EOS 之demux源码解析
EOS 之demux源码解析
Demux从Facebook的Flux Architecture架构模式和Redux(JavaScript程序的状态容器,即应用数据流框架)中汲取灵感,创建了一个后端基础架构模式。Demux赋予区块链事件溯源技术,可以准确地更新EOSIO上应用程序的可查询数据库。
Demux的一大优势是允许区块链事件自动地(并且可验证地)更新到Mongo或Postgres SQL数据库,这意味着存储在其中的数据仍然可以通过区块链进行验证。并且兼具传统数据库的灵活性和速度,及区块链的信任和不可变属性,达到了两全其美的效果。
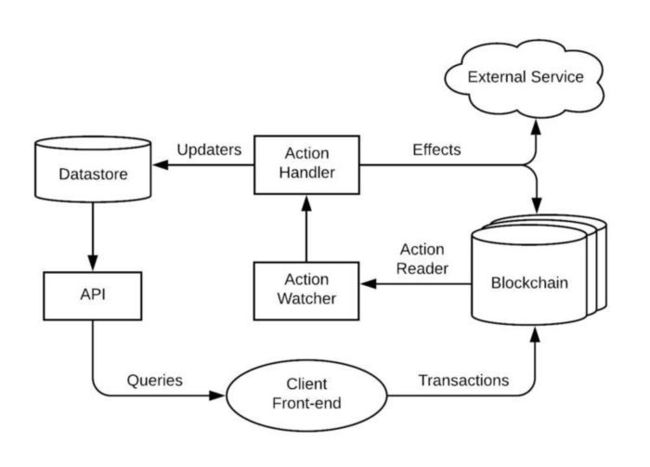
如上图所示:
Action Reader 负责读取bloackchain的数据。
Action watcher 负责调度Action Reader检测新的chain数据。
Action Handler 负责过滤和分发updaters 和effects事件。
目前我们项目是在updaters里面更新数据库数据,effects事件的具体作用还没有研究到。
通过example来解读源码
index.js
const {
readers: { eos: { NodeosActionReader } },
watchers: { BaseActionWatcher },
} = require("../../dist/")
const ObjectActionHandler = require("./ObjectActionHandler")
const updaters = require("./updaters")
const effects = require("./effects")
// 设置handler分发的updaters和effects
const actionHandler = new ObjectActionHandler(
updaters,
effects,
)
// 定义reader获取数据地址,读取位置
const actionReader = new NodeosActionReader(
"http://mainnet.eoscalgary.io", // Thanks EOS Calgary!
0, // Start at most recent blocks
true, // 设置是否获取不可逆的数据
)
// 将reader和handler设置到watcher
const actionWatcher = new BaseActionWatcher(
actionReader,
actionHandler,
500,
)
// 开始轮询监控chain数据
actionWatcher.watch()
example里面的代码就不贴了,有兴趣可以自己看看源码。
BaseActionWatcher
"use strict";
var __awaiter = (this && this.__awaiter) || function (thisArg, _arguments, P, generator) {
return new (P || (P = Promise))(function (resolve, reject) {
function fulfilled(value) { try { step(generator.next(value)); } catch (e) { reject(e); } }
function rejected(value) { try { step(generator["throw"](value)); } catch (e) { reject(e); } }
function step(result) { result.done ? resolve(result.value) : new P(function (resolve) { resolve(result.value); }).then(fulfilled, rejected); }
step((generator = generator.apply(thisArg, _arguments || [])).next());
});
};
Object.defineProperty(exports, "__esModule", { value: true });
/**
* Cooredinates implementations of `AbstractActionReader`s and `AbstractActionHandler`s in
* a polling loop.
*/
class BaseActionWatcher {
constructor(actionReader, actionHandler, pollInterval) {
this.actionReader = actionReader;
this.actionHandler = actionHandler;
this.pollInterval = pollInterval;
}
/**
* Starts a polling loop running in replay mode.
*/
replay() {
return __awaiter(this, void 0, void 0, function* () {
yield this.actionReader.seekToBlock(this.actionReader.startAtBlock);
yield this.watch();
});
}
/**
* Uses the given actionReader and actionHandler to poll and process new blocks.
