwaitTaskContinuation(internalCurrent, continuationAction, flowExecutionContext, ref stackMark);
}
}
}
if ((tc == null) & flowExecutionContext)
{
tc = new AwaitTaskContinuation(continuationAction, true, ref stackMark);
}
//根据各种条件创建TaskContinuation对象,最后需要执行它的Run方法
if (tc != null)
{
if (!this.AddTaskContinuation(tc, false))
{
tc.Run(this, false);
}
}
//否则,就执行一个非安全的方法(字面意思)
else if (!this.AddTaskContinuation(continuationAction, false))
{
AwaitTaskContinuation.UnsafeScheduleAction(continuationAction, this);
}
}重点关注这几个对象
- SynchronizationContextAwaitTaskContinuation
- TaskSchedulerAwaitTaskContinuation
方便起见我直接下载了.NET Framework 4.7的源代码
// System.Threading.Tasks.Task
/// Inlines or schedules the continuation.
/// The antecedent task, which is ignored.
/// true if inlining is permitted; otherwise, false.
[SecuritySafeCritical]
internal sealed override void Run(Task task, bool canInlineContinuationTask)
{
// If we're allowed to inline, run the action on this thread.
if (canInlineContinuationTask &&
m_syncContext == SynchronizationContext.CurrentNoFlow)
{
RunCallback(GetInvokeActionCallback(), m_action, ref Task.t_currentTask);
}
// Otherwise, Post the action back to the SynchronizationContext.
else
{
TplEtwProvider etwLog = TplEtwProvider.Log;
if (etwLog.IsEnabled())
{
m_continuationId = Task.NewId();
etwLog.AwaitTaskContinuationScheduled((task.ExecutingTaskScheduler ?? TaskScheduler.Default).Id, task.Id, m_continuationId);
}
RunCallback(GetPostActionCallback(), this, ref Task.t_currentTask);
}
// Any exceptions will be handled by RunCallback.
}
/// Gets a cached delegate for the PostAction method.
///
/// A delegate for PostAction, which expects a SynchronizationContextAwaitTaskContinuation
/// to be passed as state.
///
[MethodImpl(MethodImplOptions.AggressiveInlining)]
[SecurityCritical]
private static ContextCallback GetPostActionCallback()
{
ContextCallback callback = s_postActionCallback;
if (callback == null) { s_postActionCallback = callback = PostAction; } // lazily initialize SecurityCritical delegate
return callback;
}
/// Calls InvokeOrPostAction(false) on the supplied SynchronizationContextAwaitTaskContinuation.
/// The SynchronizationContextAwaitTaskContinuation.
[SecurityCritical]
private static void PostAction(object state)
{
var c = (SynchronizationContextAwaitTaskContinuation)state;
TplEtwProvider etwLog = TplEtwProvider.Log;
if (etwLog.TasksSetActivityIds && c.m_continuationId != 0)
{
c.m_syncContext.Post(s_postCallback, GetActionLogDelegate(c.m_continuationId, c.m_action));
}
else
{
c.m_syncContext.Post(s_postCallback, c.m_action); // s_postCallback is manually cached, as the compiler won't in a SecurityCritical method
}
}
//----------------
//AspNetSynchronizationContext
//由于目前是针对webapi的async,可以先看AspNetSynchronizationContext类型
public override void Post(SendOrPostCallback callback, Object state) {
_state.Helper.QueueAsynchronous(() => callback(state));
}
public void QueueAsynchronous(Action action) {
CheckForRequestStateIfRequired(checkForReEntry: true);
ChangeOperationCount(+1);
// This method only schedules work; it doesn't itself do any work. The lock is held for a very
// short period of time.
