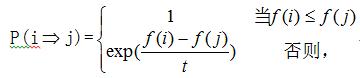TSP_旅行商问题 - 模拟退火算法(三)
一、前言
【旅行商问题】旅行商问题(TravelingSalesmanProblem,TSP)是一个经典的组合优化问题。经典的TSP可以描述为:一个商品推销员要去若干个城市推销商品,该推销员从一个城市出发,需要经过所有城市后,回到出发地。应如何选择行进路线,以使总的行程最短。从图论的角度来看,该问题实质是在一个带权完全无向图中,找一个权值最小的Hamilton回路。由于该问题的可行解是所有顶点的全排列,随着顶点数的增加,会产生组合爆炸,它是一个NP完全问题。由于其在交通运输、电路板线路设计以及物流配送等领域内有着广泛的应用,国内外学者对其进行了大量的研究。早期的研究者使用精确算法求解该问题,常用的方法包括:分枝定界法、线性规划法、动态规划法等。但是,随着问题规模的增大,精确算法将变得无能为力,因此,在后来的研究中,国内外学者重点使用近似算法或启发式算法,主要有遗传算法、模拟退火法、蚁群算法、禁忌搜索算法、贪婪算法和神经网络等。【参考百度百科】。
旅行商求解系列:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(1)TSP_旅行商问题- 蛮力法( 深度遍历优先算法DFS )
(2)TSP_旅行商问题- 动态规划
(3)TSP_旅行商问题- 模拟退火算法
(4)TSP_旅行商问题- 遗传算法
(5)TSP_旅行商问题- 粒子群算法
(6)TSP_旅行商问题- 神经网络
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
二、本文概要
1. 问题描述:
在求解实际问题,我们可以采用搜索算法,比如爬山搜索等系列算法。但这些算法都是局部优化算法,在某些实际问题中还是有很多缺点。局部搜索算法(以爬山算法为代表)的缺点:仅适用于某类组合优化问题;所得到的近似解质量通常较差;时间复杂度高,且最坏情况下的时间复杂度未知;最致命的是无法跳离局部最优的“陷阱”。
人们开始超越数学思维,从自然物理过程中寻找灵感。1982年,Kirkpatrick意识到固体退火算法与组合优化问题之间的类似性Metropolis等对孤立在恒定温度下达到热平衡的过程的模拟的启迪:把Metropolis准则引入优化过程中模拟退火算法(Simulated Annealing Algorithm,简称SAA),源于对固体退火过程的模拟,采用Metropolis接受准则,并用一组称为冷却表的参数控制算法进程,使算法在多项式时间里给出一个近似最优解。
爬山搜索为代表的局部搜索算法都是仅适用于某类组合优化问题,所得到的近似解的质量通常较差。这类方法最致命的缺点是无法跳离局部最优的“陷阱”,最终停留在某个局部最优解上。为了克服这些弱点,人们开始超脱纯数学思维,到一些自然物理过程中寻找灵感。模拟退火算法就是一个成功的典范,其思想比方法本身更为重要。2. 模拟退火算法简介:
模拟退火算法在处理全局优化、离散变量优化等困难问题中,具有传统优化算法无可比拟的优势。模拟退火算法的思想最早由Metorpolis等提出的。其出发点是基于物理中固体物质的退火过程与一般的组合优化问题之间的相似性。模拟退火法是一种通用的优化算法,其物理退火过程由以下三部分组成:
1)加温过程:其目的是增强粒子的热运动,使其偏离平衡位置。当温度足够高时,固体将熔为液体,从而消除系统原先存在的非均匀状态。
2)等温过程:对于与周围环境交换热量而温度不变的封闭系统,系统状态的自发变化总是朝自由能减少的方向进行,当自由能达到最小时,系统达到平衡状态。