*/
watch() {
return __awaiter(this, void 0, void 0, function* () {
// Record start time
const startTime = new Date().getTime();
// Process blocks until we're at the head block
let headBlockNumber = 0;
while (!headBlockNumber || this.actionReader.currentBlockNumber < headBlockNumber) {
const [blockData, isRollback] = yield this.actionReader.nextBlock();
// Handle block (and the actions within them)
let needToSeek = false;
let seekBlockNum = 0;
if (blockData) {
[needToSeek, seekBlockNum] = yield this.actionHandler.handleBlock(blockData, isRollback, this.actionReader.isFirstBlock);
}
// Seek to next needed block at the request of the action handler
if (needToSeek) {
yield this.actionReader.seekToBlock(seekBlockNum - 1);
}
headBlockNumber = this.actionReader.headBlockNumber;
}
// Record end time
const endTime = new Date().getTime();
// Calculate timing for next iteration
const duration = endTime - startTime;
let waitTime = this.pollInterval - duration;
if (waitTime < 0) {
waitTime = 0;
}
// Schedule next iteration
setTimeout(() => __awaiter(this, void 0, void 0, function* () { return yield this.watch(); }), waitTime);
});
}
}
exports.BaseActionWatcher = BaseActionWatcher;下面这段代码通过递归调用watch()一直轮询到最新数据
setTimeout(() => __awaiter(this, void 0, void 0, function* () { return yield this.watch(); }), waitTime);下面看看对ActionReader的调度,以及handler时间的分发代码
while (!headBlockNumber || this.actionReader.currentBlockNumber < headBlockNumber) {
const [blockData, isRollback] = yield this.actionReader.nextBlock()
// Handle block (and the actions within them)
let needToSeek = false
let seekBlockNum = 0
if (blockData) {
[needToSeek, seekBlockNum] = yield this.actionHandler.handleBlock(blockData, isRollback, this.actionReader.isFirstBlock)
}
// Seek to next needed block at the request of the action handler
if (needToSeek) {
yield this.actionReader.seekToBlock(seekBlockNum - 1)
}
headBlockNumber = this.actionReader.headBlockNumber
}while 的条件!headBlockNumber初始化的时候为true,这时候进入调度。通过this.actionReader.nextBlock()方法获取区块信息blockData和是否回滚isRollBack。我们再来看看ActionReader的代码,看看nextBlock()做了什么事情。
const __awaiter = (this && this.__awaiter) || function (thisArg, _arguments, P, generator) {
return new (P || (P = Promise))(((resolve, reject) => {
function fulfilled(value) { try { step(generator.next(value)) } catch (e) { reject(e) } }
function rejected(value) { try { step(generator.throw(value)) } catch (e) { reject(e) } }
function step(result) { result.done ? resolve(result.value) : new P(((resolve) => { resolve(result.value) })).then(fulfilled, rejected) }
step((generator = generator.apply(thisArg, _arguments || [])).next())
}))
}
Object.defineProperty(exports, "__esModule", { value: true })
/**
* Reads blocks from a blockchain, outputting normalized `Block` objects.
*/
class AbstractActionReader {
constructor(startAtBlock = 1, onlyIrreversible = false, maxHistoryLength = 600) {
this.startAtBlock = startAtBlock
this.onlyIrreversible = onlyIrreversible
this.maxHistoryLength = maxHistoryLength
this.headBlockNumber = 0
this.isFirstBlock = true
this.currentBlockData = null
this.blockHistory = []
this.currentBlockNumber = startAtBlock - 1
}
/**
* Loads the next block with chainInterface after validating, updating all relevant state.
* If block fails validation, rollback will be called, and will update state to last block unseen.
