从源码分析Tomcat如何处理Http请求
先看一下我的web.xml
接着看 postParseRequest , 方法中有下面一段
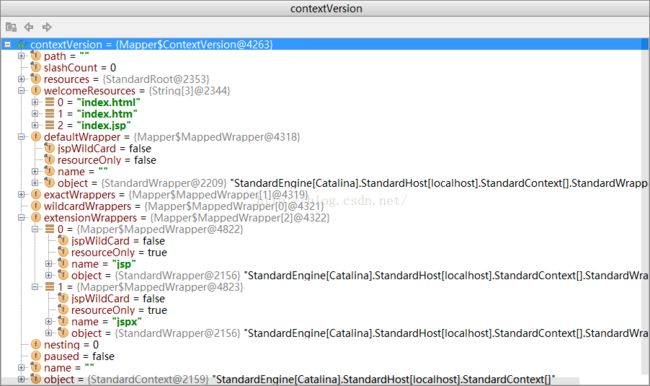
先从extraWrappers 中查找,然后从 jsp 或者 welcome wrappers中找
一直会执行到
dispatcher
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
contextConfigLocation
/WEB-INF/dispatcher-servlet.xml
1
dispatcher
/coffee
然后我发送一个 http://localhost:8088/coffee的请求
package org.apache.catalina.connector;
public class CoyoteAdapter implements Adapter {
public void service(org.apache.coyote.Request req,
org.apache.coyote.Response res)
Request request = (Request) req.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
Response response = (Response) res.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
.....
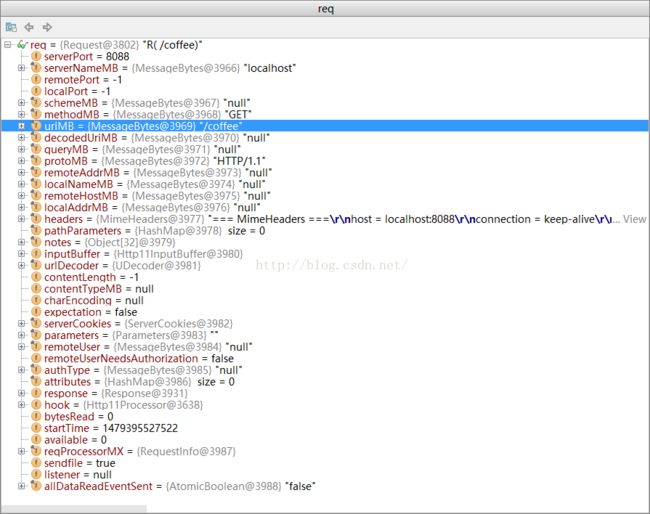
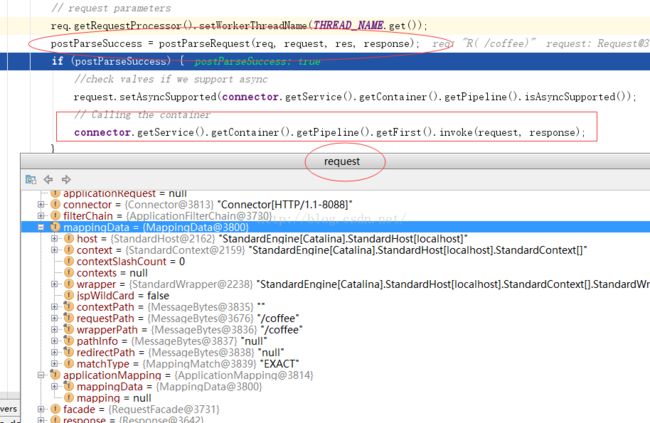
然后看一下这个req的状态
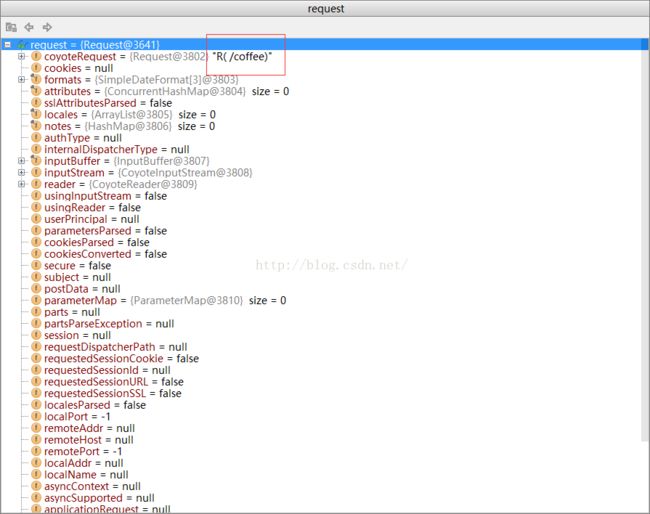
然后看一下request对象 ,相对于req request多了一些mappingData字段
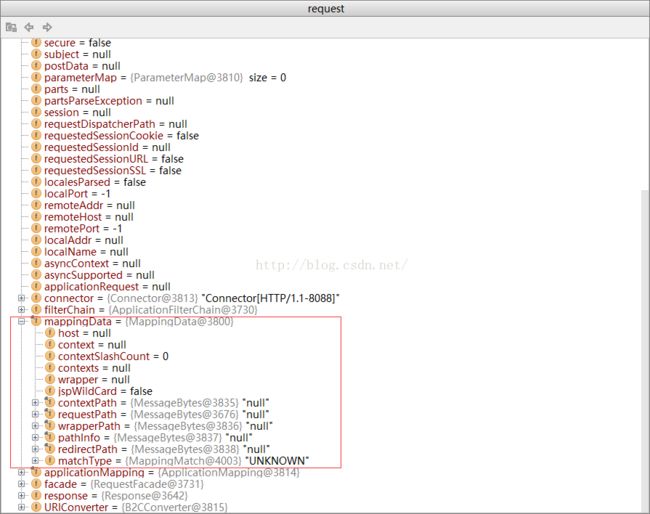
其中对应的请求 /coffee 到底会分发到哪个Servelt ,将最终取决于 mappingData是什么
接下来继续看代码。。
try {
// Parse and set Catalina and configuration specific
// request parameters
req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(THREAD_NAME.get());
postParseSuccess = postParseRequest(req, request, res, response);
if (postParseSuccess) {
//check valves if we support async
request.setAsyncSupported(connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
// Calling the container
connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}接着看 postParseRequest , 方法中有下面一段
// Version for the second mapping loop and
// Context that we expect to get for that version
String version = null;
Context versionContext = null;
boolean mapRequired = true;
while (mapRequired) {
// This will map the the latest version by default
connector.getService().getMapper().map(serverName, decodedURI,
version, request.getMappingData());package org.apache.catalina.mapper;
public final class Mapper {
/**
* Map the specified host name and URI, mutating the given mapping data.
*
* @param host Virtual host name
* @param uri URI
* @param version The version, if any, included in the request to be mapped
* @param mappingData This structure will contain the result of the mapping
* operation
* @throws IOException if the buffers are too small to hold the results of
* the mapping.
*/
public void map(MessageBytes host, MessageBytes uri, String version,
MappingData mappingData) throws IOException {
if (host.isNull()) {
host.getCharChunk().append(defaultHostName);
}
host.toChars();
uri.toChars();
internalMap(host.getCharChunk(), uri.getCharChunk(), version,
mappingData);
}/**
* Map the specified URI.