3)冷却过程:使粒子热运动减弱,系统能量下降,得到晶体结构。其中,加温过程对应算法的设定初温,等温过程对应算法的Metropolis抽样过程,冷却过程对应控制参数的下降。这里能量的变化就是目标函数,我们要得到的最优解就是能量最低态。其中Metropolis准则是SA算法收敛于全局最优解的关键所在,Metropoli、准则以一定的概率接受恶化解,这样就使算法跳离局部最优的陷阱。
3. 编程环境:
- 本文使用C++语言,在VS2010平台上编写代码和调试,下文有提供相关的代码。
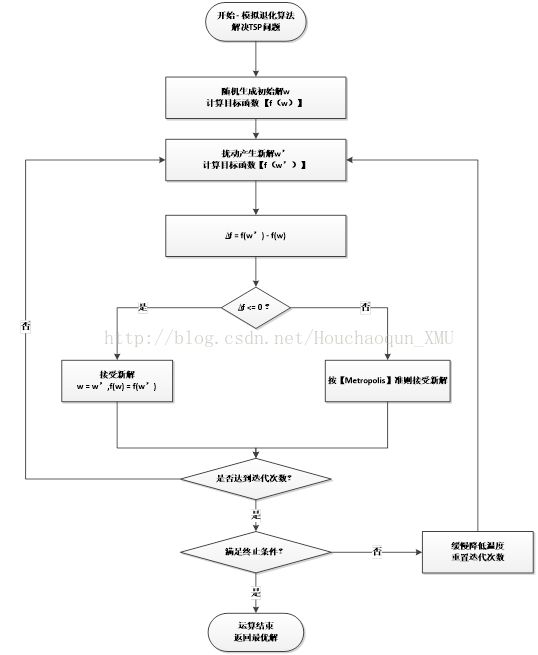
三、模拟退火算法(SA)
1. 模拟退火算法基本步骤
- (1)选S_0作为初始状态,令S (0)=S_0,同时设初始温度T,令i=0。
- (2)令 T=T_i,以T和S_i调用Metorpolis抽样算法,返回状态S作为本算法的当前解,S_i=S_0。
- (3)按照一定方式降温,即T =T_(i+1),其中T_(i+1)
- (4)检查终止条件,如果满足则转步骤 (5),否则转步骤(2)
- (5)当前解S_i为最优解,输出结果,停止。Metropolis抽样算法描述如下:
- 1)令k=0时,当前解 S (0)=S_0,在温度T下,进行以下各步操作。
- 2)按某个规定的方式根据当前解 S(k)所处的状态S产生一个近邻子集N (S(k))+S,从N(S (k))中随机得到一个新状态 S' 作为下一个候选解,计算能量之差△C' = C(S') - C(S(k))。
- 3)如果△C' < 0 ,则接受 S' 作为下一个当前解,否则,以概率exp(一△C' / T)接受 S' 作为下一个当前解。若 S' 被接受,则令S (k十1) = S' ,否则 S(k+1)=S(k)。
- 4)k =k +1,检查算法是否满足终止条件,若满足,则转步骤(5),否则转步骤(2)。
- 5)返回S(k),结束。
2. Metropolis算法解释
模拟退火算法用Metropolis算法产生组合优化问题解的序列。并由Metropolis准则对应的转移概率P:
确定是否接受从当前解i 到新解j 的转移。式中t ∈R+ 表示控制参数。开始让t 取较大的值,在进行足够多的转移后,缓慢减小t 的值(初始温度乘以退火系数,如 0.98 等),如此重复直至满足某个停止准则时算法终止。模拟退火算法依据Metropolis准则接受新解,除接受优化解外,还在一个限定范围内接受恶化解。开始时t值较大,可能接受较差的恶化解,随着t值的减小,只能接受较好的恶化解;当t值趋于零值时,就不再接受任何恶化解。这就使得算法可以跳出局部最优陷阱。在算法执行期间,随着控制参数t值的减小,算法返回某个整体最优解得概率单调增大,返回某个非最优解的概率单调减小。
3. 本文使用的结构体:
typedef struct{
int vex_num, arc_num; // 顶点数 边数
char vexs[max_vexNum]; // 顶点向量
double arcs[max_vexNum][max_vexNum]; // 邻接矩阵
}Graph;
typedef struct{
int length_path;
char path[max_vexNum];
}TSP_solution;四、程序流程
五、程序开发 - 模拟退火算法
1. 模拟退火过程:
TSP_solution SA_TSP(Graph G){
srand ( unsigned ( time(0) ) );
// 当前温度
double Current_Temperature = INITIAL_TEMPERATURE;
// 最优解
TSP_solution Best_solution;
Best_solution.length_path = MAX_INT;