*/
nextBlock() {
return __awaiter(this, void 0, void 0, function* () {
let blockData = null
let isRollback = false
// If we're on the head block, refresh current head block
//在nextBlock中通过下面代码判断是否在最新区块信息上面,不再则刷新区块信息,其中getHeadBlockNumber()在eos目录下面的NodeosActionReaders里面,就是获取最新区块链信息。没有特别的代码。
//构造函数中this.headBlockNumber = 0,所以这里回去获取区块链最新的number,并更新headBlockNumber。
if (this.currentBlockNumber === this.headBlockNumber || !this.headBlockNumber) {
this.headBlockNumber = yield this.getHeadBlockNumber()
}
// If currentBlockNumber is negative, it means we wrap to the end of the chain (most recent blocks)
// This should only ever happen when we first start, so we check that there's no block history
//判断是不是第一次启动,如果是第一次启动并将需要更新的数据指向最新的block
if (this.currentBlockNumber < 0 && this.blockHistory.length === 0) {
this.currentBlockNumber = this.headBlockNumber + this.currentBlockNumber
this.startAtBlock = this.currentBlockNumber + 1
}
// If we're now behind one or more new blocks, process them
//解析数据
if (this.currentBlockNumber < this.headBlockNumber) {
const unvalidatedBlockData = yield this.getBlock(this.currentBlockNumber + 1)
const expectedHash = this.currentBlockData !== null ? this.currentBlockData.blockHash : "INVALID"
const actualHash = unvalidatedBlockData.previousBlockHash
// Continue if the new block is on the same chain as our history, or if we've just started
//判断是否需要回滚,不回滚则将当前number获取的区块信息开始记录信息
if (expectedHash === actualHash || this.blockHistory.length === 0) {
blockData = unvalidatedBlockData // Block is now validated
if (this.currentBlockData) {
this.blockHistory.push(this.currentBlockData) // No longer current, belongs on history
}
this.blockHistory.splice(0, this.blockHistory.length - this.maxHistoryLength) // Trim history
this.currentBlockData = blockData // Replaced with the real current block
this.currentBlockNumber = this.currentBlockData.blockNumber
} else {
// Since the new block did not match our history, we can assume our history is wrong
// and need to roll back
yield this.rollback()
isRollback = true // Signal action handler that we must roll back
// Reset for safety, as new fork could have less blocks than the previous fork
this.headBlockNumber = yield this.getHeadBlockNumber()
}
}
// Let handler know if this is the earliest block we'll send
this.isFirstBlock = this.currentBlockNumber === this.startAtBlock
if (this.currentBlockData === null) {
throw Error("currentBlockData must not be null.")
}
//返回当前区块信息,是否回滚信息
return [this.currentBlockData, isRollback]
})
}
/**
* Incrementally rolls back reader state one block at a time, comparing the blockHistory with
* newly fetched blocks. Rollback is finished when either the current block's previous hash
* matches the previous block's hash, or when history is exhausted.
*
* @return {Promise}
*/
rollback() {
return __awaiter(this, void 0, void 0, function* () {
console.info("!! Fork detected !!")
let blocksToRewind
// Rewind at least 1 block back
if (this.blockHistory.length > 0) {
// TODO:
// check and throw error if undefined
const block = this.blockHistory.pop()
if (block === undefined) {
throw Error("block history should not have undefined entries.")
}
this.currentBlockData = yield this.getBlock(block.blockNumber)
blocksToRewind = 1
}
// Pop off blocks from cached block history and compare them with freshly fetched blocks
while (this.blockHistory.length > 0) {
const [cachedPreviousBlockData] = this.blockHistory.slice(-1)
const previousBlockData = yield this.getBlock(cachedPreviousBlockData.blockNumber)
// TODO:
// add null guards
const currentBlock = this.currentBlockData
if (currentBlock !== null) {
if (currentBlock.previousBlockHash === previousBlockData.blockHash) {
console.info(`✓ BLOCK ${currentBlock.blockNumber} MATCH:`)
console.info(` expected: ${currentBlock.previousBlockHash}`)
console.info(` received: ${previousBlockData.blockHash}`)
console.info(`Rewinding ${blocksToRewind} blocks to block (${currentBlock.blockNumber})...`)
break
}
console.info(`✕ BLOCK ${currentBlock.blockNumber} MISMATCH:`)
console.info(` expected: ${currentBlock.previousBlockHash}`)
console.info(` received: ${previousBlockData.blockHash}`)
console.info("Rollback history has been exhausted!")
}
this.currentBlockData = previousBlockData
this.blockHistory.pop()
blocksToRewind += 1
}
if (this.blockHistory.length === 0) {
yield this.rollbackExhausted()
}
})
}
/**
* When history is exhausted in rollback(), this is run to handle the situation. If left unimplemented,
* then only instantiate with `onlyIrreversible` set to true.
