深入分析线程池(二)—ThreadPoolExecutor常用方法
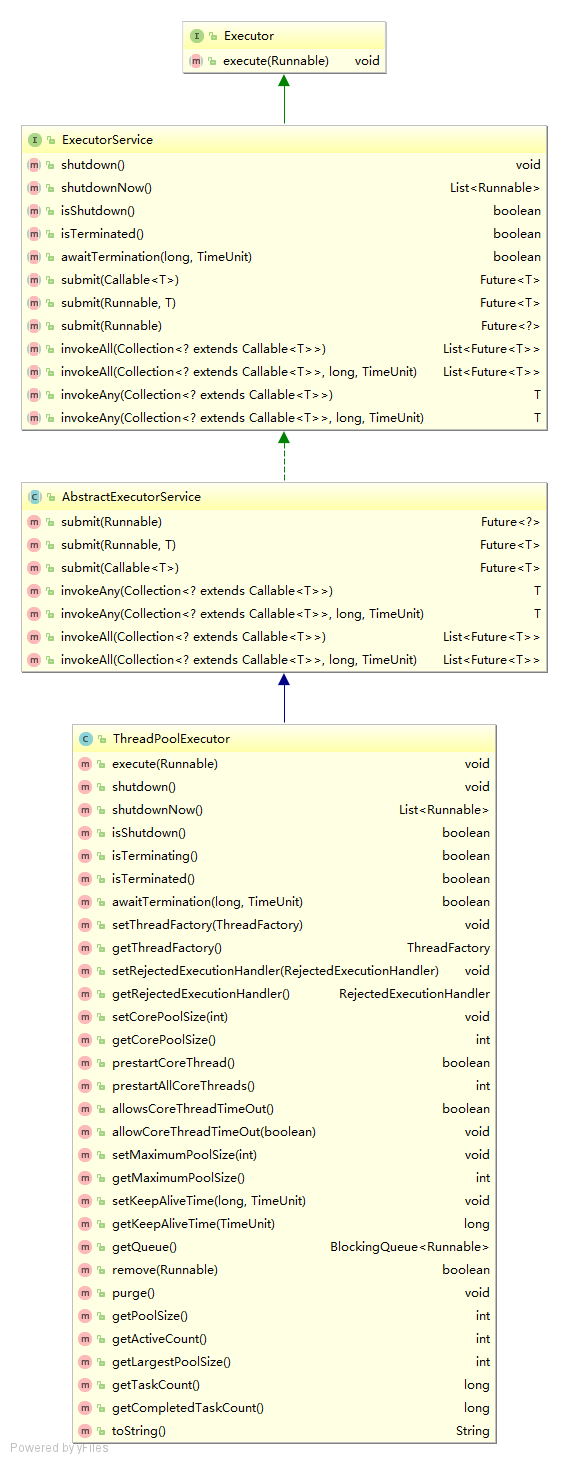
详细介绍ThreadPoolExecutor的方法:
- 方法shutdown() 和 shutdownNow()
shutdown :使当前未执行的线程继续执行,而不再添加新的任务Task,该方法不会阻塞。
shutdownNow :
1. 当在Runnable中使用 if(Thread.currentThread.isInterruptd() == true)来判断当前线程的中断状态,,中断所有的任务task,并且抛出InterruptedException异常,而未执行的线程不再执行,从任务队列中清除。
2. 如果没有if语句,则池中运行的线程直到执行完毕,而未执行的不再执行,从执行队列队列中删除。
区别:
池子调用shutdown,池中状态立马变成SHUTDOWN状态,此时再往池中添加任务,会触发拒绝策略。此时池中不会立刻退出,直到池中的任务都已经完成,才会退出。
总之:调用后,正在执行的任务和队列中的任务在后期正常执行,只是不再添加了。
池子调用shutdownNow,池中状态立马变成STOP状态,并试图停止所有正在执行的线程(除非有if判断人为的抛出异常),不再处理还在池队列中等待的任务,会返还未执行的任务。
总之:调用,停止正在执行的,用一个llist
- isShutdown()
判断线程池是否已经关闭,只要调用的shutdown()方法,则isShutdown()方法的返回值就是true。,
- isTerminating() 和 isTerminated()
前者是否正在关闭,但尚未完全终止的过程,返回true。
后者是已经关闭了。
- awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
查看在指定的时间内,池子是否已经终止工作,即最多等待多少时间后去判断池子已经终止工作。
一般和shutdown()方法配合
如果池中有任务在被执行时,调用其方法会出现阻塞,等待指定的时间,如果没有任务则不会出现阻塞。
所以这个方法和shutdown结合可以实现“等待执行完毕”的效果,就是因为其有阻塞性。
如果正在阻塞的时候,任务执行完毕,那么该会取消阻塞继续执行后面的代码。
public class test{
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
MyRunnable myrunnable = new MyRunnable();
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,9999,9999L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
pool.execute(myrunnable);
pool.shutdown();
System.out.println("begin");
// 阻塞10s(等待10s),如果改成1s,则是false,在4s之前就已经停止判断了
System.out.println(pool.awaitTermination(10,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println("end");
}
}
class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ " " + System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(4000); //睡眠4秒
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ " " + System.currentTimeMillis());
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 正在阻塞时,任务执行完毕,那么会取消阻塞
public class test{
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
MyRunnable myrunnable = new MyRunnable();
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,9999,9999L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
pool.execute(myrunnable);
pool.execute(myrunnable);
pool.execute(myrunnable);
pool.execute(myrunnable);
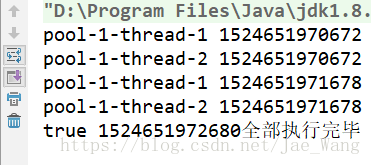
pool.shutdown();
System.out.println(pool.awaitTermination(Integer.MAX_VALUE,
TimeUnit.SECONDS)+ " " + System.currentTimeMillis()+ "全部执行完毕");
}
}
class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " "
+ System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}- setThreadFactory方法+UncaughtExceptionHandler处理异常
对线程池创建的线程进行属性定制化,当程序抛出异常时,可以自定义处理。
除了用构造方法来传递自定义ThreadFactory外,还可以使用setThreadFactory来设置自定义的线程工厂。
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThreadFactory mythreadFactory = new MyThreadFactory();