// 初始路径
for (int i = 0;i < G.vex_num; i++)
{
Best_solution.path[i] = 'A' + i;
}
random_shuffle(Best_solution.path + 1, Best_solution.path + G.vex_num);
// 当前解, 与最优解比较
TSP_solution Current_solution;
// 模拟退火过程
while(MIN_TEMPERATURE < Current_Temperature){
// cout<<"MIN_TEMPERATURE = "< (rand()*101))
{
Best_solution = Current_solution;
}
else{
// cout<<"不接受当前解."< 2. 产生新解:
TSP_solution FindNewSolution(Graph G, TSP_solution bestSolution){
// 产生新的解
TSP_solution newSolution;
// 起始城市固定为A, 终点也要返回A, 即需要关注起点A和终点A之间的所有城市
int i = rand() % (G.vex_num - 1) + 1; // % 取余 -> 即将随机数控制在[1, G.vex_num - 1]
int j = rand() % (G.vex_num - 1) + 1;
if (i > j)
{
int temp = i;
i = j;
j = temp;
}
else if (i == j)
{ // 表示产生的随机数没有改变的作用, 将此路程设置为最大并结束该函数
newSolution = bestSolution;
return newSolution;
}
/* way 2 */
int choose = rand() % 3;
if (choose == 0)
{ // 随机交换任意两个城市的位置
char temp = bestSolution.path[i];
bestSolution.path[i] = bestSolution.path[j];
bestSolution.path[j] = temp;
}else if (choose == 1)
{ // 随机逆置城市的位置
reverse(bestSolution.path + i, bestSolution.path + j);
}
else{ // 随机移位城市的位置
if (j+1 == G.vex_num) //边界处不处理
{
newSolution = bestSolution;
return newSolution;
}
rotate(bestSolution.path + i, bestSolution.path + j, bestSolution.path + j + 1);
}
newSolution = bestSolution;
newSolution.path[G.vex_num] = newSolution.path[0]; // 终点与起始点相同
newSolution.path[G.vex_num + 1] = '\0';
newSolution.length_path = CalculateLength(G, newSolution);
return newSolution;
}3. 计算TSP路径长度:
int CalculateLength(Graph G,TSP_solution newSolution){
int _length = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < G.vex_num - 1; i++)
{