*/
rollbackExhausted() {
throw Error("Rollback history has been exhausted, and no rollback exhaustion handling has been implemented.")
}
/**
* Move to the specified block.
* 跳转到指定区块,开始读取数据
*/
seekToBlock(blockNumber) {
return __awaiter(this, void 0, void 0, function* () {
// Clear current block data
this.currentBlockData = null
this.headBlockNumber = 0
// If we're going back to the first block, we don't want to get the preceding block
if (blockNumber === 1) {
this.blockHistory = []
return
}
// Check if block exists in history
let toDelete = -1
for (let i = this.blockHistory.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (this.blockHistory[i].blockNumber === blockNumber) {
break
} else {
toDelete += 1
}
}
if (toDelete >= 0) {
this.blockHistory.splice(toDelete)
this.currentBlockData = this.blockHistory.pop() || null
}
// Load current block
this.currentBlockNumber = blockNumber - 1
if (!this.currentBlockData) {
this.currentBlockData = yield this.getBlock(this.currentBlockNumber)
}
})
}
}
exports.AbstractActionReader = AbstractActionReader构造函数定义了currentBlockNumber(当前区块number),startAtBlock(开始区块number)等信息。具体的逻辑都在注释里面。
通过ActionReader获取了当前区块信息,下面看看在获取的blockData之后,ActionHandler做了什么事情。
public async handleBlock(
block: Block,
isRollback: boolean,
isFirstBlock: boolean,
isReplay: boolean = false,
): Promise<[boolean, number]> {
if (isRollback) {
await this.rollbackTo(block.blockNumber - 1)
}
if (!this.lastProcessedBlockHash && this.lastProcessedBlockNumber === 0) {
//获取indexState,这个可以在自定义handler的子类中重写,用于设置最开始的区块信息。
const { blockNumber: indexStateBlockNumber, blockHash: indexStateBlockHash } = await this.loadIndexState()
if (indexStateBlockNumber && indexStateBlockHash) {
this.lastProcessedBlockNumber = indexStateBlockNumber
this.lastProcessedBlockHash = indexStateBlockHash
}
}
const nextBlockNeeded = this.lastProcessedBlockNumber + 1
// Just processed this block; skip
//处理过的信息,最新信息已处理,不需要继续处理
if (block.blockNumber === this.lastProcessedBlockNumber
&& block.blockHash === this.lastProcessedBlockHash) {
return [false, 0]
}
// If it's the first block but we've already processed blocks, seek to next block
//如果是第一条信息,但是后续信息未处理,则返回需要跳转到指定区块,继续调用watcher更新整个区块信息。
if (isFirstBlock && this.lastProcessedBlockHash) {
return [true, nextBlockNeeded]
}
// Only check if this is the block we need if it's not the first block
//如果不是第一个区块
if (!isFirstBlock) {
//如果当前区块number不想等,则返回需要跳转到下一区块
if (block.blockNumber !== nextBlockNeeded) {
return [true, nextBlockNeeded]
}
// Block sequence consistency should be handled by the ActionReader instance
if (block.previousBlockHash !== this.lastProcessedBlockHash) {
throw Error("Block hashes do not match; block not part of current chain.")
}
}
//调用updaters和effects处理客户端数据
const handleWithArgs: (state: any, context?: any) => void = async (state: any, context: any = {}) => {
await this.handleActions(state, block, context, isReplay)
}
await this.handleWithState(handleWithArgs)
return [false, 0]
}这里就是判断获取到的数据是否需要给予updaters和effects处理,如果需要处理则调用handleWithState来通知updater和effects来处理数据。updater和effects则根据自己定义的actionTypes来处理相应数据。
其中loadIndexState()获取的信息如果和区块链上对应节点信息相同,则数据将从loadIndexState()中获取的节点信息开始更新数据,否则从reader初始化的节点数据开始获取数据。ps:为什么这么设置,目前小编还没有想明白,欢迎告知。
最后如果handler返回需要跳转到指定的block,则调用reader的seekToBlock来更新当前节点的数据。从而在指定的节点开始重新获取数据。
至此,整个抓取EOS区块链数据的递归逻辑就分析完毕。如有不当,期望指出!
谢谢。
