JAVA-IO(1)操作简介
Java IO操作主要指的是使用Java进行输入输出操作,Java的所有操作类都早Java.io包中,在使用时需要导入此包.
在整个Java.io包中,最重要的是5个类和一个接口,5个类指的是:
File,OutputStream,InputStream,Writer,Reader
一个接口指的是:
Serializable.
============================================
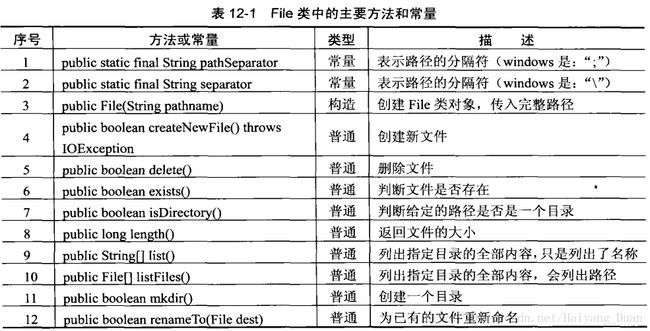
一. File类操作简介
在整个io包中,File是唯一一个与文件本身有关的类.
新建文件
String path = "C:" + File.separator + "test";
File f = new File(path);
f.createNewFile();删除文件
String path = "C:" + File.separator + "test";
File f = new File(path);
f.delete();创建文件夹
String path = "C:" + File.separator + "test";
File f = new File(path);
f.mkdir();列出指定文件夹的全部文件
public String[] list();//列出所有的名称
public File[] listFiles();//列出完整的路径 String path = "C:" + File.separator + "test";
File f = new File(path);
String[] paths = f.list();
for(int i=0;i{
System.out.println(paths[i]);
} String path = "C:" + File.separator +"test";
File f = new File(path);
File[] files = f.listFiles();
for(int i=0;i{
System.out.println(files[i]);
} 判断给定的路径是否是目录
String path = "C:" + File.separator +"test";
File f = new File(path);
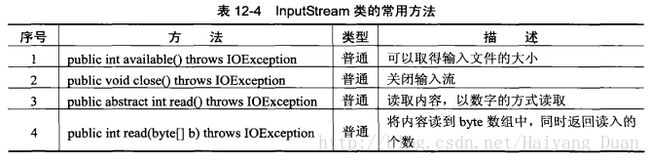
f.isDirectory();//判断二. 字节流OutputStream与InputStream
在Java中io操作也是有步骤的,以文件的操作为例:
(1)使用File类打开一个文件;
(2)通过字节流或字符流的子类置顶输出的位置;
(3)进行读写操作;
(4)关闭输入输出;
1.字节输出流OutputStream
向文件中写入数据
//文件不存在则会自动创建
File f = new File("C:" + File.separator + "test");
//写入数据
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(f);
String str = "Hello World!";
byte[] b = str.getBytes();
out.write(b);
out.close();追加新内容
File f = new File("C:" + File.separator + "test");
//参数true表示追加数据
FileOutputStream out2 = new FileOutputStream(f, true);
String str = "\r\nMy Girl!";
byte[] b = str.getBytes();
out.write(b);
out.close();2.字节输入流InputStream
读取数据
File f = new File("C:" + File.separator + "test");
//读取数据
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(f);
byte[] b = new byte[(int) f.length()];
in.read(b);
in.close();
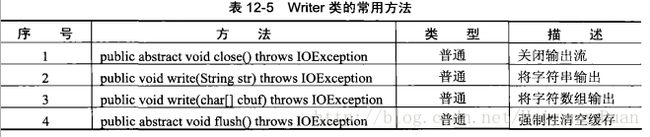
System.out.println(new String(b));三. 字符流Writer与Reader
- 字符输出流Writer
使用字符流写入数据
//使用字符流写入数据
File f = new File("C:" + File.separator + "test");
FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(f);
String str = "HELLO!";
writer.write(str);
writer.flush();
writer.close();使用字符流追加内容
File f = new File("C:" + File.separator + "test");
FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(f,true);
String str = "\r\nWORLD!";
writer.write(str);
writer.flush();
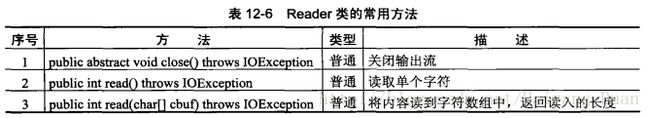
writer.close();- 字符输入流Reader
使用字符流读取数据
//使用字符流读取数据
File f = new File("C:" + File.separator + "test");
FileReader reader = new FileReader(f);
char[] c = new char[(int) f.length()];
int len = reader.read(c);
reader.close();
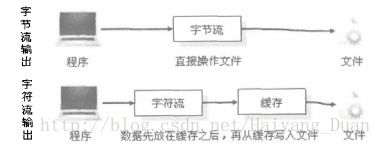
System.out.println(new String(c,0,len));&&& 字符流与字节流的区别:
对于字节流,直接操作文件数据的读写
而对于字符流,则是通过缓冲区操作数据的读写
验证:
不关闭数据流,字节流可以写成功
而字符流则不行.使用flush()方法就可以实现了
那么,使用字节流还是字符流好呢?
所有的文件包括图片在硬盘或在传输时,都是以字节的形式进行,而字符只在内存中出现,所以字节流使用较为广泛.