int _startCity = (int)newSolution.path[i] - 65;
int _endCity = (int)newSolution.path[i+1] - 65;
if (G.arcs[_startCity][_endCity] == -1)
{
return MAX_INT;
}
else{
_length += G.arcs[_startCity][_endCity];
}
}
// 判断该路径是否能回到起始城市
if (G.arcs[(int)newSolution.path[G.vex_num - 1] - 65][(int)newSolution.path[0]-65] == -1)
{
return MAX_INT;
}
else{
_length += G.arcs[(int)newSolution.path[G.vex_num - 1] - 65][(int)newSolution.path[0]-65];
// cout<<"_length = "<<_length<六、测试数据及其程序运行结果
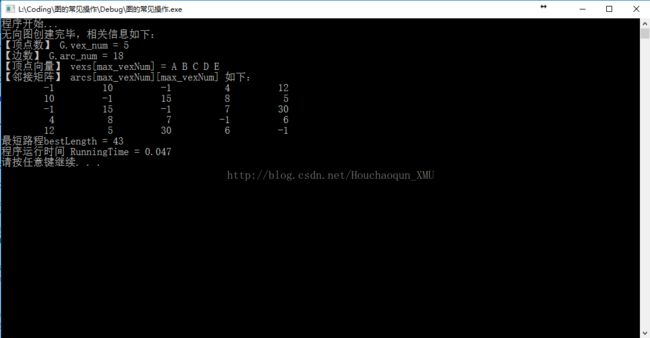
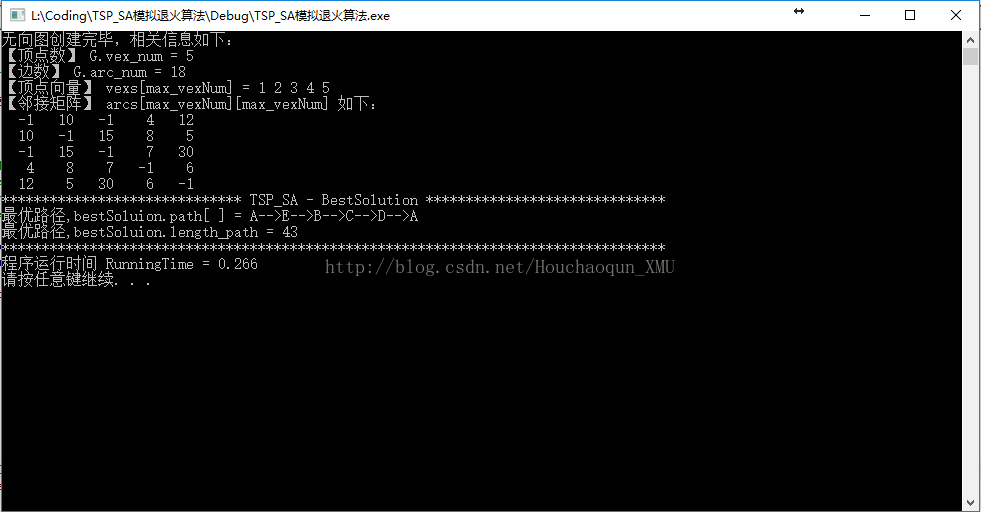
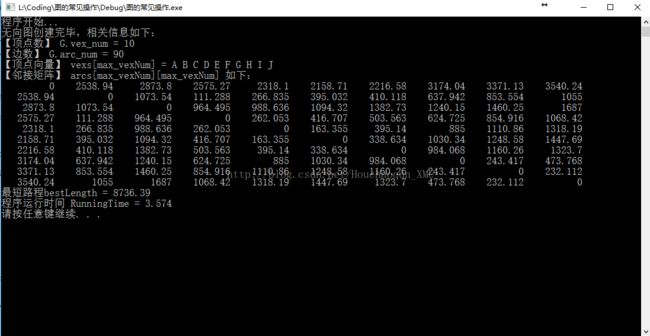
1.1 第一组测试数据(5个城市):
1.2. 第一组数据运行结果(5个城市):
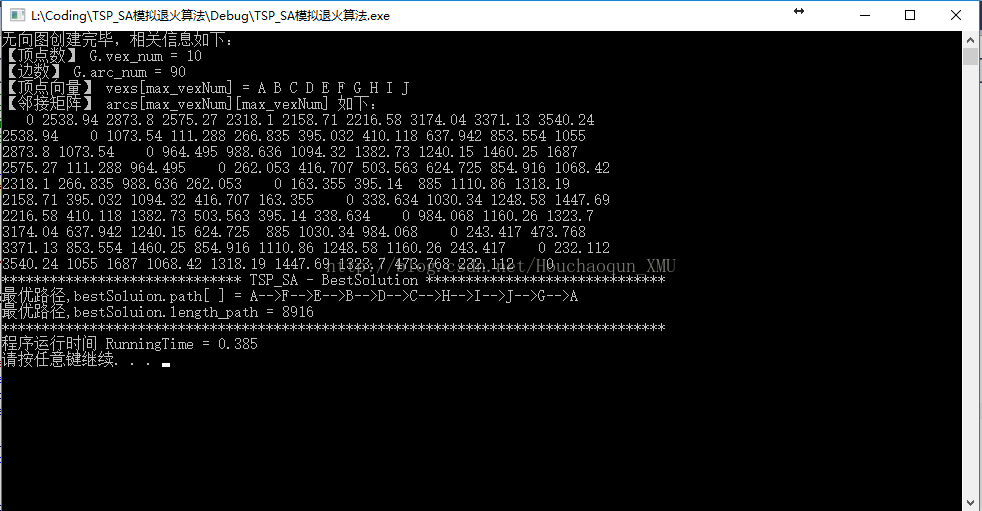
2.1 第二组测试数据(10个城市):
2.2 第二组数据运行结果(10个城市):
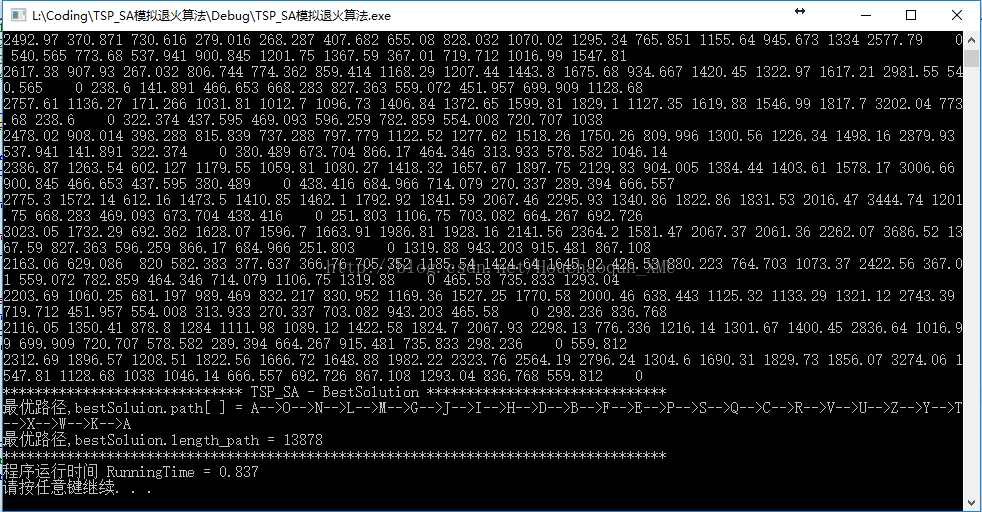
3. SA-TSP:处理26个城市的组合
七、总结 - 模拟退火算法解决TSP问题
1. 总结
理论上,模拟退火算法在某一温度下(此处初始温度为1000,最低温度为0.001,温度的下降率为0.98,Mapkov链长为500),只要计算时间足够长,就可以保证以概率1收敛于全局最优解。但在算法的实现过程中,由于计算速度和时间的限制,往往在优化结果和计算时间之间存在着矛盾,这是有待我们解决的。但模拟退火算法在解决中小规模组合优化问题上的优势是显而易见的。
2. 模拟退火算法的优缺点:(尚待完善,后续补充)
-- 优点:
1)描述简单,使用灵活,运用广泛,运行效率高;
2)需要较少的初始化条件约束,以概率 P(i) 收敛于全局最优;
3)具有并行性;
-- 缺点:
1)收敛速度慢,执行时间长;
2)参数依赖较大;
八、程序源码:
1. SA.h
#ifndef _SA_H_
#define _SA_H_
#define max_vexNum 30
#define MAX_CITYNUM 150
const int LEGNTH_Mapkob = 500;
const double SPEED = 0.98; // 退火速度
const double INITIAL_TEMPERATURE = 1000.0; // 初始温度
const double MIN_TEMPERATURE = 0.001; // 最低温度
const int MAX_INT = 999999;
typedef struct{
int vex_num, arc_num; // 顶点数 边数
char vexs[max_vexNum]; // 顶点向量
double arcs[max_vexNum][max_vexNum]; // 邻接矩阵
}Graph;
typedef struct{
int length_path;
char path[max_vexNum];
}TSP_solution;