MyRunnable myrunnable = new MyRunnable();
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,9999,9999L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(),mythreadFactory);
// 利用构造参数来传入自定义的线程工厂
// pool.setThreadFactory(mythreadFactory); 完全可以用方法来传入自定义线程工厂
pool.execute(myrunnable);
}}
class MyRunnable implements Runnable和上述一样
class MyThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread newthread = new Thread(r);
newthread.setName("wang" + new Date()); // 自定义工厂,如果出现异常是可以自定义处理的。
newthread.setUncaughtExceptionHandler(new Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler() {
@Override
public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) {
System.out.println("自定义处理异常" + t.getName() + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
return newthread;
}}- set/getRejectExecutionHandler()
可以处理任务被拒绝执行时的行动
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable myRunnable1 = new MyRunnable("wang1");
MyRunnable myRunnable2 = new MyRunnable("wang2");
MyRunnable myRunnable3 = new MyRunnable("wang3");
MyRunnable myRunnable4 = new MyRunnable("wang4");
//是直接提交的排队策略,最大3个显然会有一个拒绝
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,3,9999L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<>());
pool.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new MyRejectExecutionhandle()); //实现自定义拒绝策略
pool.execute(myRunnable1);
pool.execute(myRunnable2);
pool.execute(myRunnable3);
pool.execute(myRunnable4);
}
}
class MyRejectExecutionhandle implements RejectedExecutionHandler{
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
System.out.println(((MyRunnable)r).getUsername() + "被拒绝了");
}
}
class MyRunnable implements Runnable{ private String username;
public MyRunnable(String username){
super();
this.username = username;
}
public String getUsername(){return username;}
public void setUsername(String username){
this.username = username;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ " " + System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(4000); //睡眠4秒
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ " " + System.currentTimeMillis());
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}- prestartCoreThread() 和 prestartAllCoreThreads()
前者每次调用一次就创建一个核心线程,返回的是boolean
后者启动全部核心线程,返回的是启动核心线程的数量 - remove(Runnable)
可以删除尚未被执行的Runnable任务。 - 多个get方法
getActiveCount() : 取得多少个线程正在执行的任务
getPoolSize() : 当前池中里面有多少个线程,包括正在执行任务的线程,也包括在休眠的线程
getCompletedTaskCount() :取得已经执行完成的任务数
getCorePoolSize() : 取的构造方法传入的corePoolSize参数值
getMaximumPoolSize() : 取的构造方法中MaximumPoolSize的参数值
getPoolSize() : 取的池中有多少个线程
getTaskCount() : 取得有多少个任务发送给了线程池,运行的+ 排队的
有一点要注意: 接口Runnable在ThreadPooExecutor队列中是按顺序取出的,执行却是乱序的。