* @throws IOException
*/
private final void internalMap(CharChunk host, CharChunk uri,
String version, MappingData mappingData) throws IOException {
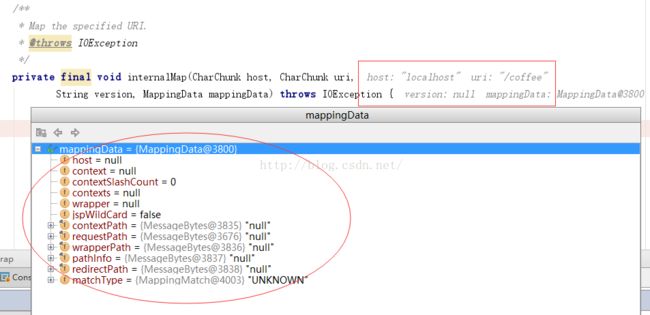
然后看一下、方法的结尾有这么一段
if (contextVersion == null) {
// Return the latest version
// The versions array is known to contain at least one element
contextVersion = contextVersions[versionCount - 1];
}
mappingData.context = contextVersion.object;
mappingData.contextSlashCount = contextVersion.slashCount;
// Wrapper mapping
if (!contextVersion.isPaused()) {
internalMapWrapper(contextVersion, uri, mappingData);
}接着看源码
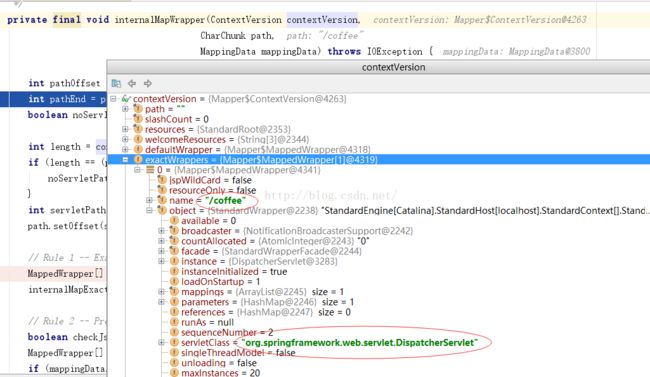
// Rule 1 -- Exact Match
MappedWrapper[] exactWrappers = contextVersion.exactWrappers;
internalMapExactWrapper(exactWrappers, path, mappingData);
// Rule 2 -- Prefix Match
boolean checkJspWelcomeFiles = false;
MappedWrapper[] wildcardWrappers = contextVersion.wildcardWrappers;先从extraWrappers 中查找,然后从 jsp 或者 welcome wrappers中找
最后是DefaultServlet
/**
* Exact mapping.
*/
private final void internalMapExactWrapper
(MappedWrapper[] wrappers, CharChunk path, MappingData mappingData) {
MappedWrapper wrapper = exactFind(wrappers, path);
if (wrapper != null) {
mappingData.requestPath.setString(wrapper.name);
mappingData.wrapper = wrapper.object;
if (path.equals("/")) {
// Special handling for Context Root mapped servlet
mappingData.pathInfo.setString("/");
mappingData.wrapperPath.setString("");
// This seems wrong but it is what the spec says...
mappingData.contextPath.setString("");
mappingData.matchType = MappingMatch.CONTEXT_ROOT;
} else {
mappingData.wrapperPath.setString(wrapper.name);
mappingData.matchType = MappingMatch.EXACT;
}
}
}
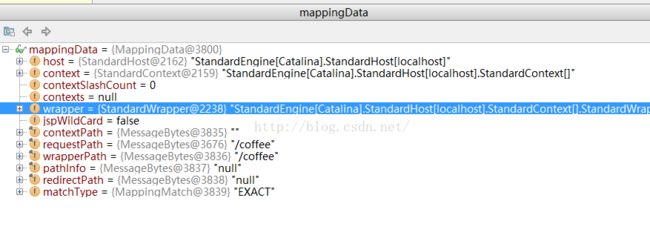
然后执行完了 、递归 回到
CoyoteAdapter # service 中
然后
connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);一直会执行到
package org.apache.catalina.core;
final class StandardWrapperValve
extends ValveBase {
@Override
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
try {// 创建servlet对象
if (!unavailable) {
servlet = wrapper.allocate();
}
}
。。。。。。。。。
if ((servlet != null) && (filterChain != null)) {
// Swallow output if needed
if (context.getSwallowOutput()) {
try {
SystemLogHandler.startCapture();
if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch();
} else {
filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(),
response.getResponse());
}
} finally {
String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture();
if (log != null && log.length() > 0) {
context.getLogger().info(log);
}
}
} else {
if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch();
} else {
filterChain.doFilter
(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
}
}
}
然后在继续往下跟踪代码
org.apache.catalina.core;
final class ApplicationFilterChain implements FilterChain {
private void internalDoFilter(ServletRequest request,
ServletResponse response) 方法中有如下代码
try {
if (ApplicationDispatcher.WRAP_SAME_OBJECT) {
lastServicedRequest.set(request);
lastServicedResponse.set(response);
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported() && !servletSupportsAsync) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR,
Boolean.FALSE);
}
// Use potentially wrapped request from this point
if ((request instanceof HttpServletRequest) &&
(response instanceof HttpServletResponse) &&
Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
Principal principal =
((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal();
Object[] args = new Object[]{req, res};
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege("service",
servlet,
classTypeUsedInService,
args,
principal);
} else {
servlet.service(request, response);
}最终分发到相应的Servlet