void CreateGraph(Graph &G);
TSP_solution SA_TSP(Graph G);
TSP_solution FindNewSolution(Graph G, TSP_solution bestSolution);
int CalculateLength(Graph G,TSP_solution newSolution);
bool Is_Accepted();
void Display(Graph G,TSP_solution bestSoluion);
#endif2. SA.cpp
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include // 本文用于输出对齐
#include
#include
#include "SA.h"
using namespace std;
// 城市数据格式转化
void CityDataTranslate(){
ifstream read_in;
read_in.open("L:\\Coding\\TSP_SA模拟退火算法\\TSP_SA模拟退火算法\\ch150.txt"); // 待转换数据
if (!read_in.is_open())
{
cout<<"文件读取失败."<> vex_num;
fout << vex_num << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < vex_num; i++)
{
read_in >> city_No[i] >> city_x[i] >> city_y[i];
fout << i + 1 <<" ";
}
fout< ABCEDA
// 3. judge whether accepted new solution or not
// 4. Simulate Annealing
TSP_solution bestSoluion = SA_TSP(G);
Display(G, bestSoluion);
time_t T_end = clock();
double RunningTime = double(T_end - T_begin)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
cout<<"程序运行时间 RunningTime = "<> G.vex_num;
// read_in >> G.arc_num;
G.arc_num = 0;
for (int i = 0;i < G.vex_num; i++)
{
read_in >> G.vexs[i];
}
G.vexs[G.vex_num] = '\0'; // char的结束符.
for (int i = 0; i < G.vex_num;i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < G.vex_num; j++)
{
read_in >> G.arcs[i][j];
// calculate the arc_num
if (G.arcs[i][j] > 0)
{
G.arc_num++;
}
}
}
// display
cout<<"无向图创建完毕,相关信息如下:"< (rand()*101))
{
Best_solution = Current_solution;
}
else{
// cout<<"不接受当前解."< 即将随机数控制在[1, G.vex_num - 1]
int j = rand() % (G.vex_num - 1) + 1;
if (i > j)
{
int temp = i;
i = j;