lock (_lockObj) {
// Task.ContinueWith 即上一个Task完成之后,再执行下一个Task,这里就是action,
// 即被Post进来的委托,也就是TaskAwait生成的Continuation/Completion委托,
// 也就是状态机MoveNext方法
Task newTask = _lastScheduledTask.ContinueWith(_ => SafeWrapCallback(action), TaskScheduler.Default);
_lastScheduledTask = newTask; // the newly-created task is now the last one
}
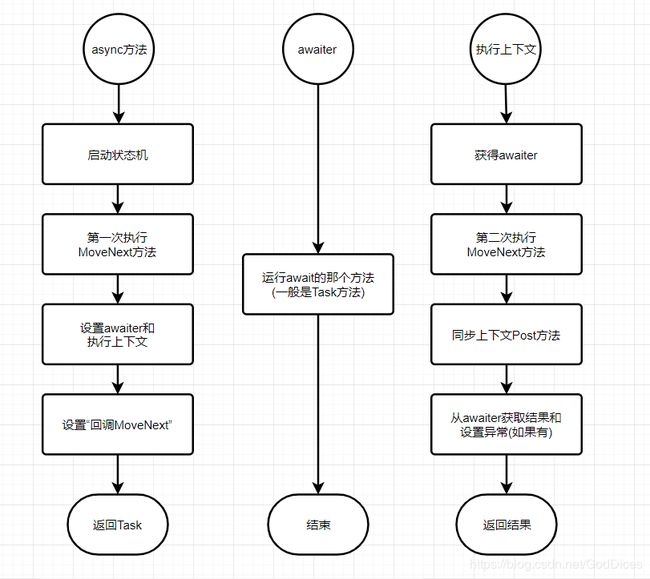
}简化代码,用下图帮助理解:
简化代码,用文字简单总结async/await关键字作用:
- 执行MoveNext方法
- await被编译成从那个被await的Task获取到的TaskAwaiter对象(awaiter)
- awaiter设置MoveNext“回调”委托和执行上下文(ExecutionContext)
- "async方法"返回,这里不会阻塞当前线程
- 于此同时执行上下文获取同步上下文(SynchronizationContext),调用它的Post方法,传入“回调”委托
- 执行"回调"委托MoveNext(顺序是Task.ContinueWith("回调"委托),这个Task就是之前被await的那个Task)
- 在MoveNext方法中恢复现场,用awaiter对象获取被await的那个Task的结果(awaiter.GetResult,其实就是Task.GetResult)
- 返回结果
关于异常处理
await之后,Task.Run报的错可以被捕获到了,原因是awaiter.GetResult会判断Task是否执行成功,如果执行失败,会throw错误,主要有TaskCanceledException(由于Task.Run里面报错,导致Task被取消抛出的异常)和AggregateException(Task包装的未处理异常)
public void GetResult()
{
ValidateEnd(m_task);
}
internal static void ValidateEnd(Task task)
{
if (task.IsWaitNotificationEnabledOrNotRanToCompletion)
{
HandleNonSuccessAndDebuggerNotification(task);
}
}
private static void HandleNonSuccessAndDebuggerNotification(Task task)
{
if (!task.IsCompleted)
{
bool taskCompleted = task.InternalWait(Timeout.Infinite, default(CancellationToken));
Contract.Assert(taskCompleted, "With an infinite timeout, the task should have always completed.");
}
task.NotifyDebuggerOfWaitCompletionIfNecessary();
if (!task.IsRanToCompletion) ThrowForNonSuccess(task);
}
private static void ThrowForNonSuccess(Task task)
{
Contract.Requires(task.IsCompleted, "Task must have been completed by now.");
Contract.Requires(task.Status != TaskStatus.RanToCompletion, "Task should not be completed successfully.");
switch (task.Status)
{
case TaskStatus.Canceled:
var oceEdi = task.GetCancellationExceptionDispatchInfo();
if (oceEdi != null)
{
oceEdi.Throw();
Contract.Assert(false, "Throw() should have thrown");
}
throw new TaskCanceledException(task);
case TaskStatus.Faulted:
var edis = task.GetExceptionDispatchInfos();
if (edis.Count > 0)
{
edis[0].Throw();
Contract.Assert(false, "Throw() should have thrown");
break; // Necessary to compile: non-reachable, but compiler can't determine that
}
else
{
Contract.Assert(false, "There should be exceptions if we're Faulted.");
throw task.Exception;
}
}
}关于SynchronizationContext
ASP.NET程序有AspNetSynchronizationContext,WindowForm程序有WindowsFormsSynchronizationContext。AspNetSynchronizationContext在执行"MoveNext回调"时,恢复HttpContext到当前执行"回调"的线程,所以如果有新线程执行MoveNext,这个线程不会丢失HttpContext(Http相关信息,我猜测是Socket)WindowsFormsSynchronizationContext会用Win32消息泵处理"回调"委托,因此这个委托会在主线程中被执行。
.NET Framework源代码可以在https://referencesource.microsoft.com/中找到。
如果有问题和错误,可以在评论指出。