j = temp;
}
else if (i == j)
{ // 表示产生的随机数没有改变的作用, 将此路程设置为最大并结束该函数
newSolution = bestSolution;
return newSolution;
}
/* way 2 */
int choose = rand() % 3;
if (choose == 0)
{ // 随机交换任意两个城市的位置
char temp = bestSolution.path[i];
bestSolution.path[i] = bestSolution.path[j];
bestSolution.path[j] = temp;
}else if (choose == 1)
{ // 随机逆置城市的位置
reverse(bestSolution.path + i, bestSolution.path + j);
}
else{ // 随机移位城市的位置
if (j+1 == G.vex_num) //边界处不处理
{
newSolution = bestSolution;
return newSolution;
}
rotate(bestSolution.path + i, bestSolution.path + j, bestSolution.path + j + 1);
}
newSolution = bestSolution;
newSolution.path[G.vex_num] = newSolution.path[0]; // 终点与起始点相同
newSolution.path[G.vex_num + 1] = '\0';
newSolution.length_path = CalculateLength(G, newSolution);
return newSolution;
}
int CalculateLength(Graph G,TSP_solution newSolution){
int _length = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < G.vex_num - 1; i++)
{
int _startCity = (int)newSolution.path[i] - 65;
int _endCity = (int)newSolution.path[i+1] - 65;
if (G.arcs[_startCity][_endCity] == -1)
{
return MAX_INT;
}
else{
_length += G.arcs[_startCity][_endCity];
}
}
// 判断该路径是否能回到起始城市
if (G.arcs[(int)newSolution.path[G.vex_num - 1] - 65][(int)newSolution.path[0]-65] == -1)
{
return MAX_INT;
}
else{
_length += G.arcs[(int)newSolution.path[G.vex_num - 1] - 65][(int)newSolution.path[0]-65];
return _length;
}
}
void Display(Graph G,TSP_solution bestSoluion){
cout<<"****************************** TSP_SA - BestSolution ******************************"<";
}
cout< 九、参考文献:
- 本文相关代码以及数据:http://download.csdn.net/detail/houchaoqun_xmu/9740079